You are looking at the documentation of a prior release. To read the documentation of the latest release, please
visit here.
New to KubeDB? Please start here.
Continuous Archiving to S3
WAL-G is used to continuously archive PostgreSQL WAL files. Please refer to continuous archiving in KubeDB to learn more about it.
Before You Begin
At first, you need to have a Kubernetes cluster, and the kubectl command-line tool must be configured to communicate with your cluster. If you do not already have a cluster, you can create one by using minikube.
Now, install KubeDB cli on your workstation and KubeDB operator in your cluster following the steps here.
Note: YAML files used in this tutorial are stored in docs/examples/postgres folder in GitHub repository kubedb/cli.
To keep things isolated, this tutorial uses a separate namespace called demo throughout this tutorial.
$ kubectl create ns demo
namespace/demo created
Create PostgreSQL with Continuous Archiving
For archiving, we need storage Secret, and storage backend information. Below is a Postgres object created with Continuous Archiving support to backup WAL files to Amazon S3.
apiVersion: kubedb.com/v1alpha1
kind: Postgres
metadata:
name: wal-postgres
namespace: demo
spec:
version: "11.1-v2"
replicas: 2
storage:
storageClassName: "standard"
accessModes:
- ReadWriteOnce
resources:
requests:
storage: 1Gi
archiver:
storage:
storageSecretName: s3-secret
s3:
bucket: kubedb
Here,
spec.archiver.storagespecifies storage information that will be used byWAL-Gstorage.storageSecretNamepoints to the Secret containing the credentials for cloud storage destination.storage.s3points to s3 storage configuration.storage.s3.bucketpoints to the bucket name used to store continuous archiving data.
Archiver Storage Secret
Storage Secret should contain credentials that will be used to access storage destination.
Storage Secret for WAL-G is needed with the following 2 keys:
| Key | Description |
|---|---|
AWS_ACCESS_KEY_ID | Required. AWS / Minio access key ID |
AWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY | Required. AWS / Minio secret access key |
$ echo -n '<your-aws-access-key-id-here>' > AWS_ACCESS_KEY_ID
$ echo -n '<your-aws-secret-access-key-here>' > AWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY
$ kubectl create secret -n demo generic s3-secret \
--from-file=./AWS_ACCESS_KEY_ID \
--from-file=./AWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY
secret "s3-secret" created
$ kubectl get secret -n demo s3-secret -o yaml
apiVersion: v1
data:
AWS_ACCESS_KEY_ID: PHlvdXItYXdzLWFjY2Vzcy1rZXktaWQtaGVyZT4=
AWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY: PHlvdXItYXdzLXNlY3JldC1hY2Nlc3Mta2V5LWhlcmU+
kind: Secret
metadata:
creationTimestamp: 2018-02-06T09:12:37Z
name: s3-secret
namespace: demo
resourceVersion: "59225"
selfLink: /api/v1/namespaces/demo/secrets/s3-secret
uid: dfbe6b06-0b1d-11e8-9fb9-42010a800064
type: Opaque
Archiver Storage Backend
To configure s3 backend, following parameters are available:
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
spec.archiver.storage.s3.endpoint | Required. For S3, use s3.amazonaws.com |
spec.archiver.storage.s3.bucket | Required. Name of Bucket |
spec.archiver.storage.s3.prefix | Optional. Path prefix into bucket where snapshot will be stores |
Now create this Postgres object with continuous archiving support.
$ kubectl create -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/kubedb/cli/0.12.0/docs/examples/postgres/snapshot/wal-postgres-s3.yaml
postgres.kubedb.com/wal-postgres created
When database is ready, WAL-G takes a base backup and uploads it to the cloud storage defined by storage backend.
Archived data is stored in a folder called {bucket}/{prefix}/kubedb/{namespace}/{postgres-name}/archive/.
You can see continuous archiving data stored in S3 bucket.
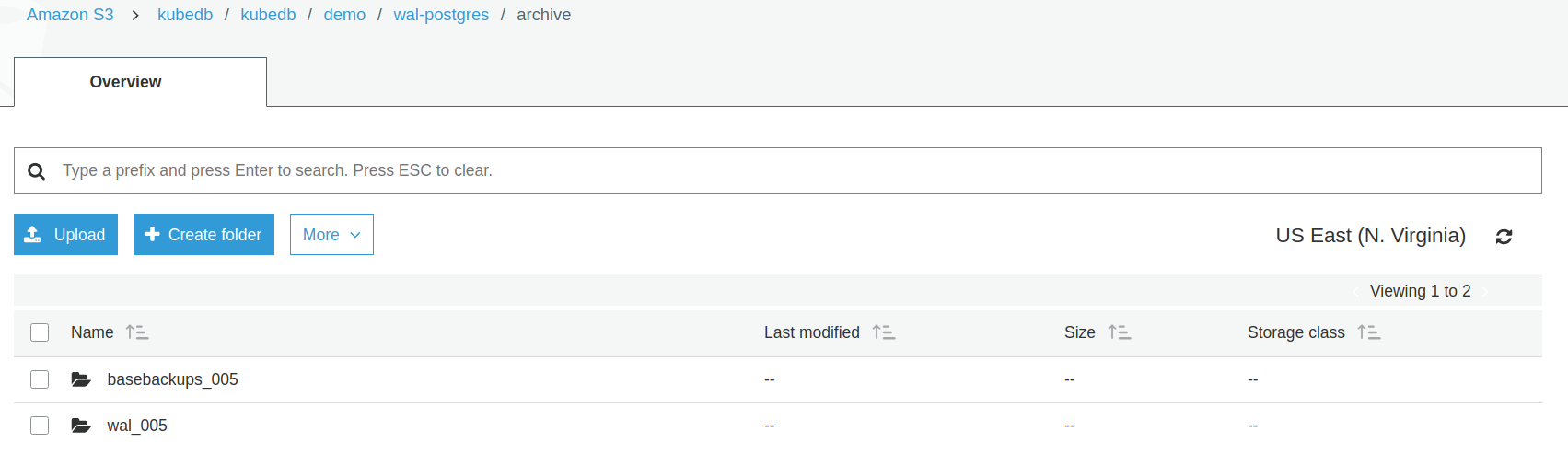
From the above image, you can see that the archived data is stored in a folder kubedb/kubedb/demo/wal-postgres/archive.
Termination Policy
If termination policy of this wal-postgres is set to WipeOut or, If Spec.WipeOut of dormant database is set to true, then the data in cloud backend will be deleted.
The data will be intact in other scenarios.
Cleaning up
To cleanup the Kubernetes resources created by this tutorial, run:
kubectl patch -n demo pg/wal-postgres -p '{"spec":{"terminationPolicy":"WipeOut"}}' --type="merge"
kubectl delete -n demo pg/wal-postgres
kubectl delete -n demo secret/s3-secret
kubectl delete ns demo
Next Steps
- Learn about initializing PostgreSQL from WAL files stored in cloud.



































