You are looking at the documentation of a prior release. To read the documentation of the latest release, please
visit here.
New to KubeDB? Please start here.
KubeDB Snapshot
KubeDB operator maintains another Custom Resource Definition (CRD) for database backups called Snapshot. Snapshot object is used to take backup or restore from a backup.
Before You Begin
At first, you need to have a Kubernetes cluster, and the kubectl command-line tool must be configured to communicate with your cluster. If you do not already have a cluster, you can create one by using minikube.
Now, install KubeDB cli on your workstation and KubeDB operator in your cluster following the steps here.
To keep things isolated, this tutorial uses a separate namespace called demo throughout this tutorial.
$ kubectl create ns demo
namespace "demo" created
$ kubectl get ns demo
NAME STATUS AGE
demo Active 5s
Note: Yaml files used in this tutorial are stored in docs/examples/postgres folder in github repository kubedb/cli.
We need an Postgres object in Running phase to perform backup operation.
apiVersion: kubedb.com/v1alpha1
kind: Postgres
metadata:
name: script-postgres
namespace: demo
spec:
version: "9.6"
storage:
storageClassName: "standard"
accessModes:
- ReadWriteOnce
resources:
requests:
storage: 50Mi
init:
scriptSource:
gitRepo:
repository: "https://github.com/kubedb/postgres-init-scripts.git"
directory: "."
If Postgres object script-postgres doesn’t exists, create it first.
$ kubedb create -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/kubedb/cli/0.8.0/docs/examples/postgres/initialization/script-postgres.yaml
postgres "script-postgres" created
$ kubedb get pg -n demo script-postgres
NAME STATUS AGE
script-postgres Running 11m
We will take backup of this PostgreSQL database script-postgres.
Instant Backup
Snapshot provides a declarative configuration for backup behavior in a Kubernetes native way.
Below is the Snapshot object created in this tutorial.
apiVersion: kubedb.com/v1alpha1
kind: Snapshot
metadata:
name: instant-snapshot
namespace: demo
labels:
kubedb.com/kind: Postgres
spec:
databaseName: script-postgres
storageSecretName: gcs-secret
gcs:
bucket: kubedb
Here,
metadata.labelsshould include the type of database.spec.databaseNameindicates the Postgres object name,script-postgres, whose snapshot is taken.spec.storageSecretNamepoints to the Secret containing the credentials for snapshot storage destination.spec.gcs.bucketpoints to the bucket name used to store the snapshot data.
In this case, kubedb.com/kind: Postgres tells KubeDB operator that this Snapshot belongs to a Postgres object.
Only PostgreSQL controller will handle this Snapshot object.
Note: Snapshot and Secret objects must be in the same namespace as Postgres,
script-postgres, in our case.
Snapshot Storage Secret
Storage Secret should contain credentials that will be used to access storage destination. In this tutorial, snapshot data will be stored in a Google Cloud Storage (GCS) bucket.
For that a storage Secret is needed with following 2 keys:
| Key | Description |
|---|---|
GOOGLE_PROJECT_ID | Required. Google Cloud project ID |
GOOGLE_SERVICE_ACCOUNT_JSON_KEY | Required. Google Cloud service account json key |
$ echo -n '<your-project-id>' > GOOGLE_PROJECT_ID
$ mv downloaded-sa-json.key > GOOGLE_SERVICE_ACCOUNT_JSON_KEY
$ kubectl create secret -n demo generic gcs-secret \
--from-file=./GOOGLE_PROJECT_ID \
--from-file=./GOOGLE_SERVICE_ACCOUNT_JSON_KEY
secret "gcs-secret" created
$ kubectl get secret -n demo gcs-secret -o yaml
apiVersion: v1
data:
GOOGLE_PROJECT_ID: PHlvdXItcHJvamVjdC1pZD4=
GOOGLE_SERVICE_ACCOUNT_JSON_KEY: ewogICJ0eXBlIjogInNlcnZpY2VfYWNjb3V...9tIgp9Cg==
kind: Secret
metadata:
creationTimestamp: 2018-02-05T06:10:50Z
name: gcs-secret
namespace: demo
resourceVersion: "3869"
selfLink: /api/v1/namespaces/demo/secrets/gcs-secret
uid: 5055ce8e-0a3b-11e8-b4de-42010a8000be
type: Opaque
Snapshot Storage Backend
KubeDB supports various cloud providers (S3, GCS, Azure, OpenStack Swift and/or locally mounted volumes) as snapshot storage backend. In this tutorial, GCS backend is used.
To configure this backend, following parameters are available:
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
spec.gcs.bucket | Required. Name of bucket |
spec.gcs.prefix | Optional. Path prefix into bucket where snapshot data will be stored |
An open source project osm is used to store snapshot data into cloud.
To lean how to configure other storage destinations for snapshot data, please visit here.
Now, create the Snapshot object.
$ kubedb create -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/kubedb/cli/0.8.0/docs/examples/postgres/snapshot/instant-snapshot.yaml
snapshot "instant-snapshot" created
Lets see Snapshot list of Postgres script-postgres.
$ kubedb get snap -n demo --selector="kubedb.com/kind=Postgres,kubedb.com/name=script-postgres"
NAME DATABASE STATUS AGE
instant-snapshot pg/script-postgres Running 42s
KubeDB operator watches for Snapshot objects using Kubernetes API. When a Snapshot object is created, it will launch a Job that runs the pg_dumpall command and
uploads the output sql file to cloud storage using osm.
Snapshot data is stored in a folder called {bucket}/{prefix}/kubedb/{namespace}/{PostgreSQL name}/{Snapshot name}/.
Once the snapshot Job is completed, you can see the output of the pg_dumpall command stored in the GCS bucket.
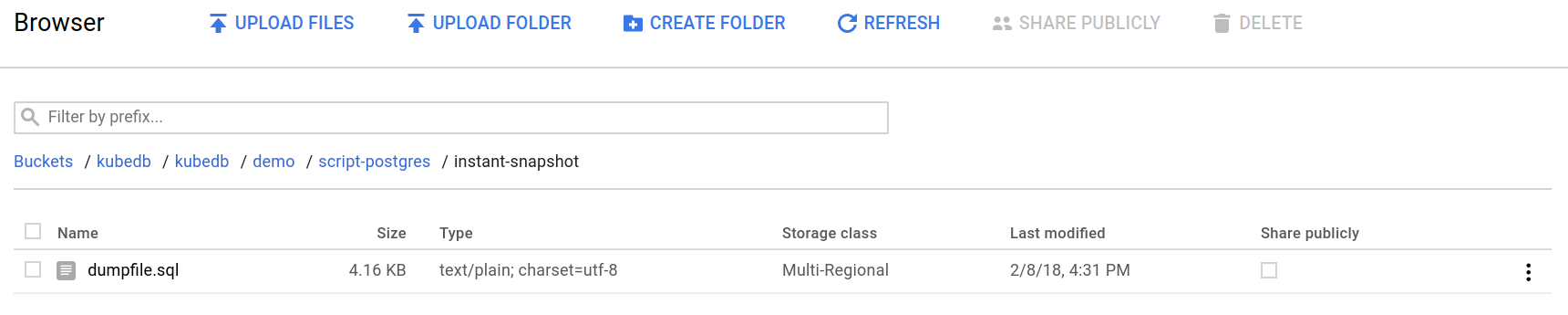
From the above image, you can see that the snapshot data file dumpfile.sql is stored in your bucket.
If you open this dumpfile.sql file, you will see the query to create dashboard TABLE.
--
-- Name: dashboard; Type: TABLE; Schema: data; Owner: postgres
--
CREATE TABLE dashboard (
id bigint NOT NULL,
version integer NOT NULL,
slug character varying(255) NOT NULL,
title character varying(255) NOT NULL,
data text NOT NULL,
org_id bigint NOT NULL,
created timestamp without time zone NOT NULL,
updated timestamp without time zone NOT NULL,
updated_by integer,
created_by integer
);
ALTER TABLE dashboard OWNER TO postgres;
Lets see the Snapshot list for Postgres script-postgres by running kubedb describe command.
$ kubedb describe pg -n demo script-postgres -S=false -W=false
Name: script-postgres
Namespace: demo
StartTimestamp: Thu, 08 Feb 2018 15:55:11 +0600
Status: Running
Init:
scriptSource:
Type: GitRepo (a volume that is pulled from git when the pod is created)
Repository: https://github.com/kubedb/postgres-init-scripts.git
Directory: .
Volume:
StorageClass: standard
Capacity: 50Mi
Access Modes: RWO
StatefulSet: script-postgres
Service: script-postgres, script-postgres-replicas
Secrets: script-postgres-auth
Topology:
Type Pod StartTime Phase
---- --- --------- -----
primary script-postgres-0 2018-02-08 15:55:29 +0600 +06 Running
Snapshots:
Name Bucket StartTime CompletionTime Phase
---- ------ --------- -------------- -----
instant-snapshot gs:kubedb Thu, 08 Feb 2018 16:30:29 +0600 Thu, 08 Feb 2018 16:31:54 +0600 Succeeded
Events:
FirstSeen LastSeen Count From Type Reason Message
--------- -------- ----- ---- -------- ------ -------
11m 11m 1 Job Controller Normal SuccessfulSnapshot Successfully completed snapshot
12m 12m 1 Snapshot Controller Normal Starting Backup running
48m 48m 1 Postgres operator Normal Successful Successfully patched StatefulSet
48m 48m 1 Postgres operator Normal Successful Successfully patched Postgres
48m 48m 1 Postgres operator Normal Successful Successfully created StatefulSet
48m 48m 1 Postgres operator Normal Successful Successfully created Postgres
48m 48m 1 Postgres operator Normal Successful Successfully created Service
48m 48m 1 Postgres operator Normal Successful Successfully created Service
Cleanup Snapshot
If you want to delete snapshot data from storage, you can delete Snapshot object.
$ kubectl delete snap -n demo instant-snapshot
snapshot "instant-snapshot" deleted
Cleaning up
To cleanup the Kubernetes resources created by this tutorial, run:
$ kubectl patch -n demo pg/script-postgres -p '{"spec":{"doNotPause":false}}' --type="merge"
$ kubectl delete -n demo pg/script-postgres
$ kubectl patch -n demo drmn/script-postgres -p '{"spec":{"wipeOut":true}}' --type="merge"
$ kubectl delete -n demo drmn/script-postgres
$ kubectl delete ns demo
Next Steps
- Setup Continuous Archiving in PostgreSQL using
wal-g - Learn how to schedule backup of PostgreSQL database.
- Learn about initializing PostgreSQL from KubeDB Snapshot.
- Want to setup PostgreSQL cluster? Check how to configure Highly Available PostgreSQL Cluster
- Wondering what features are coming next? Please visit here.
- Want to hack on KubeDB? Check our contribution guidelines.



































