You are looking at the documentation of a prior release. To read the documentation of the latest release, please
visit here.
New to KubeDB? Please start here.
Using Prometheus with KubeDB
This tutorial will show you how to monitor KubeDB databases using Prometheus.
Before You Begin
At first, you need to have a Kubernetes cluster, and the kubectl command-line tool must be configured to communicate with your cluster. If you do not already have a cluster, you can create one by using Minikube.
Now, install KubeDB cli on your workstation and KubeDB operator in your cluster following the steps here.
To keep things isolated, this tutorial uses a separate namespace called demo throughout this tutorial. Run the following command to prepare your cluster for this tutorial:
$ kubectl create ns demo
namespace "demo" created
$ kubectl get ns
NAME STATUS AGE
default Active 45m
demo Active 10s
kube-public Active 45m
kube-system Active 45m
Note that the yaml files that are used in this tutorial, stored in docs/examples folder in GitHub repository kubedb/cli.
Create a Redis database
KubeDB implements a Redis CRD to define the specification of a Redis database. Below is the Redis object created in this tutorial.
apiVersion: kubedb.com/v1alpha1
kind: Redis
metadata:
name: redis-mon-prometheus
namespace: demo
spec:
version: "4"
storage:
storageClassName: "standard"
accessModes:
- ReadWriteOnce
resources:
requests:
storage: 50Mi
monitor:
agent: prometheus.io/builtin
$ kubedb create -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/kubedb/cli/0.8.0/docs/examples/redis/monitoring/builtin-prometheus/demo-1.yaml
redis "redis-mon-prometheus" created
Here,
spec.versionis the version of Redis database. In this tutorial, a Redis 3.4 database is going to be created.spec.storagespecifies the StorageClass of PVC dynamically allocated to store data for this database. This storage spec will be passed to the StatefulSet created by KubeDB operator to run database pods. You can specify any StorageClass available in your cluster with appropriate resource requests. Since release 0.8.0, a storage spec is required for Redis.spec.monitorspecifies that built-in Prometheus is used to monitor this database instance. KubeDB operator will configure the service of this database in a way that the Prometheus server will automatically find out the service endpoint akaRedis Exporterand will receive metrics from exporter.
KubeDB operator watches for Redis objects using Kubernetes api. When a Redis object is created, KubeDB operator will create a new StatefulSet and a ClusterIP Service with the matching crd name. KubeDB operator will also create a governing service for StatefulSets with the name kubedb, if one is not already present.
$ kubedb get rd -n demo
NAME STATUS AGE
redis-mon-prometheus Running 3m
$ kubedb describe rd -n demo redis-mon-prometheus
Name: redis-mon-prometheus
Namespace: demo
StartTimestamp: Mon, 12 Feb 2018 17:21:08 +0600
Status: Running
Volume:
StorageClass: standard
Capacity: 50Mi
Access Modes: RWO
StatefulSet:
Name: redis-mon-prometheus
Replicas: 1 current / 1 desired
CreationTimestamp: Mon, 12 Feb 2018 17:21:10 +0600
Pods Status: 1 Running / 0 Waiting / 0 Succeeded / 0 Failed
Service:
Name: redis-mon-prometheus
Type: ClusterIP
IP: 10.108.237.53
Port: db 6379/TCP
Port: prom-http 56790/TCP
Monitoring System:
Agent: prometheus.io/builtin
Prometheus:
Namespace:
Interval:
Events:
FirstSeen LastSeen Count From Type Reason Message
--------- -------- ----- ---- -------- ------ -------
3m 3m 1 Redis operator Normal Successful Successfully patched StatefulSet
3m 3m 1 Redis operator Normal Successful Successfully patched Redis
3m 3m 1 Redis operator Normal Successful Successfully created StatefulSet
3m 3m 1 Redis operator Normal Successful Successfully created Redis
4m 4m 1 Redis operator Normal Successful Successfully created Service
Since spec.monitoring was configured, the database service object is configured accordingly. You can verify it running the following commands:
$ kubectl get services -n demo
NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE
kubedb ClusterIP None <none> <none> 12m
redis-mon-prometheus ClusterIP 10.108.237.53 <none> 6379/TCP,56790/TCP 12m
$ kubectl get services redis-mon-prometheus -n demo -o yaml
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
annotations:
monitoring.appscode.com/agent: prometheus.io/builtin
prometheus.io/path: /kubedb.com/v1alpha1/namespaces/demo/redises/redis-mon-prometheus/metrics
prometheus.io/port: "56790"
prometheus.io/scrape: "true"
creationTimestamp: 2018-02-12T11:21:09Z
labels:
kubedb.com/kind: Redis
kubedb.com/name: redis-mon-prometheus
name: redis-mon-prometheus
namespace: demo
resourceVersion: "48437"
selfLink: /api/v1/namespaces/demo/services/redis-mon-prometheus
uid: d337a61e-0fe6-11e8-a2d6-08002751ae8c
spec:
clusterIP: 10.108.237.53
ports:
- name: db
port: 6379
protocol: TCP
targetPort: db
- name: prom-http
port: 56790
protocol: TCP
targetPort: prom-http
selector:
kubedb.com/kind: Redis
kubedb.com/name: redis-mon-prometheus
sessionAffinity: None
type: ClusterIP
status:
loadBalancer: {}
We can see that the service contains these specific annotations. The Prometheus server will discover the exporter using these specifications.
prometheus.io/path: ...
prometheus.io/port: ...
prometheus.io/scrape: ...
Deploy and configure Prometheus Server
The Prometheus server is needed to configure so that it can discover endpoints of services. If a Prometheus server is already running in cluster and if it is configured in a way that it can discover service endpoints, no extra configuration will be needed. If there is no existing Prometheus server running, rest of this tutorial will create a Prometheus server with appropriate configuration.
The configuration file to Prometheus-Server will be provided by ConfigMap. The below config map will be created:
apiVersion: v1
kind: ConfigMap
metadata:
name: prometheus-server-conf
labels:
name: prometheus-server-conf
namespace: demo
data:
prometheus.yml: |-
global:
scrape_interval: 5s
evaluation_interval: 5s
scrape_configs:
- job_name: 'kubernetes-service-endpoints'
kubernetes_sd_configs:
- role: endpoints
relabel_configs:
- source_labels: [__meta_kubernetes_service_annotation_prometheus_io_scrape]
action: keep
regex: true
- source_labels: [__meta_kubernetes_service_annotation_prometheus_io_scheme]
action: replace
target_label: __scheme__
regex: (https?)
- source_labels: [__meta_kubernetes_service_annotation_prometheus_io_path]
action: replace
target_label: __metrics_path__
regex: (.+)
- source_labels: [__address__, __meta_kubernetes_service_annotation_prometheus_io_port]
action: replace
target_label: __address__
regex: ([^:]+)(?::\d+)?;(\d+)
replacement: $1:$2
- action: labelmap
regex: __meta_kubernetes_service_label_(.+)
- source_labels: [__meta_kubernetes_namespace]
action: replace
target_label: kubernetes_namespace
- source_labels: [__meta_kubernetes_service_name]
action: replace
target_label: kubernetes_name
$ kubectl create -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/kubedb/cli/0.8.0/docs/examples/monitoring/builtin-prometheus/demo-1.yaml
configmap "prometheus-server-conf" created
Now, the below yaml is used to deploy Prometheus in kubernetes:
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: prometheus-server
namespace: demo
spec:
replicas: 1
selector:
matchLabels:
app: prometheus-server
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: prometheus-server
spec:
containers:
- name: prometheus
image: prom/prometheus:v2.1.0
args:
- "--config.file=/etc/prometheus/prometheus.yml"
- "--storage.tsdb.path=/prometheus/"
ports:
- containerPort: 9090
volumeMounts:
- name: prometheus-config-volume
mountPath: /etc/prometheus/
- name: prometheus-storage-volume
mountPath: /prometheus/
volumes:
- name: prometheus-config-volume
configMap:
defaultMode: 420
name: prometheus-server-conf
- name: prometheus-storage-volume
emptyDir: {}
In RBAC enabled cluster
If RBAC is enabled, Run the following command to deploy prometheus in kubernetes:
$ kubectl create -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/kubedb/cli/0.8.0/docs/examples/monitoring/builtin-prometheus/rbac/demo-2.yaml
clusterrole "prometheus-server" created
serviceaccount "prometheus-server" created
clusterrolebinding "prometheus-server" created
deployment "prometheus-server" created
service "prometheus-service" created
# Verify RBAC stuffs
$ kubectl get clusterroles
NAME AGE
prometheus-server 57s
$ kubectl get clusterrolebindings
NAME AGE
prometheus-server 1m
$ kubectl get serviceaccounts -n demo
NAME SECRETS AGE
default 1 48m
prometheus-server 1 1m
In RBAC *not* enabled cluster
If RBAC is not enabled, Run the following command to prepare your cluster for this tutorial:
$ kubectl create -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/kubedb/cli/0.8.0/docs/examples/monitoring/builtin-prometheus/demo-2.yaml
deployment "prometheus-server" created
service "prometheus-service" created
$ kubectl get pods -n demo
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
prometheus-server-79c7cf44fc-xgjp7 1/1 Running 0 26s
redis-mon-prometheus-0 2/2 Running 0 13m
Prometheus Dashboard
Now to open prometheus dashboard on Browser:
$ kubectl get svc -n demo
NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE
kubedb ClusterIP None <none> <none> 14m
prometheus-service LoadBalancer 10.103.108.241 <pending> 9090:30901/TCP 51s
redis-mon-prometheus ClusterIP 10.108.237.53 <none> 6379/TCP,56790/TCP 14m
$ minikube ip
192.168.99.100
$ minikube service prometheus-service -n demo --url
http://192.168.99.100:30901
Now, open your browser and go to the following URL: http://{minikube-ip}:{prometheus-svc-nodeport} to visit Prometheus Dashboard. According to the above example, this URL will be http://192.168.99.100:30901.
Now, if you go the Prometheus Dashboard, you should see that this database endpoint as one of the targets.
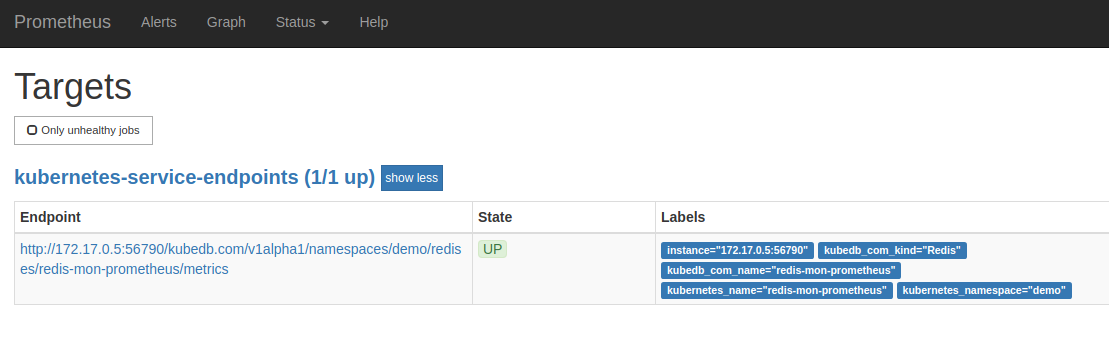
Cleaning up
To cleanup the Kubernetes resources created by this tutorial, run:
$ kubectl patch -n demo rd/redis-mon-prometheus -p '{"spec":{"doNotPause":false}}' --type="merge"
$ kubectl delete -n demo rd/redis-mon-prometheus
$ kubectl patch -n demo drmn/redis-mon-prometheus -p '{"spec":{"wipeOut":true}}' --type="merge"
$ kubectl delete -n demo drmn/redis-mon-prometheus
# In rbac enabled cluster,
# $ kubectl delete clusterrole prometheus-server
# $ kubectl delete clusterrolebindings prometheus-server
# $ kubectl delete serviceaccounts -n demo prometheus-server
$ kubectl delete ns demo
namespace "demo" deleted
Next Steps
- Monitor your Redis database with KubeDB using out-of-the-box CoreOS Prometheus Operator.
- Detail concepts of Redis object.
- Use private Docker registry to deploy Redis with KubeDB.
- Wondering what features are coming next? Please visit here.
- Want to hack on KubeDB? Check our contribution guidelines.



































