You are looking at the documentation of a prior release. To read the documentation of the latest release, please
visit here.
New to KubeDB? Please start here.
Database Snapshots
This tutorial will show you how to take snapshots of a KubeDB managed MongoDB database.
Note: The yaml files used in this tutorial are stored in docs/examples/mongodb folder in GitHub repository kubedb/cli.
Before You Begin
At first, you need to have a Kubernetes cluster, and the kubectl command-line tool must be configured to communicate with your cluster. If you do not already have a cluster, you can create one by using Minikube.
Now, install KubeDB cli on your workstation and KubeDB operator in your cluster following the steps here.
StorageClass is required to run KubeDB. Check the available StorageClass in cluster.
$ kubectl get storageclasses NAME PROVISIONER AGE standard (default) k8s.io/minikube-hostpath 4hA
MongoDBdatabase is needed to take snapshot for this tutorial. To keep things isolated, this tutorial uses a separate namespace calleddemothroughout this tutorial. Run the following command to prepare your cluster for this tutorial:$ kubectl create ns demo namespace "demo" created $ kubectl get ns NAME STATUS AGE demo Active 1m $ kubedb create -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/kubedb/cli/0.9.0/docs/examples/mongodb/snapshot/demo-1.yaml mongodb.kubedb.com/mgo-infant created
Instant Backups
You can easily take a snapshot of MongoDB database by creating a Snapshot object. When a Snapshot object is created, KubeDB operator will launch a Job that runs the mongodump command and uploads the output bson file to various cloud providers S3, GCS, Azure, OpenStack Swift and/or locally mounted volumes using osm.
In this tutorial, snapshots will be stored in a Google Cloud Storage (GCS) bucket. To do so, a secret is needed that has the following 2 keys:
| Key | Description |
|---|---|
GOOGLE_PROJECT_ID | Required. Google Cloud project ID |
GOOGLE_SERVICE_ACCOUNT_JSON_KEY | Required. Google Cloud service account json key |
$ echo -n '<your-project-id>' > GOOGLE_PROJECT_ID
$ mv downloaded-sa-json.key > GOOGLE_SERVICE_ACCOUNT_JSON_KEY
$ kubectl create secret generic mg-snap-secret -n demo \
--from-file=./GOOGLE_PROJECT_ID \
--from-file=./GOOGLE_SERVICE_ACCOUNT_JSON_KEY
secret/mg-snap-secret created
$ kubectl get secret mg-snap-secret -n demo -o yaml
apiVersion: v1
data:
GOOGLE_PROJECT_ID: PHlvdXItcHJvamVjdC1pZD4=
GOOGLE_SERVICE_ACCOUNT_JSON_KEY: ewogICJ0eXBlIjogInNlcnZpY2VfYWNjb3V...9tIgp9Cg==
kind: Secret
metadata:
creationTimestamp: 2018-02-02T10:02:09Z
name: mg-snap-secret
namespace: demo
resourceVersion: "48679"
selfLink: /api/v1/namespaces/demo/secrets/mg-snap-secret
uid: 220a7c60-0800-11e8-946f-080027c05a6e
type: Opaque
To lean how to configure other storage destinations for Snapshots, please visit here. Now, create the Snapshot object.
apiVersion: kubedb.com/v1alpha1
kind: Snapshot
metadata:
name: snapshot-infant
namespace: demo
labels:
kubedb.com/kind: MongoDB
spec:
databaseName: mgo-infant
storageSecretName: mg-snap-secret
gcs:
bucket: kubedb
$ kubedb create -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/kubedb/cli/0.9.0/docs/examples/mongodb/snapshot/demo-2.yaml
snapshot.kubedb.com/snapshot-infant created
$ kubedb get snap -n demo
NAME DATABASENAME STATUS AGE
snapshot-infant mgo-infant Running 23s
$ kubedb get snap -n demo snapshot-infant -o yaml
apiVersion: kubedb.com/v1alpha1
kind: Snapshot
metadata:
creationTimestamp: 2018-09-24T11:09:26Z
finalizers:
- kubedb.com
generation: 1
labels:
kubedb.com/kind: MongoDB
kubedb.com/name: mgo-infant
snapshot.kubedb.com/status: Running
name: snapshot-infant
namespace: demo
resourceVersion: "27413"
selfLink: /apis/kubedb.com/v1alpha1/namespaces/demo/snapshots/snapshot-infant
uid: 4ce85a07-bfea-11e8-93d2-080027e2cfdd
spec:
databaseName: mgo-infant
gcs:
bucket: kubedb
storageSecretName: mg-snap-secret
status:
phase: Running
startTime: 2018-09-24T11:09:27Z
Here,
metadata.labelsshould include the type of databasekubedb.com/kind: MongoDBwhose snapshot will be taken.spec.databaseNamepoints to the database whose snapshot is taken.spec.storageSecretNamepoints to the Secret containing the credentials for snapshot storage destination.spec.gcs.bucketpoints to the bucket name used to store the snapshot data.
You can also run the kubedb describe command to see the recent snapshots taken for a database.
$ kubedb describe mg -n demo mgo-infant
Name: mgo-infant
Namespace: demo
CreationTimestamp: Mon, 24 Sep 2018 17:04:54 +0600
Labels: <none>
Annotations: <none>
Replicas: 1 total
Status: Running
StorageType: Durable
Volume:
StorageClass: standard
Capacity: 50Mi
Access Modes: RWO
StatefulSet:
Name: mgo-infant
CreationTimestamp: Mon, 24 Sep 2018 17:04:59 +0600
Labels: kubedb.com/kind=MongoDB
kubedb.com/name=mgo-infant
Annotations: <none>
Replicas: 824641944540 desired | 1 total
Pods Status: 1 Running / 0 Waiting / 0 Succeeded / 0 Failed
Service:
Name: mgo-infant
Labels: kubedb.com/kind=MongoDB
kubedb.com/name=mgo-infant
Annotations: <none>
Type: ClusterIP
IP: 10.106.56.236
Port: db 27017/TCP
TargetPort: db/TCP
Endpoints: 172.17.0.5:27017
Service:
Name: mgo-infant-gvr
Labels: kubedb.com/kind=MongoDB
kubedb.com/name=mgo-infant
Annotations: service.alpha.kubernetes.io/tolerate-unready-endpoints=true
Type: ClusterIP
IP: None
Port: db 27017/TCP
TargetPort: 27017/TCP
Endpoints: 172.17.0.5:27017
Database Secret:
Name: mgo-infant-auth
Labels: kubedb.com/kind=MongoDB
kubedb.com/name=mgo-infant
Annotations: <none>
Type: Opaque
Data
====
user: 4 bytes
password: 16 bytes
Snapshots:
Name Bucket StartTime CompletionTime Phase
---- ------ --------- -------------- -----
snapshot-infant gs:kubedb Mon, 24 Sep 2018 17:09:27 +0600 Mon, 24 Sep 2018 17:10:17 +0600 Succeeded
Events:
Type Reason Age From Message
---- ------ ---- ---- -------
Normal Successful 6m MongoDB operator Successfully created Service
Normal Successful 5m MongoDB operator Successfully created StatefulSet
Normal Successful 5m MongoDB operator Successfully created MongoDB
Normal Successful 5m MongoDB operator Successfully patched StatefulSet
Normal Successful 5m MongoDB operator Successfully patched MongoDB
Normal Successful 5m MongoDB operator Successfully patched StatefulSet
Normal Successful 5m MongoDB operator Successfully patched MongoDB
Normal Starting 2m Job Controller Backup running
Normal SuccessfulSnapshot 1m Job Controller Successfully completed snapshot
Once the snapshot Job is complete, you should see the output of the mongodump command stored in the GCS bucket.
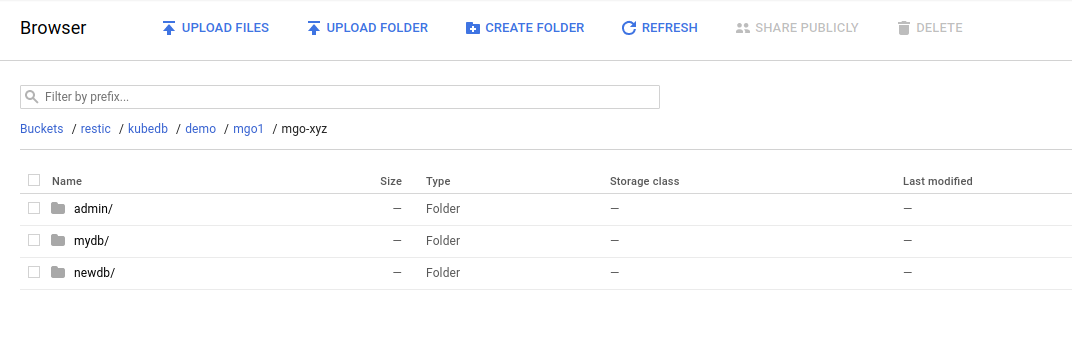
From the above image, you can see that the snapshot output is stored in a folder called {bucket}/kubedb/{namespace}/{mongodb-object}/{snapshot}/.
Restore from Snapshot
You can create a new database from a previously taken Snapshot. Specify the Snapshot name in the spec.init.snapshotSource field of a new MongoDB object. See the example mgo-recovered object below:
apiVersion: kubedb.com/v1alpha1
kind: MongoDB
metadata:
name: mgo-recovered
namespace: demo
spec:
version: "3.4-v1"
storage:
storageClassName: "standard"
accessModes:
- ReadWriteOnce
resources:
requests:
storage: 50Mi
init:
snapshotSource:
name: snapshot-infant
namespace: demo
$ kubedb create -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/kubedb/cli/0.9.0/docs/examples/mongodb/snapshot/demo-3.yaml
mongodb.kubedb.com/mgo-recovered created
Here,
spec.init.snapshotSource.namerefers to a Snapshot object for a MongoDB database in the same namespaces as this newmgo-recoveredMongoDB object.
Now, wait several seconds. KubeDB operator will create a new StatefulSet. Then KubeDB operator launches a Kubernetes Job to initialize the new database using the data from snapshot-infant Snapshot.
$ kubedb get mg -n demo
NAME VERSION STATUS AGE
mgo-infant 3.4-v1 Running 13m
mgo-recovered 3.4-v1 Initializing 57s
$ kubedb get mg -n demo
NAME VERSION STATUS AGE
mgo-infant 3.4-v1 Running 13m
mgo-recovered 3.4-v1 Running 1m
$ kubedb describe mg -n demo mgo-recovered
Name: mgo-recovered
Namespace: demo
CreationTimestamp: Mon, 24 Sep 2018 17:17:14 +0600
Labels: <none>
Annotations: kubedb.com/initialized=
Replicas: 1 total
Status: Running
StorageType: Durable
Volume:
StorageClass: standard
Capacity: 50Mi
Access Modes: RWO
StatefulSet:
Name: mgo-recovered
CreationTimestamp: Mon, 24 Sep 2018 17:17:20 +0600
Labels: kubedb.com/kind=MongoDB
kubedb.com/name=mgo-recovered
Annotations: <none>
Replicas: 824642112848 desired | 1 total
Pods Status: 1 Running / 0 Waiting / 0 Succeeded / 0 Failed
Service:
Name: mgo-recovered
Labels: kubedb.com/kind=MongoDB
kubedb.com/name=mgo-recovered
Annotations: <none>
Type: ClusterIP
IP: 10.100.10.221
Port: db 27017/TCP
TargetPort: db/TCP
Endpoints: 172.17.0.6:27017
Service:
Name: mgo-recovered-gvr
Labels: kubedb.com/kind=MongoDB
kubedb.com/name=mgo-recovered
Annotations: service.alpha.kubernetes.io/tolerate-unready-endpoints=true
Type: ClusterIP
IP: None
Port: db 27017/TCP
TargetPort: 27017/TCP
Endpoints: 172.17.0.6:27017
Database Secret:
Name: mgo-recovered-auth
Labels: kubedb.com/kind=MongoDB
kubedb.com/name=mgo-recovered
Annotations: <none>
Type: Opaque
Data
====
password: 16 bytes
user: 4 bytes
No Snapshots.
Events:
Type Reason Age From Message
---- ------ ---- ---- -------
Normal Successful 2m MongoDB operator Successfully created Service
Normal Successful 2m MongoDB operator Successfully created MongoDB
Normal Successful 2m MongoDB operator Successfully created StatefulSet
Normal Initializing 2m MongoDB operator Initializing from Snapshot: "snapshot-infant"
Normal Successful 2m MongoDB operator Successfully patched StatefulSet
Normal Successful 2m MongoDB operator Successfully patched MongoDB
Normal SuccessfulInitialize 1m Job Controller Successfully completed initialization
Normal Successful 1m MongoDB operator Successfully patched MongoDB
Normal Successful 1m MongoDB operator Successfully patched StatefulSet
Normal Initializing 1m MongoDB operator Initializing from Snapshot: "snapshot-infant"
Normal Successful 1m MongoDB operator Successfully patched StatefulSet
Normal Successful 1m MongoDB operator Successfully patched MongoDB
Normal Successful 1m MongoDB operator Successfully patched StatefulSet
Normal Successful 1m MongoDB operator Successfully patched MongoDB
Normal SuccessfulInitialize 1m Job Controller Successfully completed initialization
Cleaning up
To cleanup the Kubernetes resources created by this tutorial, run:
kubectl patch -n demo mg/mgo-infant mg/mgo-recovered -p '{"spec":{"terminationPolicy":"WipeOut"}}' --type="merge"
kubectl delete -n demo mg/mgo-infant mg/mgo-recovered
kubectl patch -n demo drmn/mgo-infant drmn/mgo-recovered -p '{"spec":{"wipeOut":true}}' --type="merge"
kubectl delete -n demo drmn/mgo-infant drmn/mgo-recovered
kubectl delete ns demo
Next Steps
- See the list of supported storage providers for snapshots here.
- Take Scheduled Snapshot of MongoDB databases using KubeDB.
- Initialize MongoDB with Script.
- Initialize MongoDB with Snapshot.
- Monitor your MongoDB database with KubeDB using out-of-the-box CoreOS Prometheus Operator.
- Monitor your MongoDB database with KubeDB using out-of-the-box builtin-Prometheus.
- Use private Docker registry to deploy MongoDB with KubeDB.
- Detail concepts of MongoDB object.
- Detail concepts of MongoDBVersion object.
- Want to hack on KubeDB? Check our contribution guidelines.



































