You are looking at the documentation of a prior release. To read the documentation of the latest release, please
visit here.
Backup Elasticsearch using Stash Auto-Backup
Stash can be configured to automatically backup any Elasticsearch database in your cluster. Stash enables cluster administrators to deploy backup blueprints ahead of time so that the database owners can easily backup their database with just a few annotations.
In this tutorial, we are going to show how you can configure a backup blueprint for Elasticsearch databases in your cluster and backup them with few annotations.
Before You Begin
- At first, you need to have a Kubernetes cluster, and the
kubectlcommand-line tool must be configured to communicate with your cluster. - Install KubeDB in your cluster following the steps here.
- Install Stash Enterprise in your cluster following the steps here.
- If you are not familiar with how Stash backup and restore Elasticsearch databases, please check the following guide here.
- If you are not familiar with how auto-backup works in Stash, please check the following guide here.
- If you are not familiar with the available auto-backup options for databases in Stash, please check the following guide here.
You should be familiar with the following Stash concepts:
In this tutorial, we are going to show backup of three different Elasticsearch databases on three different namespaces named demo, demo-2, and demo-3. Create the namespaces as below if you haven’t done it already.
❯ kubectl create ns demo
namespace/demo created
❯ kubectl create ns demo-2
namespace/demo-2 created
❯ kubectl create ns demo-3
namespace/demo-3 created
When you install the Stash Enterprise edition, it automatically installs all the official database addons. Verify that it has installed the Elasticsearch addons using the following command.
❯ kubectl get tasks.stash.appscode.com | grep elasticsearch
elasticsearch-backup-5.6.4 4d4h
elasticsearch-backup-6.2.4 4d4h
elasticsearch-backup-6.3.0 4d4h
elasticsearch-backup-6.4.0 4d4h
elasticsearch-backup-6.5.3 4d4h
elasticsearch-backup-6.8.0 4d4h
elasticsearch-backup-7.2.0 4d4h
elasticsearch-backup-7.3.2 4d4h
elasticsearch-restore-5.6.4 4d4h
elasticsearch-restore-6.2.4 4d4h
elasticsearch-restore-6.3.0 4d4h
elasticsearch-restore-6.4.0 4d4h
elasticsearch-restore-6.5.3 4d4h
elasticsearch-restore-6.8.0 4d4h
elasticsearch-restore-7.2.0 4d4h
elasticsearch-restore-7.3.2 4d4h
Prepare Backup Blueprint
To backup an Elasticsearch database using Stash, you have to create a Secret containing the backend credentials, a Repository containing the backend information, and a BackupConfiguration containing the schedule and target information. A BackupBlueprint allows you to specify a template for the Repository and the BackupConfiguration.
The BackupBlueprint is a non-namespaced CRD. So, once you have created a BackupBlueprint, you can use it to backup any Elasticsearch database of any namespace just by creating the storage Secret in that namespace and adding few annotations to your Elasticsearch CRO. Then, Stash will automatically create a Repository and a BackupConfiguration according to the template to backup the database.
Below is the BackupBlueprint object that we are going to use in this tutorial,
apiVersion: stash.appscode.com/v1beta1
kind: BackupBlueprint
metadata:
name: elasticsearch-backup-template
spec:
# ============== Blueprint for Repository ==========================
backend:
gcs:
bucket: stash-testing
prefix: stash-backup/${TARGET_NAMESPACE}/${TARGET_APP_RESOURCE}/${TARGET_NAME}
storageSecretName: gcs-secret
# ============== Blueprint for BackupConfiguration =================
# task: # Uncomment if you are not using KubeDB to deploy your database.
# name: elasticsearch-backup-7.3.2
schedule: "*/5 * * * *"
interimVolumeTemplate:
metadata:
name: ${TARGET_APP_RESOURCE}-${TARGET_NAME} # To ensure that the PVC names are unique for different database
spec:
accessModes: [ "ReadWriteOnce" ]
storageClassName: "standard"
resources:
requests:
storage: 1Gi
retentionPolicy:
name: 'keep-last-5'
keepLast: 5
prune: true
Here, we are using a GCS bucket as our backend. We are providing gcs-secret at the storageSecretName field. Hence, we have to create a secret named gcs-secret with the access credentials of our bucket in every namespace where we want to enable backup through this blueprint.
Notice the prefix field of backend section. We have used some variables in form of ${VARIABLE_NAME}. Stash will automatically resolve those variables from the database information to make the backend prefix unique for each database instance.
We have also used some variables in name field of the interimVolumeTemplate section. This is to ensure that the generated PVC name becomes unique for the database instances.
Let’s create the BackupBlueprint we have shown above,
❯ kubectl apply -f https://github.com/kubedb/docs/raw/v2021.04.16/docs/guides/elasticsearch/backup/auto-backup/examples/backupblueprint.yaml
backupblueprint.stash.appscode.com/elasticsearch-backup-template created
Now, we are ready to backup our Elasticsearch databases using few annotations. You can check available auto-backup annotations for a databases from here.
Auto-backup with default configurations
In this section, we are going to backup an Elasticsearch database of demo namespace. We are going to use the default configurations specified in the BackupBlueprint.
Create Storage Secret
At first, let’s create the gcs-secret in demo namespace with the access credentials to our GCS bucket.
❯ echo -n 'changeit' > RESTIC_PASSWORD
❯ echo -n '<your-project-id>' > GOOGLE_PROJECT_ID
❯ cat downloaded-sa-json.key > GOOGLE_SERVICE_ACCOUNT_JSON_KEY
❯ kubectl create secret generic -n demo gcs-secret \
--from-file=./RESTIC_PASSWORD \
--from-file=./GOOGLE_PROJECT_ID \
--from-file=./GOOGLE_SERVICE_ACCOUNT_JSON_KEY
secret/gcs-secret created
Create Database
Now, we are going to create an Elasticsearch CRO in demo namespace. Below is the YAML of the Elasticsearch object that we are going to create,
apiVersion: kubedb.com/v1alpha2
kind: Elasticsearch
metadata:
name: es-demo
namespace: demo
annotations:
stash.appscode.com/backup-blueprint: elasticsearch-backup-template
spec:
version: xpack-7.9.1-v1
replicas: 1
storageType: Durable
storage:
resources:
requests:
storage: 1Gi
storageClassName: standard
terminationPolicy: WipeOut
Notice the annotations section. We are pointing to the BackupBlueprint that we have created earlier though stash.appscode.com/backup-blueprint annotation. Stash will watch this annotation and create a Repository and a BackupConfiguration according to the BackupBlueprint.
Let’s create the above Elasticsearch CRO,
❯ kubectl apply -f https://github.com/kubedb/docs/raw/v2021.04.16/docs/guides/elasticsearch/backup/auto-backup/examples/es-demo.yaml
elasticsearch.kubedb.com/sample-elasticsearch created
Verify Auto-backup configured
In this section, we are going to verify whether Stash has created the respective Repository and BackupConfiguration for our Elasticsearch database we have just deployed or not.
Verify Repository
At first, let’s verify whether Stash has created a Repository for our Elasticsearch or not.
❯ kubectl get repository -n demo
NAME INTEGRITY SIZE SNAPSHOT-COUNT LAST-SUCCESSFUL-BACKUP AGE
app-es-demo 5s
Now, let’s check the YAML of the Repository.
❯ kubectl get repository -n demo app-es-demo -o yaml
apiVersion: stash.appscode.com/v1alpha1
kind: Repository
metadata:
...
name: app-es-demo
namespace: demo
spec:
backend:
gcs:
bucket: stash-testing
prefix: stash-backup/demo/elasticsearch/es-demo
storageSecretName: gcs-secret
Here, you can see that Stash has resolved the variables in prefix field and substituted them with the equivalent information from this database.
Verify BackupConfiguration
Now, let’s verify whether Stash has created a BackupConfiguration for our Elasticsearch or not.
❯ kubectl get backupconfiguration -n demo
NAME TASK SCHEDULE PAUSED AGE
app-es-demo elasticsearch-backup-7.3.2 */5 * * * * 12s
Now, let’s check the YAML of the BackupConfiguration.
❯ kubectl get backupconfiguration -n demo app-es-demo -o yaml
apiVersion: stash.appscode.com/v1beta1
kind: BackupConfiguration
metadata:
name: app-es-demo
namespace: demo
...
spec:
driver: Restic
interimVolumeTemplate:
metadata:
name: elasticsearch-es-demo
spec:
accessModes:
- ReadWriteOnce
resources:
requests:
storage: 1Gi
storageClassName: standard
status: {}
repository:
name: app-es-demo
retentionPolicy:
keepLast: 5
name: keep-last-5
prune: true
runtimeSettings: {}
schedule: '*/5 * * * *'
target:
ref:
apiVersion: appcatalog.appscode.com/v1alpha1
kind: AppBinding
name: es-demo
tempDir: {}
status:
conditions:
- lastTransitionTime: "2021-02-12T11:46:53Z"
message: Repository demo/app-es-demo exist.
reason: RepositoryAvailable
status: "True"
type: RepositoryFound
- lastTransitionTime: "2021-02-12T11:46:53Z"
message: Backend Secret demo/gcs-secret exist.
reason: BackendSecretAvailable
status: "True"
type: BackendSecretFound
- lastTransitionTime: "2021-02-12T11:46:53Z"
message: Backup target appcatalog.appscode.com/v1alpha1 appbinding/es-demo found.
reason: TargetAvailable
status: "True"
type: BackupTargetFound
- lastTransitionTime: "2021-02-12T11:46:53Z"
message: Successfully created backup triggering CronJob.
reason: CronJobCreationSucceeded
status: "True"
type: CronJobCreated
observedGeneration: 1
Notice the interimVolumeTemplate section. The variables of name field have been substituted by the equivalent information from the database.
Also, notice the target section. Stash has automatically added the Elasticsearch as the target of this BackupConfiguration.
Verify Backup
Now, let’s wait for a backup run to complete. You can watch for BackupSession as below,
❯ kubectl get backupsession -n demo -w
NAME INVOKER-TYPE INVOKER-NAME PHASE AGE
app-es-demo-1613130605 BackupConfiguration app-es-demo 0s
app-es-demo-1613130605 BackupConfiguration app-es-demo Running 10s
app-es-demo-1613130605 BackupConfiguration app-es-demo Succeeded 46s
Once the backup has been completed successfully, you should see the backed up data has been stored in the bucket at the directory pointed by the prefix field of the Repository.
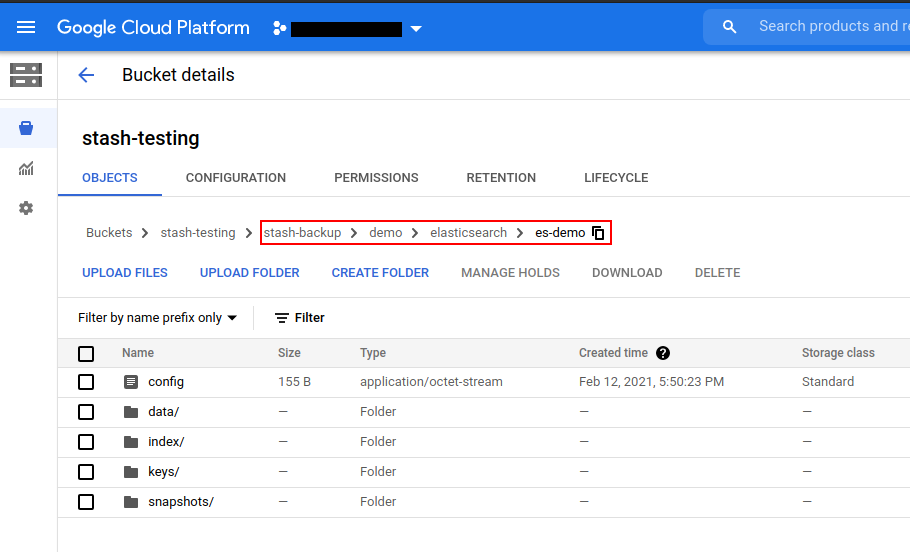
Auto-backup with a custom schedule
In this section, we are going to backup an Elasticsearch database of demo-2 namespace. This time, we are going to overwrite the default schedule used in the BackupBlueprint.
Create Storage Secret
At first, let’s create the gcs-secret in demo-2 namespace with the access credentials to our GCS bucket.
❯ kubectl create secret generic -n demo-2 gcs-secret \
--from-file=./RESTIC_PASSWORD \
--from-file=./GOOGLE_PROJECT_ID \
--from-file=./GOOGLE_SERVICE_ACCOUNT_JSON_KEY
secret/gcs-secret created
Create Database
Now, we are going to create an Elasticsearch CRO in demo-2 namespace. Below is the YAML of the Elasticsearch object that we are going to create,
apiVersion: kubedb.com/v1alpha2
kind: Elasticsearch
metadata:
name: es-demo-2
namespace: demo-2
annotations:
stash.appscode.com/backup-blueprint: elasticsearch-backup-template
stash.appscode.com/schedule: "*/3 * * * *"
spec:
version: xpack-7.9.1-v1
replicas: 1
storageType: Durable
storage:
resources:
requests:
storage: 1Gi
storageClassName: standard
terminationPolicy: WipeOut
Notice the annotations section. This time, we have passed a schedule via stash.appscode.com/schedule annotation along with the stash.appscode.com/backup-blueprint annotation.
Let’s create the above Elasticsearch CRO,
❯ kubectl apply -f https://github.com/kubedb/docs/raw/v2021.04.16/docs/guides/elasticsearch/backup/auto-backup/examples/es-demo-2.yaml
elasticsearch.kubedb.com/es-demo-2 created
Verify Auto-backup configured
Now, let’s verify whether the auto-backup has been configured properly or not.
Verify Repository
At first, let’s verify whether Stash has created a Repository for our Elasticsearch or not.
❯ kubectl get repository -n demo-2
NAME INTEGRITY SIZE SNAPSHOT-COUNT LAST-SUCCESSFUL-BACKUP AGE
app-es-demo-2 25s
Now, let’s check the YAML of the Repository.
❯ kubectl get repository -n demo-2 app-es-demo-2 -o yaml
apiVersion: stash.appscode.com/v1alpha1
kind: Repository
metadata:
name: app-es-demo-2
namespace: demo-2
...
spec:
backend:
gcs:
bucket: stash-testing
prefix: stash-backup/demo-2/elasticsearch/es-demo-2
storageSecretName: gcs-secret
Here, you can see that Stash has resolved the variables in prefix field and substituted them with the equivalent information from this new database.
Verify BackupConfiguration
Now, let’s verify whether Stash has created a BackupConfiguration for our Elasticsearch or not.
❯ kubectl get backupconfiguration -n demo-2
NAME TASK SCHEDULE PAUSED AGE
app-es-demo-2 elasticsearch-backup-7.3.2 */3 * * * * 77s
Now, let’s check the YAML of the BackupConfiguration.
❯ kubectl get backupconfiguration -n demo-2 app-es-demo-2 -o yaml
apiVersion: stash.appscode.com/v1beta1
kind: BackupConfiguration
metadata:
name: app-es-demo-2
namespace: demo-2
...
spec:
driver: Restic
interimVolumeTemplate:
metadata:
name: elasticsearch-es-demo-2
spec:
accessModes:
- ReadWriteOnce
resources:
requests:
storage: 1Gi
storageClassName: standard
status: {}
repository:
name: app-es-demo-2
retentionPolicy:
keepLast: 5
name: keep-last-5
prune: true
runtimeSettings: {}
schedule: '*/3 * * * *'
target:
ref:
apiVersion: appcatalog.appscode.com/v1alpha1
kind: AppBinding
name: es-demo-2
tempDir: {}
status:
conditions:
- lastTransitionTime: "2021-02-12T12:24:07Z"
message: Repository demo-2/app-es-demo-2 exist.
reason: RepositoryAvailable
status: "True"
type: RepositoryFound
- lastTransitionTime: "2021-02-12T12:24:07Z"
message: Backend Secret demo-2/gcs-secret exist.
reason: BackendSecretAvailable
status: "True"
type: BackendSecretFound
- lastTransitionTime: "2021-02-12T12:24:07Z"
message: Backup target appcatalog.appscode.com/v1alpha1 appbinding/es-demo-2 found.
reason: TargetAvailable
status: "True"
type: BackupTargetFound
- lastTransitionTime: "2021-02-12T12:24:07Z"
message: Successfully created backup triggering CronJob.
reason: CronJobCreationSucceeded
status: "True"
type: CronJobCreated
observedGeneration: 1
Notice the schedule section. This time the BackupConfiguration has been created with the schedule we have provided via annotation.
Also, notice the target section. Stash has automatically added the new Elasticsearch as the target of this BackupConfiguration.
Verify Backup
Now, let’s wait for a backup run to complete. You can watch for BackupSession as below,
❯ kubectl get backupsession -n demo-2 -w
NAME INVOKER-TYPE INVOKER-NAME PHASE AGE
app-es-demo-2-1613132831 BackupConfiguration app-es-demo-2 0s
app-es-demo-2-1613132831 BackupConfiguration app-es-demo-2 Running 17s
app-es-demo-2-1613132831 BackupConfiguration app-es-demo-2 Succeeded 41s
Once the backup has been completed successfully, you should see that Stash has created a new directory as pointed by the prefix field of the new Repository and stored the backed up data there.
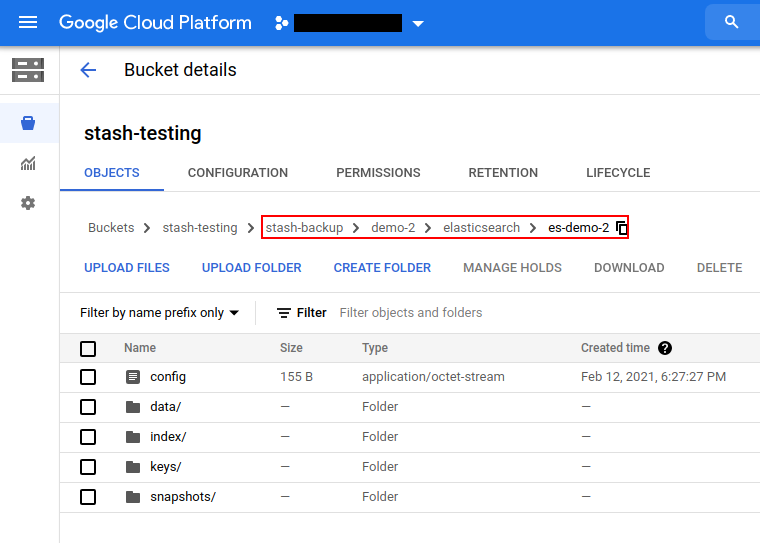
Auto-backup with custom parameters
In this section, we are going to backup an Elasticsearch database of demo-3 namespace. This time, we are going to pass some parameters for the Task through the annotations.
Create Storage Secret
At first, let’s create the gcs-secret in demo-3 namespace with the access credentials to our GCS bucket.
❯ kubectl create secret generic -n demo-3 gcs-secret \
--from-file=./RESTIC_PASSWORD \
--from-file=./GOOGLE_PROJECT_ID \
--from-file=./GOOGLE_SERVICE_ACCOUNT_JSON_KEY
secret/gcs-secret created
Create Database
Now, we are going to create an Elasticsearch CRO in demo-3 namespace. Below is the YAML of the Elasticsearch object that we are going to create,
apiVersion: kubedb.com/v1alpha2
kind: Elasticsearch
metadata:
name: es-demo-3
namespace: demo-3
annotations:
stash.appscode.com/backup-blueprint: elasticsearch-backup-template
params.stash.appscode.com/args: --ignoreType=settings,template
spec:
version: xpack-7.9.1-v1
replicas: 1
storageType: Durable
storage:
resources:
requests:
storage: 1Gi
storageClassName: standard
terminationPolicy: WipeOut
Notice the annotations section. This time, we have passed an argument via params.stash.appscode.com/args annotation along with the stash.appscode.com/backup-blueprint annotation.
Let’s create the above Elasticsearch CRO,
❯ kubectl apply -f https://github.com/kubedb/docs/raw/v2021.04.16/docs/guides/elasticsearch/backup/auto-backup/examples/es-demo-3.yaml
elasticsearch.kubedb.com/es-demo-3 created
Verify Auto-backup configured
Now, let’s verify whether the auto-backup resources has been created or not.
Verify Repository
At first, let’s verify whether Stash has created a Repository for our Elasticsearch or not.
❯ kubectl get repository -n demo-3
NAME INTEGRITY SIZE SNAPSHOT-COUNT LAST-SUCCESSFUL-BACKUP AGE
app-es-demo-3 23s
Now, let’s check the YAML of the Repository.
❯ kubectl get repository -n demo-3 app-es-demo-3 -o yaml
apiVersion: stash.appscode.com/v1alpha1
kind: Repository
metadata:
name: app-es-demo-3
namespace: demo-3
...
spec:
backend:
gcs:
bucket: stash-testing
prefix: stash-backup/demo-3/elasticsearch/es-demo-3
storageSecretName: gcs-secret
Here, you can see that Stash has resolved the variables in prefix field and substituted them with the equivalent information from this new database.
Verify BackupConfiguration
Now, let’s verify whether Stash has created a BackupConfiguration for our Elasticsearch or not.
❯ kubectl get backupconfiguration -n demo-3
NAME TASK SCHEDULE PAUSED AGE
app-es-demo-3 elasticsearch-backup-7.3.2 */5 * * * * 84s
Now, let’s check the YAML of the BackupConfiguration.
❯ kubectl get backupconfiguration -n demo-3 app-es-demo-3 -o yaml
apiVersion: stash.appscode.com/v1beta1
kind: BackupConfiguration
metadata:
name: app-es-demo-3
namespace: demo-3
...
spec:
driver: Restic
interimVolumeTemplate:
metadata:
name: elasticsearch-es-demo-3
spec:
accessModes:
- ReadWriteOnce
resources:
requests:
storage: 1Gi
storageClassName: standard
status: {}
repository:
name: app-es-demo-3
retentionPolicy:
keepLast: 5
name: keep-last-5
prune: true
runtimeSettings: {}
schedule: '*/5 * * * *'
target:
ref:
apiVersion: appcatalog.appscode.com/v1alpha1
kind: AppBinding
name: es-demo-3
task:
params:
- name: args
value: --ignoreType=settings,template
tempDir: {}
status:
conditions:
- lastTransitionTime: "2021-02-12T12:39:14Z"
message: Repository demo-3/app-es-demo-3 exist.
reason: RepositoryAvailable
status: "True"
type: RepositoryFound
- lastTransitionTime: "2021-02-12T12:39:14Z"
message: Backend Secret demo-3/gcs-secret exist.
reason: BackendSecretAvailable
status: "True"
type: BackendSecretFound
- lastTransitionTime: "2021-02-12T12:39:14Z"
message: Backup target appcatalog.appscode.com/v1alpha1 appbinding/es-demo-3 found.
reason: TargetAvailable
status: "True"
type: BackupTargetFound
- lastTransitionTime: "2021-02-12T12:39:14Z"
message: Successfully created backup triggering CronJob.
reason: CronJobCreationSucceeded
status: "True"
type: CronJobCreated
observedGeneration: 1
Notice the task section. The args parameter that we had passed via annotations has been added to the params section.
Also, notice the target section. Stash has automatically added the new Elasticsearch as the target of this BackupConfiguration.
Verify Backup
Now, let’s wait for a backup run to complete. You can watch for BackupSession as below,
❯ kubectl get backupsession -n demo-3 -w
NAME INVOKER-TYPE INVOKER-NAME PHASE AGE
app-es-demo-3-1613133604 BackupConfiguration app-es-demo-3 0s
app-es-demo-3-1613133604 BackupConfiguration app-es-demo-3 Running 5s
app-es-demo-3-1613133604 BackupConfiguration app-es-demo-3 Succeeded 48s
Once the backup has been completed successfully, you should see that Stash has created a new directory as pointed by the prefix field of the new Repository and stored the backed up data there.
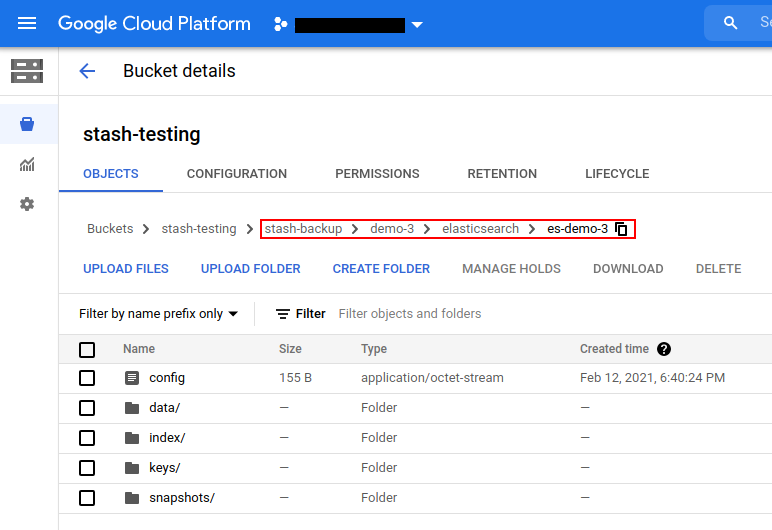
Cleanup
To cleanup the resources crated by this tutorial, run the following commands,
❯ kubectl delete -f https://github.com/kubedb/docs/raw/v2021.04.16/docs/guides/elasticsearch/backup/auto-backup/examples/
backupblueprint.stash.appscode.com "elasticsearch-backup-template" deleted
elasticsearch.kubedb.com "es-demo-2" deleted
elasticsearch.kubedb.com "es-demo-3" deleted
elasticsearch.kubedb.com "es-demo" deleted
❯ kubectl delete repository -n demo --all
repository.stash.appscode.com "app-es-demo" deleted
❯ kubectl delete repository -n demo-2 --all
repository.stash.appscode.com "app-es-demo-2" deleted
❯ kubectl delete repository -n demo-3 --all
repository.stash.appscode.com "app-es-demo-3" deleted



































