You are looking at the documentation of a prior release. To read the documentation of the latest release, please
visit here.
New to KubeDB? Please start here.
MongoDB QuickStart
This tutorial will show you how to use KubeDB to run a MongoDB database.
Before You Begin
At first, you need to have a Kubernetes cluster, and the kubectl command-line tool must be configured to communicate with your cluster. If you do not already have a cluster, you can create one by using kind.
Now, install KubeDB cli on your workstation and KubeDB operator in your cluster following the steps here.
StorageClass is required to run KubeDB. Check the available StorageClass in cluster.
$ kubectl get storageclasses NAME PROVISIONER RECLAIMPOLICY VOLUMEBINDINGMODE ALLOWVOLUMEEXPANSION AGE standard (default) rancher.io/local-path Delete WaitForFirstConsumer false 9hTo keep things isolated, this tutorial uses a separate namespace called
demothroughout this tutorial. Run the following command to prepare your cluster for this tutorial:$ kubectl create ns demo namespace/demo created
Note: The yaml files used in this tutorial are stored in docs/examples/mongodb folder in GitHub repository kubedb/docs.
Find Available MongoDBVersion
When you have installed KubeDB, it has created MongoDBVersion crd for all supported MongoDB versions. Check 0
$ kubectl get mongodbversions
NAME VERSION DB_IMAGE DEPRECATED AGE
3.4.17-v1 3.4.17 kubedb/mongo:3.4.17-v1 8h
3.4.22-v1 3.4.22 kubedb/mongo:3.4.22-v1 8h
3.6.13-v1 3.6.13 kubedb/mongo:3.6.13-v1 8h
3.6.18-percona 3.6.18 percona/percona-server-mongodb:3.6.18 8h
3.6.8-v1 3.6.8 kubedb/mongo:3.6.8-v1 8h
4.0.10-percona 4.0.10 percona/percona-server-mongodb:4.0.10 8h
4.0.11-v1 4.0.11 kubedb/mongo:4.0.11-v1 8h
4.0.3-v1 4.0.3 kubedb/mongo:4.0.3-v1 8h
4.0.5-v3 4.0.5 kubedb/mongo:4.0.5-v3 8h
4.1.13-v1 4.1.13 kubedb/mongo:4.1.13-v1 8h
4.1.4-v1 4.1.4 kubedb/mongo:4.1.4-v1 8h
4.1.7-v3 4.1.7 kubedb/mongo:4.1.7-v3 8h
4.2.3 4.2.3 kubedb/mongo:4.2.3 8h
4.2.7-percona 4.2.7 percona/percona-server-mongodb:4.2.7-7 8h
Create a MongoDB database
KubeDB implements a MongoDB CRD to define the specification of a MongoDB database. Below is the MongoDB object created in this tutorial.
apiVersion: kubedb.com/v1alpha2
kind: MongoDB
metadata:
name: mgo-quickstart
namespace: demo
spec:
version: "4.2.3"
storageType: Durable
storage:
storageClassName: "standard"
accessModes:
- ReadWriteOnce
resources:
requests:
storage: 1Gi
terminationPolicy: DoNotTerminate
$ kubectl create -f https://github.com/kubedb/docs/raw/v2021.11.24/docs/examples/mongodb/quickstart/demo-1.yaml
mongodb.kubedb.com/mgo-quickstart created
Here,
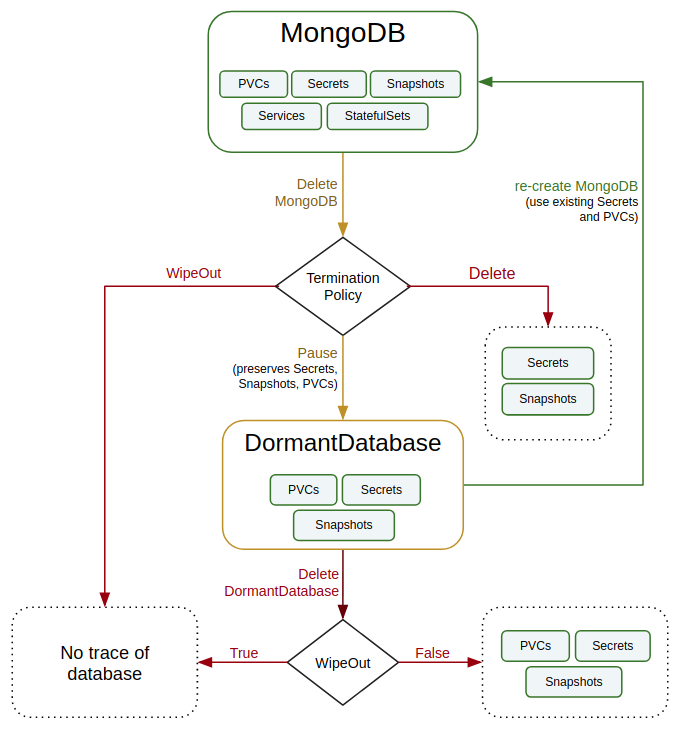
spec.versionis name of the MongoDBVersion crd where the docker images are specified. In this tutorial, a MongoDB 4.2.3 database is created.spec.storageTypespecifies the type of storage that will be used for MongoDB database. It can beDurableorEphemeral. Default value of this field isDurable. IfEphemeralis used then KubeDB will create MongoDB database usingEmptyDirvolume. In this case, you don’t have to specifyspec.storagefield. This is useful for testing purposes.spec.storagespecifies PVC spec that will be dynamically allocated to store data for this database. This storage spec will be passed to the StatefulSet created by KubeDB operator to run database pods. You can specify any StorageClass available in your cluster with appropriate resource requests.spec.terminationPolicygives flexibility whether tonullify(reject) the delete operation ofMongoDBcrd or which resources KubeDB should keep or delete when you deleteMongoDBcrd. If admission webhook is enabled, It prevents users from deleting the database as long as thespec.terminationPolicyis set toDoNotTerminate. Learn details of allTerminationPolicyhere
Note:
spec.storagesection is used to create PVC for database pod. It will create PVC with storage size specified instorage.resources.requests field. Don’t specify limits here. PVC does not get resized automatically.
KubeDB operator watches for MongoDB objects using Kubernetes api. When a MongoDB object is created, KubeDB operator will create a new StatefulSet and a Service with the matching MongoDB object name. KubeDB operator will also create a governing service for StatefulSets with the name <mongodb-name>-pods.
$ kubectl dba describe mg -n demo mgo-quickstart
Name: mgo-quickstart
Namespace: demo
CreationTimestamp: Thu, 11 Feb 2021 10:54:22 +0600
Labels: <none>
Annotations: kubectl.kubernetes.io/last-applied-configuration={"apiVersion":"kubedb.com/v1alpha2","kind":"MongoDB","metadata":{"annotations":{},"name":"mgo-quickstart","namespace":"demo"},"spec":{"storage":{"acces...
Replicas: 1 total
Status: Ready
StorageType: Durable
Volume:
StorageClass: standard
Capacity: 1Gi
Access Modes: RWO
Paused: false
Halted: false
Termination Policy: DoNotTerminate
StatefulSet:
Name: mgo-quickstart
CreationTimestamp: Thu, 11 Feb 2021 10:54:22 +0600
Labels: app.kubernetes.io/component=database
app.kubernetes.io/instance=mgo-quickstart
app.kubernetes.io/managed-by=kubedb.com
app.kubernetes.io/name=mongodbs.kubedb.com
Annotations: <none>
Replicas: 824639033752 desired | 1 total
Pods Status: 1 Running / 0 Waiting / 0 Succeeded / 0 Failed
Service:
Name: mgo-quickstart
Labels: app.kubernetes.io/component=database
app.kubernetes.io/instance=mgo-quickstart
app.kubernetes.io/managed-by=kubedb.com
app.kubernetes.io/name=mongodbs.kubedb.com
Annotations: <none>
Type: ClusterIP
IP: fd00:10:96::cc87
Port: primary 27017/TCP
TargetPort: db/TCP
Endpoints: [fd00:10:244::27]:27017
Service:
Name: mgo-quickstart-pods
Labels: app.kubernetes.io/component=database
app.kubernetes.io/instance=mgo-quickstart
app.kubernetes.io/managed-by=kubedb.com
app.kubernetes.io/name=mongodbs.kubedb.com
Annotations: <none>
Type: ClusterIP
IP: None
Port: db 27017/TCP
TargetPort: db/TCP
Endpoints: [fd00:10:244::27]:27017
Auth Secret:
Name: mgo-quickstart-auth
Labels: app.kubernetes.io/component=database
app.kubernetes.io/instance=mgo-quickstart
app.kubernetes.io/managed-by=kubedb.com
app.kubernetes.io/name=mongodbs.kubedb.com
Annotations: <none>
Type: Opaque
Data:
username: 4 bytes
password: 16 bytes
AppBinding:
Metadata:
Annotations:
kubectl.kubernetes.io/last-applied-configuration: {"apiVersion":"kubedb.com/v1alpha2","kind":"MongoDB","metadata":{"annotations":{},"name":"mgo-quickstart","namespace":"demo"},"spec":{"storage":{"accessModes":["ReadWriteOnce"],"resources":{"requests":{"storage":"1Gi"}},"storageClassName":"standard"},"storageType":"Durable","terminationPolicy":"DoNotTerminate","version":"4.2.3"}}
Creation Timestamp: 2021-02-11T04:54:40Z
Labels:
app.kubernetes.io/component: database
app.kubernetes.io/instance: mgo-quickstart
app.kubernetes.io/managed-by: kubedb.com
app.kubernetes.io/name: mongodbs.kubedb.com
Name: mgo-quickstart
Namespace: demo
Spec:
Client Config:
Service:
Name: mgo-quickstart
Port: 27017
Scheme: mongodb
Secret:
Name: mgo-quickstart-auth
Type: kubedb.com/mongodb
Version: 4.2.3
Events:
Type Reason Age From Message
---- ------ ---- ---- -------
Normal Successful 46s MongoDB operator Successfully created Service
Normal Successful 46s MongoDB operator Successfully stats service
Normal Successful 46s MongoDB operator Successfully stats service
Normal Successful 46s MongoDB operator Successfully created stats service
Normal Successful 28s MongoDB operator Successfully patched MongoDB
Normal Successful 28s MongoDB operator Successfully stats service
Normal Successful 28s MongoDB operator Successfully patched StatefulSet demo/mgo-quickstart
Normal Successful 28s MongoDB operator Successfully patched MongoDB
Normal Successful 28s MongoDB operator Successfully created appbinding
Normal Successful 28s MongoDB operator Successfully stats service
Normal Successful 28s MongoDB operator Successfully stats service
Normal Successful 28s MongoDB operator Successfully patched StatefulSet demo/mgo-quickstart
Normal Successful 4s MongoDB operator Successfully stats service
Normal Successful 4s MongoDB operator Successfully patched StatefulSet demo/mgo-quickstart
Normal Successful 4s MongoDB operator Successfully patched MongoDB
Normal Successful 4s MongoDB operator Successfully stats service
Normal Successful 4s MongoDB operator Successfully patched StatefulSet demo/mgo-quickstart
Normal Successful 4s MongoDB operator Successfully patched MongoDB
Normal Successful 4s MongoDB operator Successfully stats service
Normal Successful 4s MongoDB operator Successfully patched StatefulSet demo/mgo-quickstart
Normal Successful 4s MongoDB operator Successfully patched MongoDB
$ kubectl get statefulset -n demo
NAME READY AGE
mgo-quickstart 1/1 105s
$ kubectl get pvc -n demo
NAME STATUS VOLUME CAPACITY ACCESS MODES STORAGECLASS AGE
datadir-mgo-quickstart-0 Bound pvc-9c738632-29cf-11e9-aebf-080027875192 1Gi RWO standard 16m
$ kubectl get pv -n demo
NAME CAPACITY ACCESS MODES RECLAIM POLICY STATUS CLAIM STORAGECLASS REASON AGE
pvc-9c738632-29cf-11e9-aebf-080027875192 1Gi RWO Delete Bound demo/datadir-mgo-quickstart-0 standard 17m
$ kubectl get service -n demo
NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE
mgo-quickstart ClusterIP 10.111.237.184 <none> 27017/TCP 18m
mgo-quickstart-pods ClusterIP None <none> 27017/TCP 18m
KubeDB operator sets the status.phase to Ready once the database is successfully created. Run the following command to see the modified MongoDB object:
$ kubectl get mg -n demo mgo-quickstart -o yaml
apiVersion: kubedb.com/v1alpha2
kind: MongoDB
metadata:
annotations:
kubectl.kubernetes.io/last-applied-configuration: |
{"apiVersion":"kubedb.com/v1alpha2","kind":"MongoDB","metadata":{"annotations":{},"name":"mgo-quickstart","namespace":"demo"},"spec":{"storage":{"accessModes":["ReadWriteOnce"],"resources":{"requests":{"storage":"1Gi"}},"storageClassName":"standard"},"storageType":"Durable","terminationPolicy":"DoNotTerminate","version":"4.2.3"}}
creationTimestamp: "2021-02-09T14:06:57Z"
finalizers:
- kubedb.com
generation: 2
managedFields:
- apiVersion: kubedb.com/v1alpha2
fieldsType: FieldsV1
fieldsV1:
f:metadata:
f:annotations:
.: {}
f:kubectl.kubernetes.io/last-applied-configuration: {}
f:spec:
.: {}
f:storage:
.: {}
f:accessModes: {}
f:resources:
.: {}
f:requests:
.: {}
f:storage: {}
f:storageClassName: {}
f:storageType: {}
f:terminationPolicy: {}
f:version: {}
manager: kubectl-client-side-apply
operation: Update
time: "2021-02-09T14:06:57Z"
- apiVersion: kubedb.com/v1alpha2
fieldsType: FieldsV1
fieldsV1:
f:metadata:
f:finalizers: {}
f:spec:
f:authSecret:
.: {}
f:name: {}
f:status:
.: {}
f:conditions: {}
f:observedGeneration: {}
f:phase: {}
manager: mg-operator
operation: Update
time: "2021-02-09T14:06:57Z"
name: mgo-quickstart
namespace: demo
resourceVersion: "59940"
uid: b0bcf12e-7a3a-4f15-9493-461e6087964b
spec:
authSecret:
name: mgo-quickstart-auth
podTemplate:
controller: {}
metadata: {}
spec:
affinity:
podAntiAffinity:
preferredDuringSchedulingIgnoredDuringExecution:
- podAffinityTerm:
labelSelector:
matchLabels:
app.kubernetes.io/instance: mgo-quickstart
app.kubernetes.io/managed-by: kubedb.com
app.kubernetes.io/name: mongodbs.kubedb.com
namespaces:
- demo
topologyKey: kubernetes.io/hostname
weight: 100
- podAffinityTerm:
labelSelector:
matchLabels:
app.kubernetes.io/instance: mgo-quickstart
app.kubernetes.io/managed-by: kubedb.com
app.kubernetes.io/name: mongodbs.kubedb.com
namespaces:
- demo
topologyKey: failure-domain.beta.kubernetes.io/zone
weight: 50
livenessProbe:
exec:
command:
- bash
- -c
- "set -x; if [[ $(mongo admin --host=localhost --username=$MONGO_INITDB_ROOT_USERNAME
--password=$MONGO_INITDB_ROOT_PASSWORD --authenticationDatabase=admin
--quiet --eval \"db.adminCommand('ping').ok\" ) -eq \"1\" ]]; then \n
\ exit 0\n fi\n exit 1"
failureThreshold: 3
periodSeconds: 10
successThreshold: 1
timeoutSeconds: 5
readinessProbe:
exec:
command:
- bash
- -c
- "set -x; if [[ $(mongo admin --host=localhost --username=$MONGO_INITDB_ROOT_USERNAME
--password=$MONGO_INITDB_ROOT_PASSWORD --authenticationDatabase=admin
--quiet --eval \"db.adminCommand('ping').ok\" ) -eq \"1\" ]]; then \n
\ exit 0\n fi\n exit 1"
failureThreshold: 3
periodSeconds: 10
successThreshold: 1
timeoutSeconds: 1
resources:
limits:
cpu: 500m
memory: 1Gi
requests:
cpu: 500m
memory: 1Gi
serviceAccountName: mgo-quickstart
replicas: 1
sslMode: disabled
storage:
accessModes:
- ReadWriteOnce
resources:
requests:
storage: 1Gi
storageClassName: standard
storageEngine: wiredTiger
storageType: Durable
terminationPolicy: DoNotTerminate
version: 4.2.3
status:
conditions:
- lastTransitionTime: "2021-02-09T14:06:57Z"
message: 'The KubeDB operator has started the provisioning of MongoDB: demo/mgo-quickstart'
reason: DatabaseProvisioningStartedSuccessfully
status: "True"
type: ProvisioningStarted
- lastTransitionTime: "2021-02-09T14:07:16Z"
message: All desired replicas are ready.
reason: AllReplicasReady
status: "True"
type: ReplicaReady
- lastTransitionTime: "2021-02-09T14:07:42Z"
message: 'The MongoDB: demo/mgo-quickstart is accepting client requests.'
observedGeneration: 2
reason: DatabaseAcceptingConnectionRequest
status: "True"
type: AcceptingConnection
- lastTransitionTime: "2021-02-09T14:07:42Z"
message: 'The MongoDB: demo/mgo-quickstart is ready.'
observedGeneration: 2
reason: ReadinessCheckSucceeded
status: "True"
type: Ready
- lastTransitionTime: "2021-02-09T14:07:42Z"
message: 'The MongoDB: demo/mgo-quickstart is successfully provisioned.'
observedGeneration: 2
reason: DatabaseSuccessfullyProvisioned
status: "True"
type: Provisioned
observedGeneration: 2
phase: Ready
Please note that KubeDB operator has created a new Secret called mgo-quickstart-auth (format: {mongodb-object-name}-auth) for storing the password for mongodb superuser. This secret contains a username key which contains the username for MongoDB superuser and a password key which contains the password for MongoDB superuser.
If you want to use custom or existing secret please specify that when creating the MongoDB object using spec.authSecret.name. While creating this secret manually, make sure the secret contains these two keys containing data username and password. For more details, please see here.
Now, you can connect to this database through mongo-shell. In this tutorial, we are connecting to the MongoDB server from inside the pod.
$ kubectl get secrets -n demo mgo-quickstart-auth -o jsonpath='{.data.\username}' | base64 -d
root
$ kubectl get secrets -n demo mgo-quickstart-auth -o jsonpath='{.data.\password}' | base64 -d
t1QJppJw_B13UIES
$ kubectl exec -it mgo-quickstart-0 -n demo sh
> mongo admin
> db.auth("root","t1QJppJw_B13UIES")
1
> show dbs
admin 0.000GB
local 0.000GB
mydb 0.000GB
> show users
{
"_id" : "admin.root",
"userId" : UUID("7e7f3e5d-4ebd-438a-9c40-91ed59bf242f"),
"user" : "root",
"db" : "admin",
"roles" : [
{
"role" : "root",
"db" : "admin"
}
],
"mechanisms" : [
"SCRAM-SHA-1",
"SCRAM-SHA-256"
]
}
> use newdb
switched to db newdb
> db.movie.insert({"name":"batman"});
WriteResult({ "nInserted" : 1 })
> db.movie.find().pretty()
{ "_id" : ObjectId("5a2e435d7ec14e7bda785f16"), "name" : "batman" }
> exit
bye
DoNotTerminate Property
When terminationPolicy is DoNotTerminate, KubeDB takes advantage of ValidationWebhook feature in Kubernetes 1.9.0 or later clusters to implement DoNotTerminate feature. If admission webhook is enabled, It prevents users from deleting the database as long as the spec.terminationPolicy is set to DoNotTerminate. You can see this below:
$ kubectl delete mg mgo-quickstart -n demo
Error from server (BadRequest): admission webhook "mongodb.validators.kubedb.com" denied the request: mongodb "mgo-quickstart" can't be halted. To delete, change spec.terminationPolicy
Halt Database
When TerminationPolicy is set to halt, and you delete the mongodb object, the KubeDB operator will delete the StatefulSet and its pods but leaves the PVCs, secrets and database backup (snapshots) intact. Learn details of all TerminationPolicy here.
You can also keep the mongodb object and halt the database to resume it again later. If you halt the database, the kubedb operator will delete the statefulsets and services but will keep the mongodb object, pvcs, secrets and backup (snapshots).
To halt the database, first you have to set the terminationPolicy to Halt in existing database. You can use the below command to set the terminationPolicy to Halt, if it is not already set.
$ kubectl patch -n demo mg/mgo-quickstart -p '{"spec":{"terminationPolicy":"Halt"}}' --type="merge"
mongodb.kubedb.com/mgo-quickstart patched
Then, you have to set the spec.halted as true to set the database in a Halted state. You can use the below command.
$ kubectl patch -n demo mg/mgo-quickstart -p '{"spec":{"halted":true}}' --type="merge"
mongodb.kubedb.com/mgo-quickstart patched
After that, kubedb will delete the statefulsets and services and you can see the database Phase as Halted.
Now, you can run the following command to get all mongodb resources in demo namespaces,
$ kubectl get mg,sts,svc,secret,pvc -n demo
NAME VERSION STATUS AGE
mongodb.kubedb.com/mgo-quickstart 4.2.3 Halted 9m43s
NAME TYPE DATA AGE
secret/default-token-x2zcl kubernetes.io/service-account-token 3 47h
secret/mgo-quickstart-auth Opaque 2 23h
NAME STATUS VOLUME CAPACITY ACCESS MODES STORAGECLASS AGE
persistentvolumeclaim/datadir-mgo-quickstart-0 Bound pvc-816daa52-ee40-496f-a148-c75344a1b433 1Gi RWO standard 9m43s
Resume Halted Database
Now, to resume the database, i.e. to get the same database setup back again, you have to set the the spec.halted as false. You can use the below command.
$ kubectl patch -n demo mg/mgo-quickstart -p '{"spec":{"halted":false}}' --type="merge"
mongodb.kubedb.com/mgo-quickstart patched
When the database is resumed successfully, you can see the database Status is set to Ready.
$ kubectl get mg -n demo
NAME VERSION STATUS AGE
mgo-quickstart 4.2.3 Ready 6m27s
Now, If you again exec into the pod and look for previous data, you will see that, all the data persists.
$ kubectl exec -it mgo-quickstart-0 -n demo bash
mongodb@mgo-quickstart-0:/$ mongo admin -u root -p 7QiqLcuSCmZ8PU5a
rs0:PRIMARY> use newdb
switched to db newdb
rs0:PRIMARY> db.movie.find()
{ "_id" : ObjectId("6024b3e47c614cd582c9bb44"), "name" : "batman" }
Cleaning up
To cleanup the Kubernetes resources created by this tutorial, run:
kubectl patch -n demo mg/mgo-quickstart -p '{"spec":{"terminationPolicy":"WipeOut"}}' --type="merge"
kubectl delete -n demo mg/mgo-quickstart
kubectl delete ns demo
Tips for Testing
If you are just testing some basic functionalities, you might want to avoid additional hassles due to some safety features that are great for production environment. You can follow these tips to avoid them.
- Use
storageType: Ephemeral. Databases are precious. You might not want to lose your data in your production environment if database pod fail. So, we recommend usingspec.storageType: Durableand provide storage spec inspec.storagesection. For testing purpose, you can just usespec.storageType: Ephemeral. KubeDB will use emptyDir for storage. You will not require to providespec.storagesection. - Use
terminationPolicy: WipeOut. It is nice to be able to resume database. So, we haveHaltoption which preserves all yourPVCs,Secrets,Snapshotsetc. If you don’t want to resume database, you can just usespec.terminationPolicy: WipeOut. It will delete everything created by KubeDB for a particular MongoDB crd when you delete the mongodb object. For more details about termination policy, please visit here.
Next Steps
- Backup and Restore MongoDB databases using Stash.
- Initialize MongoDB with Script.
- Monitor your MongoDB database with KubeDB using out-of-the-box Prometheus operator.
- Monitor your MongoDB database with KubeDB using out-of-the-box builtin-Prometheus.
- Use private Docker registry to deploy MongoDB with KubeDB.
- Detail concepts of MongoDB object.
- Detail concepts of MongoDBVersion object.
- Want to hack on KubeDB? Check our contribution guidelines.






























