You are looking at the documentation of a prior release. To read the documentation of the latest release, please
visit here.
New to KubeDB? Please start here.
Redis Sentinel
Redis Sentinel is a high-availability solution for Redis, which provides automatic failover and monitoring for Redis instances. It helps to ensure that in the event of a Redis instance failure, Sentinel can detect the failure and automatically promote one of the slaves to be the new master, providing a highly available and self-healing Redis setup. Additionally, Redis Sentinel provides notifications and other tools for monitoring the health of Redis instances and handling failures.
So in practical terms, what do you get with Redis Sentinel?
High Availability: Redis Sentinel provides automatic failover and monitoring, ensuring that in the event of a Redis instance failure, there is always a functioning master available.
Self-healing : Sentinel can detect failures and promote a slave to be the new master, reducing downtime and ensuring continuous operation of the Redis setup.
Monitoring : Sentinel provides a suite of monitoring and notification tools for keeping track of the health of Redis instances and detecting failures.
Load balancing: Sentinel can be used to manage multiple Redis instances and provide load balancing, distributing clients across multiple Redis instances for better performance and reliability.
Scalability: Redis Sentinel can be used to create a scalable Redis setup, allowing multiple Redis instances to be added and managed as needed.
Simplified administration: Redis Sentinel provides a centralized management interface for Redis instances, making it easier to manage and monitor large-scale Redis setups.
Redis Sentinel TCP ports
Redis Sentinel instances typically use two TCP ports for communication:
Port 26379: This is the default port used for inter-Sentinel communication, allowing Sentinels to communicate with each other and maintain a consistent view of the Redis cluster.
Port 6379: This is the default port used for communication with Redis instances. Sentinels use this port to monitor and manage Redis instances, including promoting slaves to masters in the event of a failure.
It is possible to configure Redis Sentinel to use different ports, but the default ports are commonly used and are a good starting point for most Redis Sentinel installations.
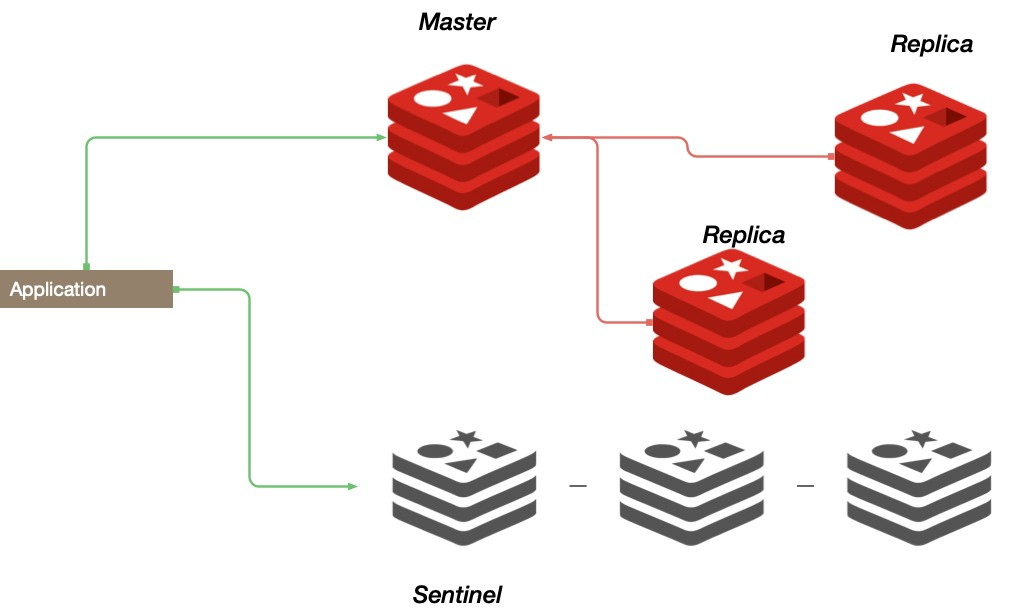
Redis Sentinel master-replica model
In Redis Sentinel mode, the master-replica model works as follows:
Monitoring: Redis Sentinels continuously monitor the health of the Redis master and replica instances in the cluster, checking for failures or other issues.
Failover: In the event of a failure of the master instance, Redis Sentinels automatically promote one of the replica instances to be the new master, ensuring that the Redis setup remains available. The Sentinels communicate with each other to coordinate the failover process and ensure that all instances are aware of the change in the cluster’s state.
Data Replication: The master instance continuously replicates its data to the replica instances, ensuring that the data remains consistent across all instances in the cluster.
Load Balancing: Redis Sentinels can be configured to distribute read operations across multiple replica instances, improving performance and reducing the load on the master instance.
Automatic Recovery: In the event of a failure, Redis Sentinels can automatically recover the cluster by promoting a new master instance and re-establishing data replication.
Overall, the master-replica model in Redis Sentinel mode helps to ensure high availability, reliability, and scalability for Redis setups by continuously monitoring the health of the cluster and automatically failing over to a replica instance in the event of a failure.
Redis Sentinel configuration parameters
Redis Sentinel has a number of configuration parameters that can be set to control its behavior. Some of the most important parameters include:
- sentinel announce-ip
: This parameter sets the IP address that Sentinels should use when announcing themselves to the cluster. - sentinel announce-port
: This parameter sets the port that Sentinels should use when announcing themselves to the cluster. - sentinel monitor
- sentinel parallel-syncs
- sentinel down-after-milliseconds
: This parameter sets the amount of time that Sentinels should wait before considering a Redis instance to be down. - sentinel failover-timeout
: This parameter sets the maximum amount of time that Sentinels should wait for a failover to complete. - sentinel auth-user
- sentinel auth-pass
These are just a few of the many configuration parameters that can be set for Redis Sentinel. By carefully setting these parameters, administrators can configure Redis Sentinel to meet the specific needs of their deployments and ensure optimal performance and reliability.
To learn more about Redis Sentinel , head over to Official Documentation
Next Steps
- Deploy Redis Sentinel using KubeDB.
- Detail concepts of Redis object.
- Detail concepts of RedisVersion object.



































