You are looking at the documentation of a prior release. To read the documentation of the latest release, please
visit here.
New to KubeDB? Please start here.
Monitoring Memcached Using Prometheus operator
Prometheus operator provides simple and Kubernetes native way to deploy and configure Prometheus server. This tutorial will show you how to use Prometheus operator to monitor Memcached database deployed with KubeDB.
The following diagram shows how KubeDB Provisioner operator monitor Memcached using Prometheus Operator. Open the image in a new tab to see the enlarged version.
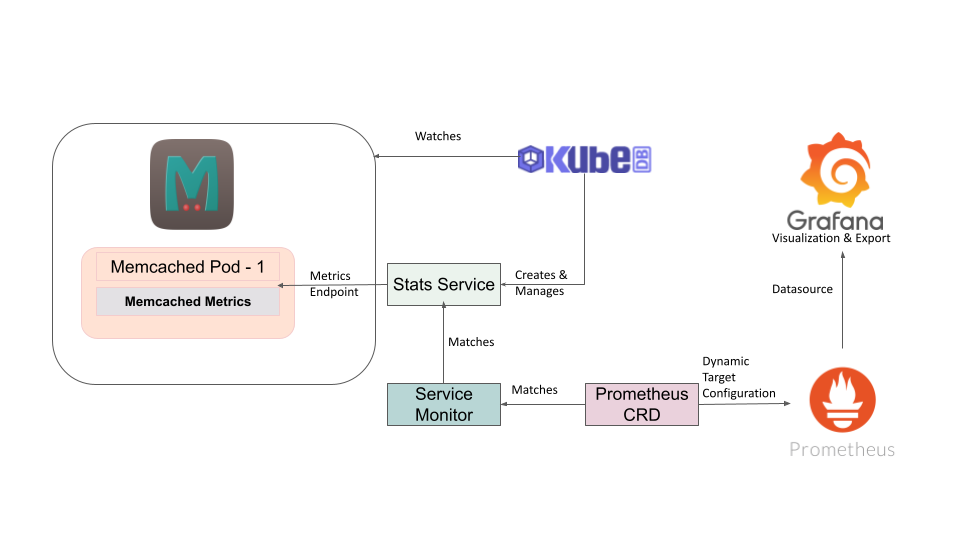
Before You Begin
At first, you need to have a Kubernetes cluster, and the kubectl command-line tool must be configured to communicate with your cluster. If you do not already have a cluster, you can create one by using kind.
To learn how Prometheus monitoring works with KubeDB in general, please visit here.
We need a Prometheus operator instance running. If you don’t already have a running instance, deploy one following the docs from here.
To keep Prometheus resources isolated, we are going to use a separate namespace called
monitoringto deploy respective monitoring resources. We are going to deploy database indemonamespace.$ kubectl create ns monitoring namespace/monitoring created $ kubectl create ns demo namespace/demo created
Note: YAML files used in this tutorial are stored in docs/examples/memcached folder in GitHub repository kubedb/docs.
Find out required labels for ServiceMonitor
We need to know the labels used to select ServiceMonitor by a Prometheus crd. We are going to provide these labels in spec.monitor.prometheus.labels field of Memcached crd so that KubeDB creates ServiceMonitor object accordingly.
At first, let’s find out the available Prometheus server in our cluster.
$ kubectl get prometheus --all-namespaces
NAMESPACE NAME VERSION DESIRED READY RECONCILED AVAILABLE AGE
monitoring prometheus-kube-prometheus-prometheus v2.54.1 1 1 True True 3m
If you don’t have any Prometheus server running in your cluster, deploy one following the guide specified in Before You Begin section.
Now, let’s view the YAML of the available Prometheus server prometheus in monitoring namespace.
$ kubectl get prometheus -n monitoring prometheus-kube-prometheus-prometheus -o yaml
apiVersion: monitoring.coreos.com/v1
kind: Prometheus
metadata:
annotations:
meta.helm.sh/release-name: prometheus
meta.helm.sh/release-namespace: monitoring
creationTimestamp: "2024-09-17T13:24:28Z"
generation: 1
labels:
app: kube-prometheus-stack-prometheus
app.kubernetes.io/instance: prometheus
app.kubernetes.io/managed-by: Helm
app.kubernetes.io/part-of: kube-prometheus-stack
app.kubernetes.io/version: 62.7.0
chart: kube-prometheus-stack-62.7.0
heritage: Helm
release: prometheus
name: prometheus-kube-prometheus-prometheus
namespace: monitoring
resourceVersion: "396596"
uid: ee3cb256-1f08-4bd4-966a-2050822affbf
spec:
alerting:
alertmanagers:
- apiVersion: v2
name: prometheus-kube-prometheus-alertmanager
namespace: monitoring
pathPrefix: /
port: http-web
automountServiceAccountToken: true
enableAdminAPI: false
evaluationInterval: 30s
externalUrl: http://prometheus-kube-prometheus-prometheus.monitoring:9090
hostNetwork: false
image: quay.io/prometheus/prometheus:v2.54.1
listenLocal: false
logFormat: logfmt
logLevel: info
paused: false
podMonitorNamespaceSelector: {}
podMonitorSelector:
matchLabels:
release: prometheus
portName: http-web
probeNamespaceSelector: {}
probeSelector:
matchLabels:
release: prometheus
replicas: 1
retention: 10d
routePrefix: /
ruleNamespaceSelector: {}
ruleSelector:
matchLabels:
release: prometheus
scrapeConfigNamespaceSelector: {}
scrapeConfigSelector:
matchLabels:
release: prometheus
scrapeInterval: 30s
securityContext:
fsGroup: 2000
runAsGroup: 2000
runAsNonRoot: true
runAsUser: 1000
seccompProfile:
type: RuntimeDefault
serviceAccountName: prometheus-kube-prometheus-prometheus
serviceMonitorNamespaceSelector: {}
serviceMonitorSelector:
matchLabels:
release: prometheus
shards: 1
tsdb:
outOfOrderTimeWindow: 0s
version: v2.54.1
walCompression: true
status:
availableReplicas: 1
conditions:
- lastTransitionTime: "2024-09-17T13:24:45Z"
message: ""
observedGeneration: 1
reason: ""
status: "True"
type: Available
- lastTransitionTime: "2024-09-17T13:24:45Z"
message: ""
observedGeneration: 1
reason: ""
status: "True"
type: Reconciled
paused: false
replicas: 1
selector: app.kubernetes.io/instance=prometheus-kube-prometheus-prometheus,app.kubernetes.io/managed-by=prometheus-operator,app.kubernetes.io/name=prometheus,operator.prometheus.io/name=prometheus-kube-prometheus-prometheus,prometheus=prometheus-kube-prometheus-prometheus
shardStatuses:
- availableReplicas: 1
replicas: 1
shardID: "0"
unavailableReplicas: 0
updatedReplicas: 1
shards: 1
unavailableReplicas: 0
updatedReplicas: 1
Notice the spec.serviceMonitorSelector section. Here, release: prometheus label is used to select ServiceMonitor crd. So, we are going to use this label in spec.monitor.prometheus.labels field of Memcached crd.
Deploy Memcached with Monitoring Enabled
At first, let’s deploy an Memcached server with monitoring enabled. Below is the Memcached object that we are going to create.
apiVersion: kubedb.com/v1
kind: Memcached
metadata:
name: memcached
namespace: demo
spec:
replicas: 1
version: "1.6.22"
deletionPolicy: WipeOut
podTemplate:
spec:
containers:
- name: memcached
resources:
limits:
cpu: 500m
memory: 128Mi
requests:
cpu: 250m
memory: 64Mi
monitor:
agent: prometheus.io/operator
prometheus:
serviceMonitor:
labels:
release: prometheus
interval: 10s
Here,
monitor.agent: prometheus.io/operatorindicates that we are going to monitor this server using Prometheus operator.monitor.prometheus.namespace: monitoringspecifies that KubeDB should createServiceMonitorinmonitoringnamespace.monitor.prometheus.labelsspecifies that KubeDB should createServiceMonitorwith these labels.monitor.prometheus.intervalindicates that the Prometheus server should scrape metrics from this database with 10 seconds interval.
Let’s create the Memcached object that we have shown above,
$ kubectl create -f https://github.com/kubedb/docs/raw/v2024.11.18/docs/examples/memcached/monitoring/memcached.yaml
memcached.kubedb.com/memcached created
Now, wait for the database to go into Running state.
$ kubectl get mc -n demo memcached
NAME VERSION STATUS AGE
memcached 1.6.22 Ready 2m
KubeDB will create a separate stats service with name {Memcached crd name}-stats for monitoring purpose.
$ kubectl get svc -n demo --selector="app.kubernetes.io/instance=memcached"
NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE
memcached ClusterIP 10.96.91.51 <none> 11211/TCP 3m9s
memcached-pods ClusterIP None <none> 11211/TCP 3m9s
memcached-stats ClusterIP 10.96.50.21 <none> 56790/TCP 3m9s
Here, memcached-stats service has been created for monitoring purpose.
Let’s describe this stats service.
$ kubectl describe svc -n demo memcached-stats
Name: memcached-stats
Namespace: demo
Labels: app.kubernetes.io/component=database
app.kubernetes.io/instance=memcached
app.kubernetes.io/managed-by=kubedb.com
app.kubernetes.io/name=memcacheds.kubedb.com
kubedb.com/role=stats
Annotations: monitoring.appscode.com/agent: prometheus.io/operator
Selector: app.kubernetes.io/instance=memcached,app.kubernetes.io/managed-by=kubedb.com,app.kubernetes.io/name=memcacheds.kubedb.com
Type: ClusterIP
IP Family Policy: SingleStack
IP Families: IPv4
IP: 10.96.50.21
IPs: 10.96.50.21
Port: metrics 56790/TCP
TargetPort: metrics/TCP
Endpoints: 10.244.0.7:56790
Session Affinity: None
Events: <none>
Notice the Labels and Port fields. ServiceMonitor will use these information to target its endpoints.
KubeDB will also create a ServiceMonitor crd in monitoring namespace that select the endpoints of memcached-stats service. Verify that the ServiceMonitor crd has been created.
$ kubectl get servicemonitor -n demo
NAME AGE
memcached-stats 5m
Let’s verify that the ServiceMonitor has the label that we had specified in spec.monitor section of Memcached crd.
$ kubectl get servicemonitor -n demo memcached-stats -o yaml
apiVersion: monitoring.coreos.com/v1
kind: ServiceMonitor
metadata:
creationTimestamp: "2024-09-17T13:32:15Z"
generation: 1
labels:
app.kubernetes.io/component: database
app.kubernetes.io/instance: memcached
app.kubernetes.io/managed-by: kubedb.com
app.kubernetes.io/name: memcacheds.kubedb.com
release: prometheus
name: memcached-stats
namespace: demo
ownerReferences:
- apiVersion: v1
blockOwnerDeletion: true
controller: true
kind: Service
name: memcached-stats
uid: 6c05bc95-c26c-4b0b-988f-2ecc58e983bf
resourceVersion: "397210"
uid: b14633ab-338d-43a6-87bc-2ab77d761cf4
spec:
endpoints:
- honorLabels: true
path: /metrics
port: metrics
namespaceSelector:
matchNames:
- demo
selector:
matchLabels:
app.kubernetes.io/component: database
app.kubernetes.io/instance: memcached
app.kubernetes.io/managed-by: kubedb.com
app.kubernetes.io/name: memcacheds.kubedb.com
kubedb.com/role: stats
Notice that the ServiceMonitor has label release: prometheus that we had specified in Memcached crd.
Also notice that the ServiceMonitor has selector which match the labels we have seen in the memcached-stats service. It also, target the prom-http port that we have seen in the stats service.
Verify Monitoring Metrics
At first, let’s find out the respective Prometheus pod for prometheus Prometheus server.
$ kubectl get pod -n monitoring -l=app.kubernetes.io/name=prometheus
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
prometheus-prometheus-kube-prometheus-prometheus-0 2/2 Running 0 16m
Prometheus server is listening to port 9090 of prometheus-prometheus-0 pod. We are going to use port forwarding to access Prometheus dashboard.
Run following command on a separate terminal to forward the port 9090 of prometheus-prometheus-0 pod,
$ kubectl port-forward -n monitoring svc/prometheus-kube-prometheus-prometheus 9090
Forwarding from 127.0.0.1:9090 -> 9090
Forwarding from [::1]:9090 -> 9090
Now, we can access the dashboard at localhost:9090. Open http://localhost:9090 in your browser. You should see prom-http endpoint of memcached-stats service as one of the targets.
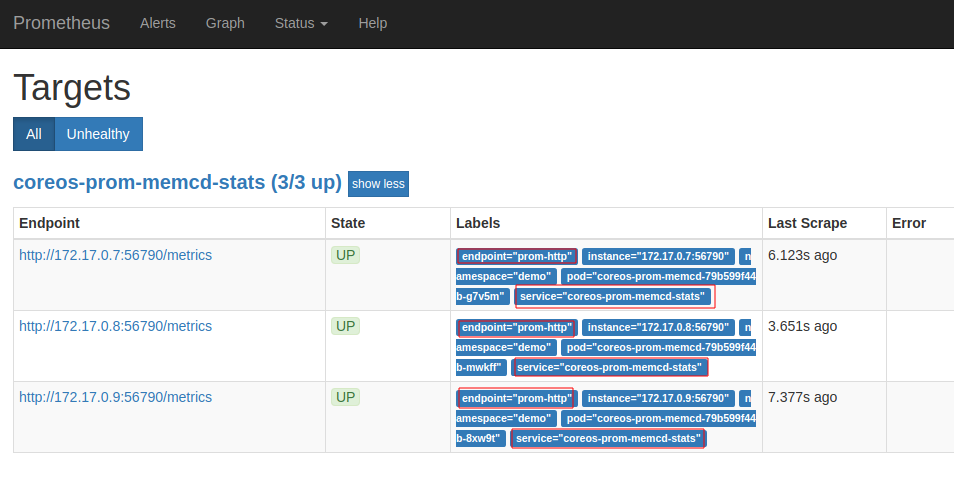
Check the endpoint and service labels marked by red rectangle. It verifies that the target is our expected database. Now, you can view the collected metrics and create a graph from homepage of this Prometheus dashboard. You can also use this Prometheus server as data source for Grafana and create beautiful dashboard with collected metrics.
Cleaning up
To cleanup the Kubernetes resources created by this tutorial, run following commands
# cleanup database
kubectl delete -n demo mc/memcached
# cleanup prometheus resources
kubectl delete -n monitoring prometheus prometheus
kubectl delete -n monitoring clusterrolebinding prometheus
kubectl delete -n monitoring clusterrole prometheus
kubectl delete -n monitoring serviceaccount prometheus
kubectl delete -n monitoring service prometheus-operated
# cleanup prometheus operator resources
kubectl delete -n monitoring deployment prometheus-operator
kubectl delete -n dmeo serviceaccount prometheus-operator
kubectl delete clusterrolebinding prometheus-operator
kubectl delete clusterrole prometheus-operator
# delete namespace
kubectl delete ns monitoring
kubectl delete ns demo
Next Steps
- Monitor your Memcached server with KubeDB using out-of-the-box builtin-Prometheus.
- Detail concepts of Memcached object.
- Use private Docker registry to deploy Memcached with KubeDB.
- Want to hack on KubeDB? Check our contribution guidelines.



































