You are looking at the documentation of a prior release. To read the documentation of the latest release, please
visit here.
New to KubeDB? Please start here.
MongoDB Arbiter
Arbiter is a member of MongoDB ReplicaSet. It does not have a copy of data set and cannot become a primary. In some circumstances (such as when you have a primary and a secondary, but cost constraints prohibit adding another secondary), you may choose to add an arbiter to your replica set. Replica sets may have arbiters to add a vote in elections for primary. Arbiters always have exactly 1 election vote, and thus allow replica sets to have an uneven number of voting members without the overhead of an additional member that replicates data. By default, it is a priority-0 member.
For example, in the following replica set with a 2 data bearing members (the primary and a secondary), an arbiter allows the set to have an odd number of votes to break a tie:
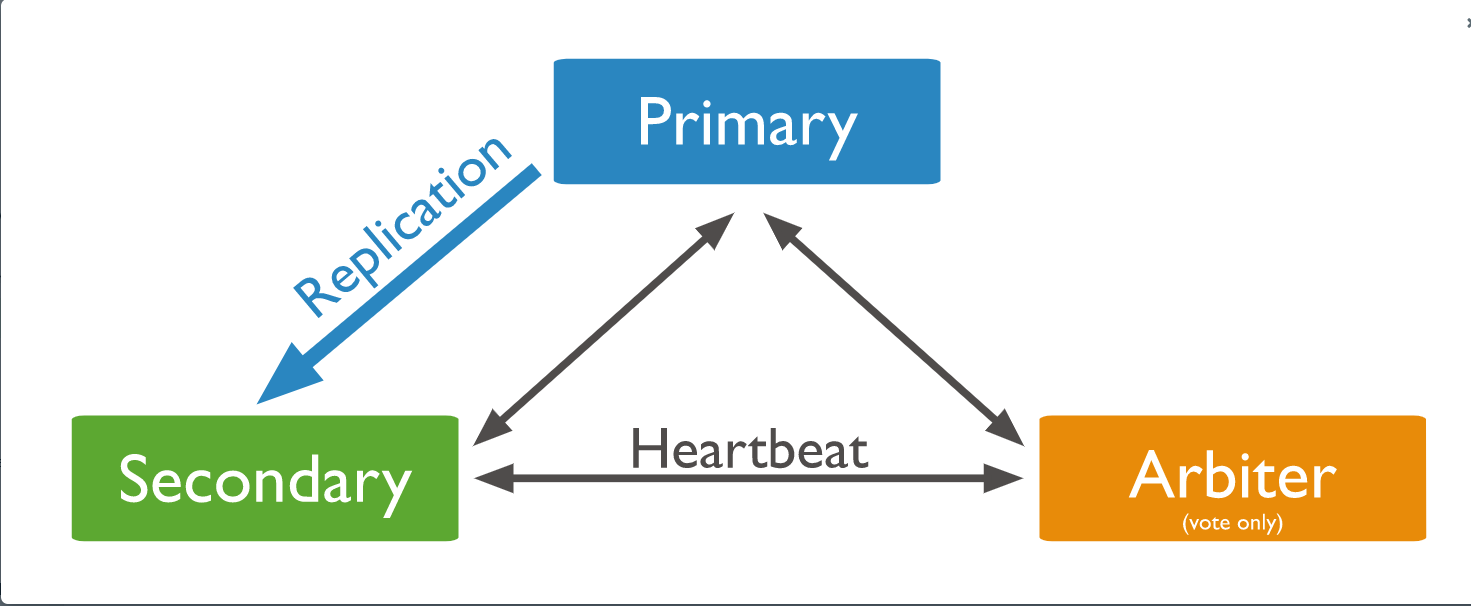
Considerations
There are some important considerations that should be taken care of by the Database administrators when deploying MongoDB.
Priority
Starting in MongoDB 3.6, arbiters have priority 0. When you update a replica set to MongoDB 3.6, if the existing configuration has an arbiter with priority 1, MongoDB 3.6 reconfigures the arbiter to have priority 0.
IMPORTANT: Do not run an arbiter on systems that also host the primary or the secondary members of the replica set. [reference].
Performance Issues
If you are using a three-member primary-secondary-arbiter (PSA) architecture, consider the following:
The write concern “majority” can cause performance issues if a secondary is unavailable or lagging.See Mitigate Performance Issues with PSA Replica Set to mitigate these issues.
If you are using a global default “majority” and the write concern is less than the size of the majority, your queries may return stale (not fully replicated) data.
Concerns with multiple Arbiters
Using multiple arbiters on same replicaSet can causes data inconsistency. Multiple arbiters prevent the reliable use of the majority write concern. For more details in this concerns, read this.
By considering this issue into account, KubeDB doesn’t support multiple arbiter to be deployed in a single replicaset.
Security
As arbiters do not store data, they do not possess the internal table of user and role mappings used for authentication. Thus When running with authorization, arbiters exchange credentials with other members of the set to authenticate.
Also MongoDB doc suggests to use TLS to avoid leaking unencrypted data when arbiter communicates with other replicaset member.
Protocol version
For replica sets, the write concern { w: 1 } only provides acknowledgement of write operations on the primary. Data may be rolled back if the primary steps down before the write operations have replicated to any of the secondaries. This type behaviour is called w:1 roolback.
For the following MongoDB versions, pv1 (protocol version 1, which is default Starting in 4.0) increases the likelihood of w:1 rollbacks compared to pv0 (no longer supported in MongoDB 4.0+) for replica sets with arbiters:
i) MongoDB 3.4.1
ii) MongoDB 3.4.0
iii) MongoDB 3.2.11 or earlier
Next Steps
- Deploy MongoDB ReplicaSet with Arbiter using KubeDB.
- Detail concepts of MongoDB object.
- Detail concepts of MongoDBVersion object.
- Want to hack on KubeDB? Check our contribution guidelines.
NB: The images in this page are taken from MongoDB website.



































