You are looking at the documentation of a prior release. To read the documentation of the latest release, please
visit here.
New to KubeDB? Please start here.
KubeDB - SingleStore Cluster
This tutorial will show you how to use KubeDB to provision a singlestore cluster.
Before You Begin
Before proceeding:
Read singlestore cluster concept to learn about SingleStore cluster.
You need to have a Kubernetes cluster, and the kubectl command-line tool must be configured to communicate with your cluster. If you do not already have a cluster, you can create one by using kind.
Now, install KubeDB cli on your workstation and KubeDB operator in your cluster following the steps here.
To keep things isolated, this tutorial uses a separate namespace called
demothroughout this tutorial. Run the following command to prepare your cluster for this tutorial:$ kubectl create ns demo namespace/demo created
Note: The yaml files used in this tutorial are stored in docs/examples/singlestore folder in GitHub repository kubedb/docs.
Create SingleStore License Secret
We need SingleStore License to create SingleStore Database. So, Ensure that you have acquired a license and then simply pass the license by secret.
$ kubectl create secret generic -n demo license-secret \
--from-literal=username=license \
--from-literal=password='your-license-set-here'
secret/license-secret created
Create a SingleStore database
KubeDB implements a Singlestore CRD to define the specification of a SingleStore database. Below is the Singlestore object created in this tutorial.
apiVersion: kubedb.com/v1alpha2
kind: Singlestore
metadata:
name: sample-sdb
namespace: demo
spec:
version: "8.7.10"
topology:
aggregator:
replicas: 1
podTemplate:
spec:
containers:
- name: singlestore
resources:
limits:
memory: "2Gi"
cpu: "0.6"
requests:
memory: "2Gi"
cpu: "0.6"
storage:
storageClassName: "standard"
accessModes:
- ReadWriteOnce
resources:
requests:
storage: 1Gi
leaf:
replicas: 2
podTemplate:
spec:
containers:
- name: singlestore
resources:
limits:
memory: "2Gi"
cpu: "0.6"
requests:
memory: "2Gi"
cpu: "0.6"
storage:
storageClassName: "standard"
accessModes:
- ReadWriteOnce
resources:
requests:
storage: 10Gi
licenseSecret:
name: license-secret
storageType: Durable
deletionPolicy: WipeOut
$ kubectl create -f https://github.com/kubedb/docs/raw/v2024.11.18/docs/guides/singlestore/clustering/singlestore-clustering/examples/sample-sdb.yaml
singlestore.kubedb.com/sample-sdb created
Here,
spec.versionis the name of the SinglestoreVersion CRD where the docker images are specified. In this tutorial, a SingleStore8.7.10database is going to be created.spec.topologyspecifies that it will be used as cluster mode. If this field is nil it will be work as standalone mode.spec.topology.aggregator.replicasorspec.topology.leaf.replicasspecifies that the number replicas that will be used for aggregator or leaf.spec.storageTypespecifies the type of storage that will be used for SingleStore database. It can beDurableorEphemeral. Default value of this field isDurable. IfEphemeralis used then KubeDB will create SingleStore database usingEmptyDirvolume. In this case, you don’t have to specifyspec.storagefield. This is useful for testing purposes.spec.topology.aggregator.storageorspec.topology.leaf.storagespecifies the StorageClass of PVC dynamically allocated to store data for this database. This storage spec will be passed to the PetSet created by KubeDB operator to run database pods. You can specify any StorageClass available in your cluster with appropriate resource requests.spec.deletionPolicygives flexibility whether tonullify(reject) the delete operation ofSinglestorecrd or which resources KubeDB should keep or delete when you deleteSinglestorecrd. If admission webhook is enabled, It prevents users from deleting the database as long as thespec.deletionPolicyis set toDoNotTerminate. Learn details of allDeletionPolicyhere
Note:
spec.storagesection is used to create PVC for database pod. It will create PVC with storage size specified instorage.resources.requestsfield. Don’t specify limits here. PVC does not get resized automatically.
KubeDB operator watches for Singlestore objects using Kubernetes api. When a Singlestore object is created, KubeDB operator will create new PetSet and Service with the matching SingleStore object name. KubeDB operator will also create a governing service for PetSets, if one is not already present.
$ kubectl get petset,pvc,pv,svc -n demo
NAME AGE
petset.apps.k8s.appscode.com/sample-sdb-aggregator 16m
petset.apps.k8s.appscode.com/sample-sdb-leaf 16m
NAME STATUS VOLUME CAPACITY ACCESS MODES STORAGECLASS VOLUMEATTRIBUTESCLASS AGE
persistentvolumeclaim/data-sample-sdb-aggregator-0 Bound pvc-a6c9041cba69454a 10Gi RWO linode-block-storage-retain <unset> 16m
persistentvolumeclaim/data-sample-sdb-leaf-0 Bound pvc-674ba189a2f24383 10Gi RWO linode-block-storage-retain <unset> 16m
persistentvolumeclaim/data-sample-sdb-leaf-1 Bound pvc-16e4224adec54d96 10Gi RWO linode-block-storage-retain <unset> 16m
NAME CAPACITY ACCESS MODES RECLAIM POLICY STATUS CLAIM STORAGECLASS VOLUMEATTRIBUTESCLASS REASON AGE
persistentvolume/pvc-16e4224adec54d96 10Gi RWO Retain Bound demo/data-sample-sdb-leaf-1 linode-block-storage-retain <unset> 16m
persistentvolume/pvc-674ba189a2f24383 10Gi RWO Retain Bound demo/data-sample-sdb-leaf-0 linode-block-storage-retain <unset> 16m
persistentvolume/pvc-a6c9041cba69454a 10Gi RWO Retain Bound demo/data-sample-sdb-aggregator-0 linode-block-storage-retain <unset> 16m
NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE
service/sample-sdb ClusterIP 10.128.15.230 <none> 3306/TCP,8081/TCP 16m
service/sample-sdb-pods ClusterIP None <none> 3306/TCP 16m
KubeDB operator sets the status.phase to Running once the database is successfully created. Run the following command to see the modified Singlestore object:
$ kubectl get sdb -n demo sample-sdb -oyaml
kind: Singlestore
metadata:
annotations:
kubectl.kubernetes.io/last-applied-configuration: |
{"apiVersion":"kubedb.com/v1alpha2","kind":"Singlestore","metadata":{"annotations":{},"name":"sample-sdb","namespace":"demo"},"spec":{"deletionPolicy":"WipeOut","licenseSecret":{"name":"license-secret"},"storageType":"Durable","topology":{"aggregator":{"podTemplate":{"spec":{"containers":[{"name":"singlestore","resources":{"limits":{"cpu":"0.6","memory":"2Gi"},"requests":{"cpu":"0.6","memory":"2Gi"}}}]}},"replicas":1,"storage":{"accessModes":["ReadWriteOnce"],"resources":{"requests":{"storage":"1Gi"}}}},"leaf":{"podTemplate":{"spec":{"containers":[{"name":"singlestore","resources":{"limits":{"cpu":"0.6","memory":"2Gi"},"requests":{"cpu":"0.6","memory":"2Gi"}}}]}},"replicas":2,"storage":{"accessModes":["ReadWriteOnce"],"resources":{"requests":{"storage":"10Gi"}}}}},"version":"8.7.10"}}
creationTimestamp: "2024-10-01T09:39:36Z"
finalizers:
- kubedb.com
generation: 2
name: sample-sdb
namespace: demo
resourceVersion: "117016"
uid: 22b254e0-d185-413c-888f-ca4c2524e909
spec:
authSecret:
name: sample-sdb-root-cred
deletionPolicy: WipeOut
healthChecker:
failureThreshold: 1
periodSeconds: 10
timeoutSeconds: 10
licenseSecret:
name: license-secret
storageType: Durable
topology:
aggregator:
podTemplate:
controller: {}
metadata: {}
spec:
containers:
- name: singlestore
resources:
limits:
cpu: 600m
memory: 2Gi
requests:
cpu: 600m
memory: 2Gi
securityContext:
allowPrivilegeEscalation: false
capabilities:
drop:
- ALL
runAsGroup: 998
runAsNonRoot: true
runAsUser: 999
seccompProfile:
type: RuntimeDefault
- name: singlestore-coordinator
resources:
limits:
memory: 256Mi
requests:
cpu: 200m
memory: 256Mi
securityContext:
allowPrivilegeEscalation: false
capabilities:
drop:
- ALL
runAsGroup: 998
runAsNonRoot: true
runAsUser: 999
seccompProfile:
type: RuntimeDefault
initContainers:
- name: singlestore-init
resources:
limits:
memory: 512Mi
requests:
cpu: 200m
memory: 512Mi
securityContext:
allowPrivilegeEscalation: false
capabilities:
drop:
- ALL
runAsGroup: 998
runAsNonRoot: true
runAsUser: 999
seccompProfile:
type: RuntimeDefault
podPlacementPolicy:
name: default
securityContext:
fsGroup: 999
replicas: 1
storage:
accessModes:
- ReadWriteOnce
resources:
requests:
storage: 1Gi
leaf:
podTemplate:
controller: {}
metadata: {}
spec:
containers:
- name: singlestore
resources:
limits:
cpu: 600m
memory: 2Gi
requests:
cpu: 600m
memory: 2Gi
securityContext:
allowPrivilegeEscalation: false
capabilities:
drop:
- ALL
runAsGroup: 998
runAsNonRoot: true
runAsUser: 999
seccompProfile:
type: RuntimeDefault
- name: singlestore-coordinator
resources:
limits:
memory: 256Mi
requests:
cpu: 200m
memory: 256Mi
securityContext:
allowPrivilegeEscalation: false
capabilities:
drop:
- ALL
runAsGroup: 998
runAsNonRoot: true
runAsUser: 999
seccompProfile:
type: RuntimeDefault
initContainers:
- name: singlestore-init
resources:
limits:
memory: 512Mi
requests:
cpu: 200m
memory: 512Mi
securityContext:
allowPrivilegeEscalation: false
capabilities:
drop:
- ALL
runAsGroup: 998
runAsNonRoot: true
runAsUser: 999
seccompProfile:
type: RuntimeDefault
podPlacementPolicy:
name: default
securityContext:
fsGroup: 999
replicas: 2
storage:
accessModes:
- ReadWriteOnce
resources:
requests:
storage: 10Gi
version: 8.7.10
status:
conditions:
- lastTransitionTime: "2024-10-01T09:39:36Z"
message: 'The KubeDB operator has started the provisioning of Singlestore: demo/sample-sdb'
observedGeneration: 1
reason: DatabaseProvisioningStartedSuccessfully
status: "True"
type: ProvisioningStarted
- lastTransitionTime: "2024-10-01T09:57:51Z"
message: All leaf replicas are ready for Singlestore demo/sample-sdb
observedGeneration: 2
reason: AllReplicasReady
status: "True"
type: ReplicaReady
- lastTransitionTime: "2024-10-01T09:41:04Z"
message: database demo/sample-sdb is accepting connection
observedGeneration: 2
reason: AcceptingConnection
status: "True"
type: AcceptingConnection
- lastTransitionTime: "2024-10-01T09:41:04Z"
message: database demo/sample-sdb is ready
observedGeneration: 2
reason: AllReplicasReady
status: "True"
type: Ready
- lastTransitionTime: "2024-10-01T09:41:05Z"
message: 'The Singlestore: demo/sample-sdb is successfully provisioned.'
observedGeneration: 2
reason: DatabaseSuccessfullyProvisioned
status: "True"
type: Provisioned
phase: Ready
Connect with SingleStore database
KubeDB operator has created a new Secret called sample-sdb-root-cred (format: {singlestore-object-name}-root-cred) for storing the password for singlestore superuser. This secret contains a username key which contains the username for SingleStore superuser and a password key which contains the password for SingleStore superuser.
If you want to use an existing secret please specify that when creating the SingleStore object using spec.authSecret.name. While creating this secret manually, make sure the secret contains these two keys containing data username and password and also make sure of using root as value of username. For more details see here.
Now, we need username and password to connect to this database from kubectl exec command. In this example sample-sdb-root-cred secret holds username and password
$ kubectl get pod -n demo sample-sdb-master-aggregator-0 -oyaml | grep podIP
podIP: 10.244.0.14
$ kubectl get secrets -n demo sample-sdb-root-cred -o jsonpath='{.data.\username}' | base64 -d
root
$ kubectl get secrets -n demo sample-sdb-root-cred -o jsonpath='{.data.\password}' | base64 -d
J0h_BUdJB8mDO31u
we will exec into the pod sample-sdb-master-aggregator-0 and connect to the database using username and password
$ kubectl exec -it -n demo sample-sdb-aggregator-0 -- bash
Defaulting container name to singlestore.
Use 'kubectl describe pod/sample-sdb-aggregator-0 -n demo' to see all of the containers in this pod.
[memsql@sample-sdb-master-aggregator-0 /]$ memsql -uroot -p"J0h_BUdJB8mDO31u"
singlestore-client: [Warning] Using a password on the command line interface can be insecure.
Welcome to the MySQL monitor. Commands end with ; or \g.
Your MySQL connection id is 1114
Server version: 5.7.32 SingleStoreDB source distribution (compatible; MySQL Enterprise & MySQL Commercial)
Copyright (c) 2000, 2016, Oracle and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved.
Oracle is a registered trademark of Oracle Corporation and/or its
affiliates. Other names may be trademarks of their respective
owners.
Type 'help;' or '\h' for help. Type '\c' to clear the current input statement.
singlestore> show databases;
+--------------------+
| Database |
+--------------------+
| cluster |
| information_schema |
| memsql |
| singlestore_health |
+--------------------+
4 rows in set (0.00 sec)
singlestore> CREATE TABLE playground.equipment ( id INT NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT, type VARCHAR(50), quant INT, color VARCHAR(25), PRIMARY KEY(id));
Query OK, 0 rows affected, 1 warning (0.27 sec)
singlestore> SHOW TABLES IN playground;
+----------------------+
| Tables_in_playground |
+----------------------+
| equipment |
+----------------------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
singlestore> INSERT INTO playground.equipment (type, quant, color) VALUES ("slide", 2, "blue");
Query OK, 1 row affected (1.15 sec)
singlestore> SELECT * FROM playground.equipment;
+----+-------+-------+-------+
| id | type | quant | color |
+----+-------+-------+-------+
| 1 | slide | 2 | blue |
+----+-------+-------+-------+
1 row in set (0.14 sec)
singlestore> exit
Bye
You can also connect with database management tools like singlestore-studio
You can simply access to SingleStore studio by forwarding the Primary service port to any of your localhost port. Or, Accessing through ExternalP’s 8081 port is also an option.
$ kubectl port-forward -n demo service/sample-sdb 8081
Forwarding from 127.0.0.1:8081 -> 8081
Forwarding from [::1]:8081 -> 8081
Lets, open your browser and go to the http://localhost:8081 or with TLS https://localhost:8081 then click on Add or Create Cluster option.
Then choose Add Existing Cluster and click on next and you will get an interface like that below:
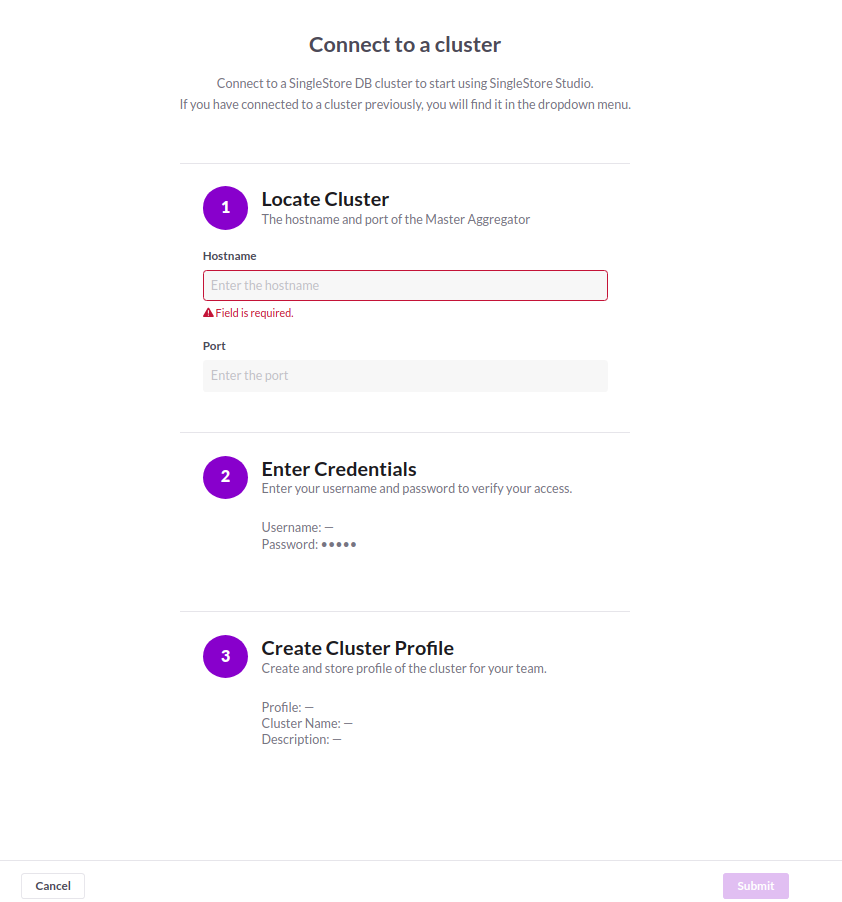
After giving the all information you can see like this below UI image.
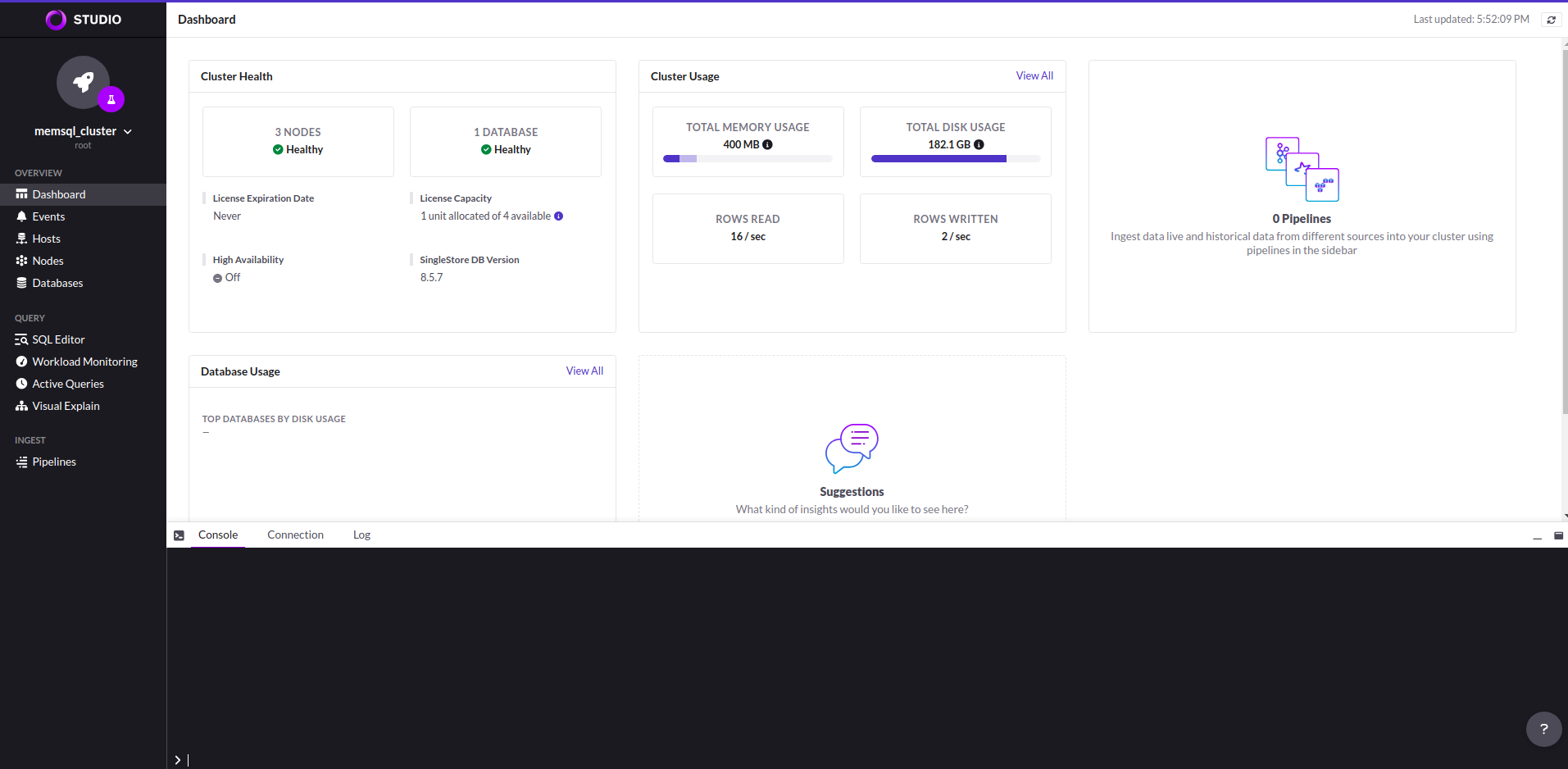
Cleaning up
To cleanup the Kubernetes resources created by this tutorial, run:
kubectl patch -n demo singlestore/sample-sdb -p '{"spec":{"deletionPolicy":"WipeOut"}}' --type="merge"
kubectl delete -n demo singlestore/sample-sdb
kubectl delete ns demo



































