You are looking at the documentation of a prior release. To read the documentation of the latest release, please
visit here.
New to KubeDB? Please start here.
Horizontal Scaling Overview
This guide will give you an overview of how KubeDB Ops Manager scales up/down the number of members of a MSSQLServer.
Before You Begin
- You should be familiar with the following
KubeDBconcepts:
How Horizontal Scaling Process Works
The following diagram shows how KubeDB Ops Manager used to scale up the number of members of a MSSQLServer cluster. Open the image in a new tab to see the enlarged version.
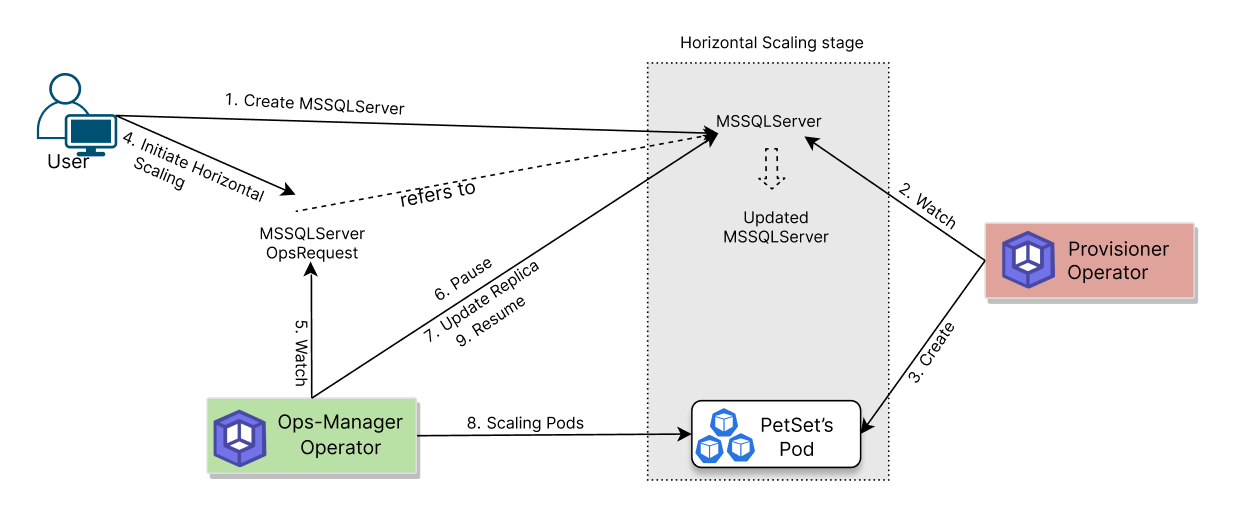
The horizontal scaling process consists of the following steps:
At first, a user creates a
MSSQLServerCR.KubeDBprovisioner operator watches for theMSSQLServerCR.When it finds one, it creates a
PetSetand related necessary stuff like secret, service, etc.Then, in order to scale the cluster up or down, the user creates a
MSSQLServerOpsRequestCR with the desired number of replicas after scaling.KubeDBOps Manager watches forMSSQLServerOpsRequest.When it finds one, it halts the
MSSQLServerobject so that theKubeDBprovisioner operator doesn’t perform any operation on theMSSQLServerduring the scaling process.Then
KubeDBOps Manager will add nodes in case of scale up or remove nodes in case of scale down.Then the
KubeDBOps Manager will scale the PetSet replicas to reach the expected number of replicas for the cluster.After successful scaling of the PetSet’s replica, the
KubeDBOps Manager updates thespec.replicasfield ofMSSQLServerobject to reflect the updated cluster state.After successful scaling of the
MSSQLServerreplicas, theKubeDBOps Manager resumes theMSSQLServerobject so that theKubeDBprovisioner operator can resume its usual operations.
In the next doc, we are going to show a step-by-step guide on scaling of a MSSQLServer cluster using Horizontal Scaling.



































