You are looking at the documentation of a prior release. To read the documentation of the latest release, please
visit here.
New to KubeDB? Please start here.
FerretDB QuickStart
This tutorial will show you how to use KubeDB to run a FerretDB database.
Before You Begin
At first, you need to have a Kubernetes cluster, and the kubectl command-line tool must be configured to communicate with your cluster. If you do not already have a cluster, you can create one by using kind.
StorageClass is required to run KubeDB. Check the available StorageClass in cluster.
$ kubectl get storageclasses NAME PROVISIONER RECLAIMPOLICY VOLUMEBINDINGMODE ALLOWVOLUMEEXPANSION AGE standard (default) rancher.io/local-path Delete WaitForFirstConsumer false 2m5sTo keep things isolated, this tutorial uses a separate namespace called
demothroughout this tutorial. Run the following command to prepare your cluster for this tutorial:$ kubectl create ns demo namespace/demo created
Note: The yaml files used in this tutorial are stored in docs/examples/mongodb folder in GitHub repository kubedb/docs.
Find Available FerretDBVersion
When you have installed KubeDB, it has created FerretDBVersion CR for all supported FerretDB versions.
$ kubectl get ferretdbversions
NAME VERSION DB_IMAGE DEPRECATED AGE
1.18.0 1.18.0 ghcr.io/appscode-images/ferretdb:1.18.0 false 7m10s
Create a FerretDB database
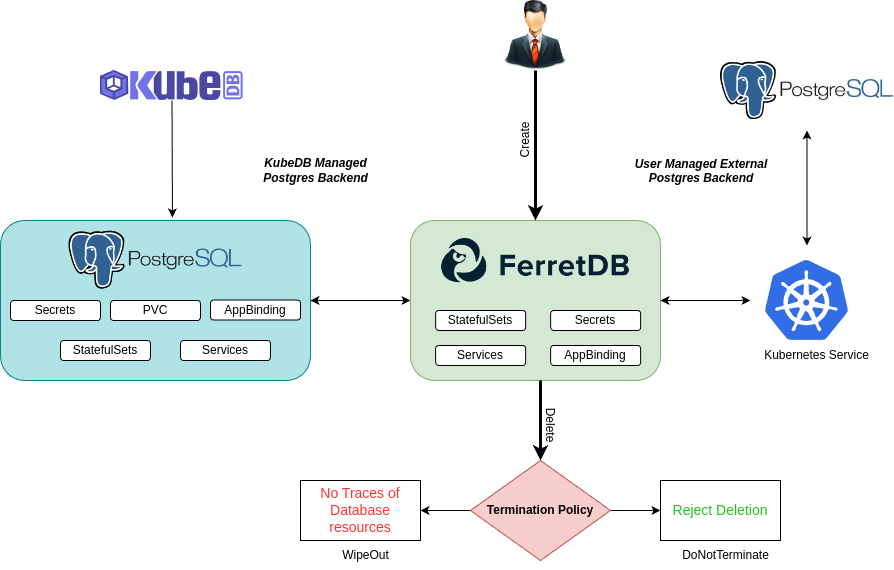
FerretDB use Postgres as it’s main backend. Currently, KubeDB supports Postgres backend as database engine for FerretDB. Users can use its own Postgres or let KubeDB create and manage backend engine with KubeDB native Postgres.
KubeDB implements a FerretDB CR to define the specification of a FerretDB database.
Create a FerretDB database with KubeDB managed Postgres
To use KubeDB managed Postgres as backend engine, user need to specify that in spec.backend.externallyManaged section of FerretDB CRO yaml. Below is the FerretDB object created in this tutorial.
apiVersion: kubedb.com/v1alpha2
kind: FerretDB
metadata:
name: ferret
namespace: demo
spec:
version: "1.18.0"
authSecret:
externallyManaged: false
sslMode: disabled
storageType: Durable
storage:
accessModes:
- ReadWriteOnce
resources:
requests:
storage: 500Mi
backend:
externallyManaged: false
deletionPolicy: WipeOut
$ kubectl create -f https://github.com/kubedb/docs/raw/v2024.7.3-rc.0/docs/examples/ferredb/quickstart/ferretdb-internal.yaml
ferretdb.kubedb.com/ferret created
Here,
spec.versionis name of the FerretDBVersion CR where the docker images are specified. In this tutorial, a FerretDB 1.18.0 database is created.spec.storageTypespecifies the type of storage that will be used for FerretDB database. It can beDurableorEphemeral. Default value of this field isDurable. IfEphemeralis used then KubeDB will create FerretDB database usingEmptyDirvolume. In this case, you don’t have to specifyspec.storagefield. This is useful for testing purposes.spec.storagespecifies PVC spec that will be dynamically allocated to store data for this database. This storage spec will be passed to the StatefulSet created by KubeDB operator to run database pods. You can specify any StorageClass available in your cluster with appropriate resource requests.spec.deletionPolicygives flexibility whether tonullify(reject) the delete operation ofFerretDBCR or which resources KubeDB should keep or delete when you deleteFerretDBCR. If admission webhook is enabled, It prevents users from deleting the database as long as thespec.deletionPolicyis set toDoNotTerminate. Learn details of allDeletionPolicyherespec.backenddenotes the backend database information for FerretDB instance.spec.replicasdenotes the number of replicas in the replica-set.
Note:
spec.storagesection is used to create PVC for database pod. It will create PVC with storage size specified instorage.resources.requests field. Don’t specify limits here. PVC does not get resized automatically.
KubeDB operator watches for FerretDB objects using Kubernetes api. When a FerretDB object is created, KubeDB operator will create a new StatefulSet and a Service with the matching FerretDB object name. KubeDB operator will also create a governing service for StatefulSets with the name <ferretdb-name>-pods.
Here spec.backend.externallyManaged section is false. So backend Postgres database will be managed by internally through KubeDB.
KubeDB will create a Postgres database alongside with FerretDB for FerretDB’s backend engine.
KubeDB operator sets the status.phase to Ready once the database is successfully provisioned and ready to use.
$ kubectl get ferretdb -n demo
NAME NAMESPACE VERSION STATUS AGE
ferret demo 1.18.0 Ready 25m
$ kubectl get postgres -n demo
NAME VERSION STATUS AGE
ferret-pg-backend 13.13 Ready 25m
Let’s describe FerretDB object ferret
$ kubectl describe ferretdb ferret -n demo
Name: ferret
Namespace: demo
Labels: <none>
Annotations: <none>
API Version: kubedb.com/v1alpha2
Kind: FerretDB
Metadata:
Creation Timestamp: 2024-03-12T05:04:34Z
Finalizers:
kubedb.com
Generation: 4
Resource Version: 4127
UID: 73247297-139b-4dfe-8f9d-9baf2b092364
Spec:
Auth Secret:
Name: ferret-pg-backend-auth
Backend:
Externally Managed: false
Linked DB: ferretdb
Postgres:
Service:
Name: ferret-pg-backend
Namespace: demo
Pg Port: 5432
URL: postgres://ferret-pg-backend.demo.svc.cluster.local:5432/ferretdb
Version: 13.13
Health Checker:
Failure Threshold: 1
Period Seconds: 10
Timeout Seconds: 10
Pod Template:
Controller:
Metadata:
Spec:
Containers:
Name: ferretdb
Resources:
Limits:
Memory: 1Gi
Requests:
Cpu: 500m
Memory: 1Gi
Security Context:
Allow Privilege Escalation: false
Capabilities:
Drop:
ALL
Run As Group: 1000
Run As Non Root: true
Run As User: 1000
Seccomp Profile:
Type: RuntimeDefault
Security Context:
Fs Group: 1000
Replicas: 1
Ssl Mode: disabled
Storage:
Access Modes:
ReadWriteOnce
Resources:
Requests:
Storage: 500Mi
Storage Type: Durable
Deletion Policy: WipeOut
Version: 1.18.0
Status:
Conditions:
Last Transition Time: 2024-03-12T05:04:34Z
Message: The KubeDB operator has started the provisioning of FerretDB: demo/ferret
Observed Generation: 3
Reason: DatabaseProvisioningStartedSuccessfully
Status: True
Type: ProvisioningStarted
Last Transition Time: 2024-03-12T05:23:58Z
Message: All replicas are ready for FerretDB demo/ferret
Observed Generation: 4
Reason: AllReplicasReady
Status: True
Type: ReplicaReady
Last Transition Time: 2024-03-12T05:06:20Z
Message: The FerretDB: demo/ferret is accepting client requests.
Observed Generation: 4
Reason: DatabaseAcceptingConnectionRequest
Status: True
Type: AcceptingConnection
Last Transition Time: 2024-03-12T05:06:20Z
Message: The FerretDB: demo/ferret is ready.
Observed Generation: 4
Reason: ReadinessCheckSucceeded
Status: True
Type: Ready
Last Transition Time: 2024-03-12T05:06:20Z
Message: The FerretDB: demo/ferret is successfully provisioned.
Observed Generation: 4
Reason: DatabaseSuccessfullyProvisioned
Status: True
Type: Provisioned
Phase: Ready
$ kubectl get petset -n demo
NAME READY AGE
ferret 1/1 29m
$ kubectl get statefulset -n demo
NAME READY AGE
ferret-pg-backend 2/2 30m
ferret-pg-backend-arbiter 1/1 29m
$ kubectl get appbindings -n demo
NAME TYPE VERSION AGE
ferret kubedb.com/ferret 1.18.0 29m
ferret-pg-backend kubedb.com/postgres 13.13 30m
$ kubectl get pvc -n demo
NAME STATUS VOLUME CAPACITY ACCESS MODES STORAGECLASS VOLUMEATTRIBUTESCLASS AGE
data-ferret-pg-backend-0 Bound pvc-b887a566-2dbd-4377-8752-f31622efbb34 500Mi RWO standard <unset> 30m
data-ferret-pg-backend-1 Bound pvc-43de8679-7004-469d-a8a5-37363f81d839 500Mi RWO standard <unset> 29m
data-ferret-pg-backend-arbiter-0 Bound pvc-8ab3e7b5-4ecc-4ddd-9a9a-16b4f59f6538 2Gi RWO standard <unset> 29m
$ kubectl get pv -n demo
NAME CAPACITY ACCESS MODES RECLAIM POLICY STATUS CLAIM STORAGECLASS VOLUMEATTRIBUTESCLASS REASON AGE
pvc-43de8679-7004-469d-a8a5-37363f81d839 500Mi RWO Delete Bound demo/data-ferret-pg-backend-1 standard <unset> 30m
pvc-8ab3e7b5-4ecc-4ddd-9a9a-16b4f59f6538 2Gi RWO Delete Bound demo/data-ferret-pg-backend-arbiter-0 standard <unset> 29m
pvc-b887a566-2dbd-4377-8752-f31622efbb34 500Mi RWO Delete Bound demo/data-ferret-pg-backend-0 standard <unset> 30m
$ kubectl get service -n demo
NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE
ferret ClusterIP 10.96.234.250 <none> 27017/TCP 30m
ferret-pg-backend ClusterIP 10.96.130.0 <none> 5432/TCP,2379/TCP 30m
ferret-pg-backend-pods ClusterIP None <none> 5432/TCP,2380/TCP,2379/TCP 30m
ferret-pg-backend-standby ClusterIP 10.96.250.98 <none> 5432/TCP 30m
Run the following command to see the modified FerretDB object:
$ kubectl get ferretdb ferret -n demo -oyaml
apiVersion: kubedb.com/v1alpha2
kind: FerretDB
metadata:
annotations:
kubectl.kubernetes.io/last-applied-configuration: |
{"apiVersion":"kubedb.com/v1alpha2","kind":"FerretDB","metadata":{"annotations":{},"name":"ferret","namespace":"demo"},"spec":{"authSecret":{"externallyManaged":false},"backend":{"externallyManaged":false},"sslMode":"disabled","storage":{"accessModes":["ReadWriteOnce"],"resources":{"requests":{"storage":"500Mi"}}},"deletionPolicy":"WipeOut","version":"1.18.0"}}
creationTimestamp: "2024-03-12T05:04:34Z"
finalizers:
- kubedb.com
generation: 4
name: ferret
namespace: demo
resourceVersion: "5030"
uid: 73247297-139b-4dfe-8f9d-9baf2b092364
spec:
authSecret:
name: ferret-pg-backend-auth
backend:
externallyManaged: false
linkedDB: ferretdb
postgres:
service:
name: ferret-pg-backend
namespace: demo
pgPort: 5432
url: postgres://ferret-pg-backend.demo.svc.cluster.local:5432/ferretdb
version: "13.13"
healthChecker:
failureThreshold: 1
periodSeconds: 10
timeoutSeconds: 10
podTemplate:
controller: {}
metadata: {}
spec:
containers:
- name: ferretdb
resources:
limits:
memory: 1Gi
requests:
cpu: 500m
memory: 1Gi
securityContext:
allowPrivilegeEscalation: false
capabilities:
drop:
- ALL
runAsGroup: 1000
runAsNonRoot: true
runAsUser: 1000
seccompProfile:
type: RuntimeDefault
securityContext:
fsGroup: 1000
replicas: 1
sslMode: disabled
storage:
accessModes:
- ReadWriteOnce
resources:
requests:
storage: 500Mi
storageType: Durable
deletionPolicy: WipeOut
version: 1.18.0
status:
conditions:
- lastTransitionTime: "2024-03-12T05:04:34Z"
message: 'The KubeDB operator has started the provisioning of FerretDB: demo/ferret'
observedGeneration: 3
reason: DatabaseProvisioningStartedSuccessfully
status: "True"
type: ProvisioningStarted
- lastTransitionTime: "2024-03-12T05:33:58Z"
message: All replicas are ready for FerretDB demo/ferret
observedGeneration: 4
reason: AllReplicasReady
status: "True"
type: ReplicaReady
- lastTransitionTime: "2024-03-12T05:06:20Z"
message: 'The FerretDB: demo/ferret is accepting client requests.'
observedGeneration: 4
reason: DatabaseAcceptingConnectionRequest
status: "True"
type: AcceptingConnection
- lastTransitionTime: "2024-03-12T05:06:20Z"
message: 'The FerretDB: demo/ferret is ready.'
observedGeneration: 4
reason: ReadinessCheckSucceeded
status: "True"
type: Ready
- lastTransitionTime: "2024-03-12T05:06:20Z"
message: 'The FerretDB: demo/ferret is successfully provisioned.'
observedGeneration: 4
reason: DatabaseSuccessfullyProvisioned
status: "True"
type: Provisioned
phase: Ready
Please note that KubeDB operator has created a new Secret called ferret-pg-backend-auth (format: {ferretdb-object-name}-backend-auth) for storing the password for postgres superuser. This secret contains a username key which contains the username for FerretDB superuser and a password key which contains the password for FerretDB superuser.
If you want to use custom or existing secret please specify that when creating the FerretDB object using spec.authSecret.name. While creating this secret manually, make sure the secret contains these two keys containing data username and password. For more details, please see here.
Now, you can connect to this database by port-forwarding primary service ferret and connecting with mongo-shell locally
$ kubectl get secrets -n demo ferret-pg-backend-auth -o jsonpath='{.data.\username}' | base64 -d
postgres
$ kubectl get secrets -n demo ferret-pg-backend-auth -o jsonpath='{.data.\\password}' | base64 -d
UxV5a35kURSFE(;5
$ kubectl port-forward svc/ferret -n demo 27017
Forwarding from 127.0.0.1:27017 -> 27017
Forwarding from [::1]:27017 -> 27017
Handling connection for 27017
Handling connection for 27017
Now in another terminal
$ mongosh 'mongodb://postgres:UxV5a35kURSFE(;5@localhost:27017/ferretdb?authMechanism=PLAIN'
Current Mongosh Log ID: 65efeea2a3347fff66d04c70
Connecting to: mongodb://<credentials>@localhost:27017/ferretdb?authMechanism=PLAIN&directConnection=true&serverSelectionTimeoutMS=2000&appName=mongosh+2.1.5
Using MongoDB: 7.0.42
Using Mongosh: 2.1.5
For mongosh info see: https://docs.mongodb.com/mongodb-shell/
------
The server generated these startup warnings when booting
2024-03-12T05:56:50.979Z: Powered by FerretDB v1.18.0 and PostgreSQL 13.13 on x86_64-pc-linux-musl, compiled by gcc.
2024-03-12T05:56:50.979Z: Please star us on GitHub: https://github.com/FerretDB/FerretDB.
2024-03-12T05:56:50.979Z: The telemetry state is undecided.
2024-03-12T05:56:50.979Z: Read more about FerretDB telemetry and how to opt out at https://beacon.ferretdb.io.
------
ferretdb>
ferretdb> show dbs
kubedb_system 80.00 KiB
ferretdb> use mydb
switched to db mydb
mydb> db.movies.insertOne({"top gun": "maverick"})
{
acknowledged: true,
insertedId: ObjectId('65efeee6a3347fff66d04c71')
}
mydb> db.movies.find()
[
{ _id: ObjectId('65efeee6a3347fff66d04c71'), 'top gun': 'maverick' }
]
mydb> show dbs
kubedb_system 80.00 KiB
mydb 80.00 KiB
mydb> exit
All these data inside FerretDB is also storing inside ferret-pg-backend Postgres.
Create a FerretDB database with externally managed Postgres
If user wants to use its own Postgres database as backend engine, he can specify it in spec.backend.postgres section. Below is the FerretDB object created in this tutorial.
apiVersion: kubedb.com/v1alpha2
kind: FerretDB
metadata:
name: ferretdb-external
namespace: demo
spec:
version: "1.18.0"
authSecret:
externallyManaged: true
name: ha-postgres-auth
sslMode: disabled
storageType: Durable
storage:
storageClassName: "standard"
accessModes:
- ReadWriteOnce
resources:
requests:
storage: 500Mi
backend:
externallyManaged: true
postgres:
service:
name: ha-postgres
namespace: demo
pgPort: 5432
deletionPolicy: WipeOut
$ kubectl create -f https://github.com/kubedb/docs/raw/v2024.7.3-rc.0/docs/examples/ferredb/quickstart/ferretdb-external.yaml
ferretdb.kubedb.com/ferretdb-external created
Here,
spec.postgres.serivceis service information of users external postgres exist in the cluster.spec.authSecret.nameis the name of the authentication secret of users external postgres database.
KubeDB will deploy a FerretDB database and connect with the users given external postgres through service.
Run the following command to see the modified FerretDB object:
$ kubectl get ferretdb ferretdb-external -n demo -oyaml
apiVersion: kubedb.com/v1alpha2
kind: FerretDB
metadata:
annotations:
kubectl.kubernetes.io/last-applied-configuration: |
{"apiVersion":"kubedb.com/v1alpha2","kind":"FerretDB","metadata":{"annotations":{},"name":"ferretdb-external","namespace":"demo"},"spec":{"authSecret":{"externallyManaged":true,"name":"ha-postgres-auth"},"backend":{"externallyManaged":true,"postgres":{"service":{"name":"ha-postgres","namespace":"demo","pgPort":5432}}},"sslMode":"disabled","storage":{"accessModes":["ReadWriteOnce"],"resources":{"requests":{"storage":"100Mi"}},"storageClassName":"standard"},"storageType":"Durable","deletionPolicy":"WipeOut","version":"1.18.0"}}
creationTimestamp: "2024-03-12T06:30:22Z"
finalizers:
- kubedb.com
generation: 3
name: ferretdb-external
namespace: demo
resourceVersion: "10959"
uid: 8380f0a1-c8e9-42e2-8fa9-6ce5870d02f4
spec:
authSecret:
externallyManaged: true
name: ha-postgres-auth
backend:
externallyManaged: true
linkedDB: postgres
postgres:
service:
name: ha-postgres
namespace: demo
pgPort: 5432
url: postgres://ha-postgres.demo.svc.cluster.local:5432/postgres
healthChecker:
failureThreshold: 1
periodSeconds: 10
timeoutSeconds: 10
podTemplate:
controller: {}
metadata: {}
spec:
containers:
- name: ferretdb
resources:
limits:
memory: 1Gi
requests:
cpu: 500m
memory: 1Gi
securityContext:
allowPrivilegeEscalation: false
capabilities:
drop:
- ALL
runAsGroup: 1000
runAsNonRoot: true
runAsUser: 1000
seccompProfile:
type: RuntimeDefault
securityContext:
fsGroup: 1000
replicas: 1
sslMode: disabled
storage:
accessModes:
- ReadWriteOnce
resources:
requests:
storage: 500Mi
storageClassName: standard
storageType: Durable
deletionPolicy: WipeOut
version: 1.18.0
status:
conditions:
- lastTransitionTime: "2024-03-12T06:30:22Z"
message: 'The KubeDB operator has started the provisioning of FerretDB: demo/ferretdb-external'
observedGeneration: 2
reason: DatabaseProvisioningStartedSuccessfully
status: "True"
type: ProvisioningStarted
- lastTransitionTime: "2024-03-12T06:33:58Z"
message: All replicas are ready for FerretDB demo/ferretdb-external
observedGeneration: 3
reason: AllReplicasReady
status: "True"
type: ReplicaReady
- lastTransitionTime: "2024-03-12T06:30:34Z"
message: 'The FerretDB: demo/ferretdb-external is accepting client requests.'
observedGeneration: 3
reason: DatabaseAcceptingConnectionRequest
status: "True"
type: AcceptingConnection
- lastTransitionTime: "2024-03-12T06:30:34Z"
message: 'The FerretDB: demo/ferretdb-external is ready.'
observedGeneration: 3
reason: ReadinessCheckSucceeded
status: "True"
type: Ready
- lastTransitionTime: "2024-03-12T06:30:34Z"
message: 'The FerretDB: demo/ferretdb-external is successfully provisioned.'
observedGeneration: 3
reason: DatabaseSuccessfullyProvisioned
status: "True"
type: Provisioned
phase: Ready
Cleaning up
If you don’t set the deletionPolicy, then the kubeDB set the DeletionPolicy to WipeOut by-default for FerretDB.
WipeOut
If you want to cleanup each of the Kubernetes resources created by this tutorial, run:
$ kubectl delete -n demo fr/ferret
$ kubectl get fr,sts,svc,secret,pvc,petset -n demo
NAME TYPE DATA AGE
$ kubectl delete ns demo
Tips for Testing
If you are just testing some basic functionalities, you might want to avoid additional hassles due to some safety features that are great for production environment. You can follow these tips to avoid them.
- Use
storageType: Ephemeral. Databases are precious. You might not want to lose your data in your production environment if database pod fail. So, we recommend usingspec.storageType: Durableand provide storage spec inspec.storagesection. For testing purpose, you can just usespec.storageType: Ephemeral. KubeDB will use emptyDir for storage. You will not require to providespec.storagesection.



































