You are looking at the documentation of a prior release. To read the documentation of the latest release, please
visit here.
Backup and Restore Redis database using Stash
Stash 0.9.0+ supports backup and restoration of Redis databases. This guide will show you how you can backup and restore your Redis database with Stash.
Before You Begin
- At first, you need to have a Kubernetes cluster, and the
kubectlcommand-line tool must be configured to communicate with your cluster. If you do not already have a cluster, you can create one by using Minikube. - Install KubeDB in your cluster following the steps here.
- Install Stash in your cluster following the steps here.
- Install Stash
kubectlplugin following the steps here. - If you are not familiar with how Stash backup and restore Redis databases, please check the following guide here:
You have to be familiar with following custom resources:
To keep things isolated, we are going to use a separate namespace called demo throughout this tutorial. Create the demo namespace if you haven’t created it already.
$ kubectl create ns demo
namespace/demo created
Backup Redis
This section will demonstrate how to backup a Redis database. Here, we are going to deploy a Resis database using KubeDB. Then, we are going to backup this database into a GCS bucket. Finally, we are going to restore the backed-up data into another Redis database.
Deploy Sample Redis Database
Let’s deploy a sample Redis database and insert some data into it.
Create Redis CRD:
Below is the YAML of a sample Redis crd that we are going to create for this tutorial:
apiVersion: kubedb.com/v1
kind: Redis
metadata:
name: sample-redis
namespace: demo
spec:
version: 6.0.20
storageType: Durable
storage:
storageClassName: "standard"
accessModes:
- ReadWriteOnce
resources:
requests:
storage: 1Gi
Create the above Redis crd,
$ kubectl apply -f https://github.com/kubedb/docs/raw/v2024.8.21/docs/guides/redis/backup/standalone/examples/redis.yaml
redis.kubedb.com/sample-redis created
KubeDB will deploy a Redis database according to the above specification. It will also create the necessary secrets and services to access the database.
Let’s check if the database is ready to use,
❯ kubectl get rd -n demo
NAME VERSION STATUS AGE
sample-redis 6.0.20 Ready 58s
The database is Ready. Verify that KubeDB has created a Secret and a Service for this database using the following commands,
❯ kubectl get secret -n demo -l=app.kubernetes.io/instance=sample-redis
NAME TYPE DATA AGE
sample-redis-auth kubernetes.io/basic-auth 2 90s
sample-redis-config Opaque 1 90s
❯ kubectl get service -n demo -l=app.kubernetes.io/instance=sample-redis
NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE
sample-redis ClusterIP 10.96.179.49 <none> 6379/TCP 116s
sample-redis-pods ClusterIP None <none> 6379/TCP 116s
Here, we have to use the service sample-redis and secret sample-redis-auth to connect with the database.
Insert Sample Data
Now, we are going to exec into the database pod and create some sample data. Kubedb has created a secret with access credentials. Let’s find out the credentials from the Secret,
❯ kubectl get secret -n demo sample-redis-auth -o yaml
apiVersion: v1
data:
password: Q3l4cjttTzE3OEsuMCQ3Nw==
username: cm9vdA==
kind: Secret
metadata:
creationTimestamp: "2022-02-04T05:59:53Z"
labels:
app.kubernetes.io/component: database
app.kubernetes.io/instance: sample-redis
app.kubernetes.io/managed-by: kubedb.com
app.kubernetes.io/name: redises.kubedb.com
name: sample-redis-auth
namespace: demo
resourceVersion: "422952"
uid: 58e3ac2b-51fe-4845-8bb1-959e51f52015
type: kubernetes.io/basic-auth
Here, we are going to use password to authenticate and insert the sample data.
At first, let’s export the password as environment variables to make further commands re-usable.
export PASSWORD=$(kubectl get secrets -n demo sample-redis-auth -o jsonpath='{.data.\password}' | base64 -d)
Now, let’s exec into the database pod and insert some sample data,
❯ kubectl exec -it -n demo sample-redis-0 -- redis-cli -a $PASSWORD
Warning: Using a password with '-a' or '-u' option on the command line interface may not be safe.
# insert some key value pairs
127.0.0.1:6379> set key1 value1
OK
127.0.0.1:6379> set key2 value2
OK
# check the inserted data
127.0.0.1:6379> get key1
"value1"
127.0.0.1:6379> get key2
"value2"
# exit from redis-cli
127.0.0.1:6379> exit
We have successfully deployed a Redis database and inserted some sample data into it. Now, we are ready to backup our database into our desired backend using Stash.
Prepare for Backup
In this section, we are going to prepare the necessary resources (i.e. database connection information, backend information, etc.) before backup.
Verify Stash Redis Addon Installed
When you install the Stash, it automatically installs all the official database addons. Verify that it has installed the Redis addons using the following command.
$ kubectl get tasks.stash.appscode.com | grep redis
redis-backup-5.0.13 1h
redis-backup-6.2.5 1h
redis-restore-5.0.13 1h
redis-restore-6.2.5 1h
Ensure AppBinding
Stash needs to know how to connect with the database. An AppBinding exactly provides this information. It holds the Service and Secret information of the database. You have to point to the respective AppBinding as a target of backup instead of the database itself.
Verify that the AppBinding has been created successfully using the following command,
❯ kubectl get appbindings -n demo
NAME TYPE VERSION AGE
sample-redis kubedb.com/redis 6.0.20 2m54s
Let’s check the YAML of the above AppBinding,
❯ kubectl get appbindings -n demo sample-redis -o yaml
apiVersion: appcatalog.appscode.com/v1alpha1
kind: AppBinding
metadata:
labels:
app.kubernetes.io/component: database
app.kubernetes.io/instance: sample-redis
app.kubernetes.io/managed-by: kubedb.com
app.kubernetes.io/name: redises.kubedb.com
name: sample-redis
namespace: demo
...
clientConfig:
service:
name: sample-redis
port: 6379
scheme: redis
parameters:
apiVersion: config.kubedb.com/v1alpha1
kind: RedisConfiguration
stash:
addon:
backupTask:
name: redis-backup-6.2.5
restoreTask:
name: redis-restore-6.2.5
secret:
name: sample-redis-auth
type: kubedb.com/redis
version: 6.0.20
Stash requires the following fields to set in AppBinding’s Spec section.
spec.clientConfig.service.namespecifies the name of the service that connects to the database.spec.secretspecifies the name of the secret that holds necessary credentials to access the database.spec.parameters.stashspecifies the Stash Addons that will be used to backup and restore this database.spec.typespecifies the types of the app that this AppBinding is pointing to. KubeDB generated AppBinding follows the following format:<app group>/<app resource type>.
We will use this Appbinding later for connecting into this database.
Prepare Backend
We are going to store our backed up data into a GCS bucket. So, we need to create a Secret with GCS credentials and a Repository object with the bucket information. If you want to use a different backend, please read the respective backend configuration doc from here.
Create Storage Secret:
At first, let’s create a secret called gcs-secret with access credentials to our desired GCS bucket,
$ echo -n 'changeit' > RESTIC_PASSWORD
$ echo -n '<your-project-id>' > GOOGLE_PROJECT_ID
$ cat downloaded-sa-key.json > GOOGLE_SERVICE_ACCOUNT_JSON_KEY
$ kubectl create secret generic -n demo gcs-secret \
--from-file=./RESTIC_PASSWORD \
--from-file=./GOOGLE_PROJECT_ID \
--from-file=./GOOGLE_SERVICE_ACCOUNT_JSON_KEY
secret/gcs-secret created
Create Repository:
Now, crete a Repository object with the information of your desired bucket. Below is the YAML of Repository object we are going to create,
apiVersion: stash.appscode.com/v1alpha1
kind: Repository
metadata:
name: gcs-repo
namespace: demo
spec:
backend:
gcs:
bucket: stash-testing
prefix: /demo/redis/sample-redis
storageSecretName: gcs-secret
Let’s create the Repository we have shown above,
$ kubectl apply -f https://github.com/kubedb/docs/raw/v2024.8.21/docs/guides/redis/backup/standalone/examples/repository.yaml
repository.stash.appscode.com/gcs-repo created
Now, we are ready to backup our database into our GCS bucket.
Backup
To schedule a backup, we have to create a BackupConfiguration object targeting the respective AppBinding of our desired database. Then Stash will create a CronJob to periodically backup the database.
Create BackupConfiguration
Below is the YAML for BackupConfiguration object we care going to use to backup the sample-redis database we have deployed earlier,
apiVersion: stash.appscode.com/v1beta1
kind: BackupConfiguration
metadata:
name: sample-redis-backup
namespace: demo
spec:
schedule: "*/5 * * * *"
repository:
name: gcs-repo
target:
ref:
apiVersion: appcatalog.appscode.com/v1alpha1
kind: AppBinding
name: sample-redis
retentionPolicy:
name: keep-last-5
keepLast: 5
prune: true
Here,
.spec.schedulespecifies that we want to backup the database at 5 minutes intervals..spec.repository.namespecifies the Repository CR name we have created earlier with backend information..spec.target.refrefers to the AppBinding object that holds the connection information of our targeted database..spec.retentionPolicyspecifies a policy indicating how we want to cleanup the old backups.
Let’s create the BackupConfiguration object we have shown above,
$ kubectl apply -f https://github.com/kubedb/docs/raw/v2024.8.21/docs/guides/redis/backup/standalone/examples/backupconfiguration.yaml
backupconfiguration.stash.appscode.com/sample-redis-backup created
Verify Backup Setup Successful
If everything goes well, the phase of the BackupConfiguration should be Ready. The Ready phase indicates that the backup setup is successful. Let’s verify the Phase of the BackupConfiguration,
$ kubectl get backupconfiguration -n demo
NAME TASK SCHEDULE PAUSED PHASE AGE
sample-redis-backup redis-backup-6.2.5 */5 * * * * Ready 11s
Verify CronJob
Stash will create a CronJob with the schedule specified in spec.schedule field of BackupConfiguration object.
Verify that the CronJob has been created using the following command,
❯ kubectl get cronjob -n demo
NAME SCHEDULE SUSPEND ACTIVE LAST SCHEDULE AGE
stash-backup-sample-redis-backup */5 * * * * False 0 <none> 14s
Wait for BackupSession
The sample-redis-backup CronJob will trigger a backup on each scheduled slot by creating a BackupSession object.
Now, wait for a schedule to appear. Run the following command to watch for a BackupSession object,
❯ kubectl get backupsession -n demo -w
NAME INVOKER-TYPE INVOKER-NAME PHASE DURATION AGE
sample-redis-backup-1627490702 BackupConfiguration sample-redis-backup 0s
sample-redis-backup-1627490702 BackupConfiguration sample-redis-backup Running 0s
sample-redis-backup-1627490702 BackupConfiguration sample-redis-backup Succeeded 1m18.098555424s 78s
Here, the phase Succeeded means that the backup process has been completed successfully.
Verify Backup
Now, we are going to verify whether the backed up data is present in the backend or not. Once a backup is completed, Stash will update the respective Repository object to reflect the backup completion. Check that the repository gcs-repo has been updated by the following command,
$ kubectl get repository -n demo gcs-repo
NAME INTEGRITY SIZE SNAPSHOT-COUNT LAST-SUCCESSFUL-BACKUP AGE
gcs-repo true 1.327 MiB 1 60s 8m
Now, if we navigate to the GCS bucket, we will see the backed up data has been stored in demo/redis/sample-redis directory as specified by .spec.backend.gcs.prefix field of the Repository object.
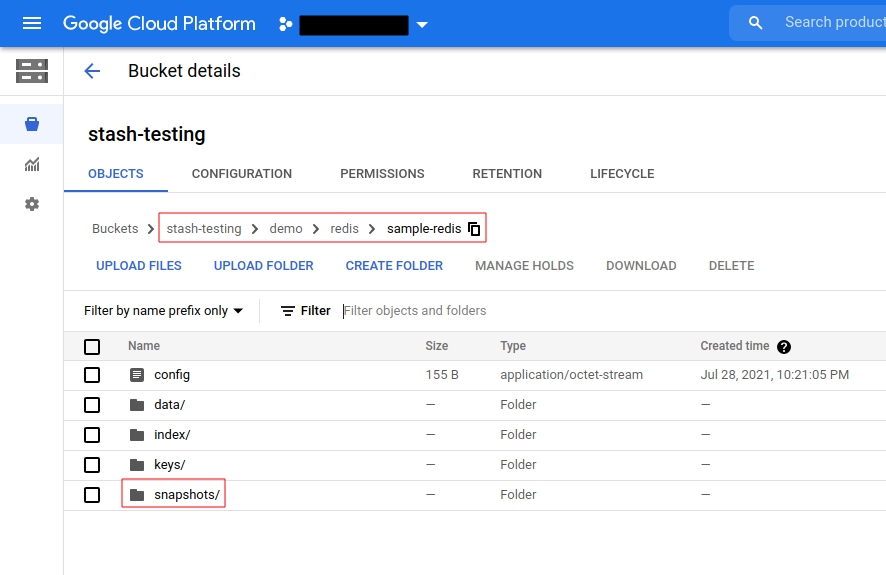
Note: Stash keeps all the backed up data encrypted. So, data in the backend will not make any sense until they are decrypted.
Restore Redis
If you have followed the previous sections properly, you should have a successful logical backup of your Redis database. Now, we are going to show how you can restore the database from the backed up data.
Restore Into the Same Database
You can restore your data into the same database you have backed up from or into a different database in the same cluster or a different cluster. In this section, we are going to show you how to restore in the same database which may be necessary when you have accidentally deleted any data from the running database.
Temporarily Pause Backup
At first, let’s stop taking any further backup of the database so that no backup runs after we delete the sample data. We are going to pause the BackupConfiguration object. Stash will stop taking any further backup when the BackupConfiguration is paused.
Let’s pause the sample-redis-backup BackupConfiguration,
❯ kubectl patch backupconfiguration -n demo sample-redis-backup --type="merge" --patch='{"spec": {"paused": true}}'
backupconfiguration.stash.appscode.com/sample-redis-backup patched
Or you can use the Stash kubectl plugin to pause the BackupConfiguration,
❯ kubectl stash pause backup -n demo --backupconfig=sample-redis-backup
BackupConfiguration demo/sample-redis-backup has been paused successfully.
Verify that the BackupConfiguration has been paused,
❯ kubectl get backupconfiguration -n demo sample-redis-backup
NAME TASK SCHEDULE PAUSED PHASE AGE
sample-redis-backup redis-backup-6.2.5 */5 * * * * true Ready 4h47m
Notice the PAUSED column. Value true for this field means that the BackupConfiguration has been paused.
Stash will also suspend the respective CronJob.
❯ kubectl get cronjob -n demo
NAME SCHEDULE SUSPEND ACTIVE LAST SCHEDULE AGE
stash-backup-sample-redis-backup */5 * * * * True 0 113s 4h48m
Simulate Disaster
Now, let’s simulate an accidental deletion scenario. Here, we are going to exec into the database pod and delete the sample data we have inserted earlier.
❯ kubectl exec -it -n demo sample-redis-0 -- redis-cli -a $PASSWORD
Warning: Using a password with '-a' or '-u' option on the command line interface may not be safe.
# delete the sample data
127.0.0.1:6379> del key1 key2
(integer) 2
# verify that the sample data has been deleted
127.0.0.1:6379> get key1
(nil)
127.0.0.1:6379> get key2
(nil)
127.0.0.1:6379> exit
Create RestoreSession
To restore the database, you have to create a RestoreSession object pointing to the AppBinding of the targeted database.
Here, is the YAML of the RestoreSession object that we are going to use for restoring our sample-redis database.
apiVersion: stash.appscode.com/v1beta1
kind: RestoreSession
metadata:
name: sample-redis-restore
namespace: demo
spec:
repository:
name: gcs-repo
target:
ref:
apiVersion: appcatalog.appscode.com/v1alpha1
kind: AppBinding
name: sample-redis
rules:
- snapshots: [latest]
Here,
.spec.repository.namespecifies the Repository object that holds the backend information where our backed up data has been stored..spec.target.refrefers to the respective AppBinding of thesample-redisdatabase..spec.rulesspecifies that we are restoring data from the latest backup snapshot of the database.
Let’s create the RestoreSession object object we have shown above,
$ kubectl apply -f https://github.com/kubedb/docs/raw/v2024.8.21/docs/guides/redis/backup/standalone/examples/restoresession.yaml
restoresession.stash.appscode.com/sample-redis-restore created
Once, you have created the RestoreSession object, Stash will create a restore Job. Run the following command to watch the phase of the RestoreSession object,
❯ kubectl get restoresession -n demo -w
NAME REPOSITORY PHASE DURATION AGE
sample-redis-restore gcs-repo Running 6s
sample-redis-restore gcs-repo Running 16s
sample-redis-restore gcs-repo Succeeded 16s
sample-redis-restore gcs-repo Succeeded 16.324570911s 16s
The Succeeded phase means that the restore process has been completed successfully.
Verify Restored Data
Now, let’s exec into the database pod and verify whether data actual data has been restored or not,
❯ kubectl exec -it -n demo sample-redis-0 -- redis-cli -a $PASSWORD
Warning: Using a password with '-a' or '-u' option on the command line interface may not be safe.
127.0.0.1:6379> get key1
"value1"
127.0.0.1:6379> get key2
"value2"
127.0.0.1:6379> exit
Hence, we can see from the above output that the deleted data has been restored successfully from the backup.
Resume Backup
Since our data has been restored successfully we can now resume our usual backup process. Resume the BackupConfiguration using following command,
❯ kubectl patch backupconfiguration -n demo sample-redis-backup --type="merge" --patch='{"spec": {"paused": false}}'
backupconfiguration.stash.appscode.com/sample-redis-backup patched
Or you can use the Stash kubectl plugin to resume the BackupConfiguration
❯ kubectl stash resume -n demo --backupconfig=sample-redis-backup
BackupConfiguration demo/sample-redis-backup has been resumed successfully.
Verify that the BackupConfiguration has been resumed,
❯ kubectl get backupconfiguration -n demo sample-redis-backup
NAME TASK SCHEDULE PAUSED PHASE AGE
sample-redis-backup redis-backup-6.2.5 */5 * * * * false Ready 4h54m
Here, false in the PAUSED column means the backup has been resume successfully. The CronJob also should be resumed now.
❯ kubectl get cronjob -n demo
NAME SCHEDULE SUSPEND ACTIVE LAST SCHEDULE AGE
stash-backup-sample-redis-backup */5 * * * * False 0 3m24s 4h54m
Here, False in the SUSPEND column means the CronJob is no longer suspended and will trigger in the next schedule.
Restore Into Different Database of the Same Namespace
If you want to restore the backed up data into a different database of the same namespace, you need to have another AppBinding pointing to the desired database. Then, you have to create the RestoreSession pointing to the new AppBinding.
Restore Into Different Namespace
If you want to restore into a different namespace of the same cluster, you have to create the Repository, backend Secret, AppBinding, in the desired namespace. You can use Stash kubectl plugin to easily copy the resources into a new namespace. Then, you have to create the RestoreSession object in the desired namespace pointing to the Repository, AppBinding of that namespace.
Restore Into Different Cluster
If you want to restore into a different cluster, you have to install Stash in the desired cluster. Then, you have to install Stash Redis addon in that cluster too. Then, you have to create the Repository, backend Secret, AppBinding, in the desired cluster. Finally, you have to create the RestoreSession object in the desired cluster pointing to the Repository, AppBinding of that cluster.
Cleanup
To cleanup the Kubernetes resources created by this tutorial, run:
kubectl delete -n demo backupconfiguration sample-redis-backup
kubectl delete -n demo restoresession sample-redis-restore
kubectl delete -n demo repository gcs-repo
# delete the database resources
kubectl delete redis sample-redis -n demo
#delete the namespace
kubectl delete ns demo



































