You are looking at the documentation of a prior release. To read the documentation of the latest release, please
visit here.
New to KubeDB? Please start here.
SchemaRegistry QuickStart
This tutorial will show you how to use KubeDB to run a Schema Registry.
Before You Begin
At first, you need to have a Kubernetes cluster, and the kubectl command-line tool must be configured to communicate with your cluster. If you do not already have a cluster, you can create one by using kind.
Now, install the KubeDB operator in your cluster following the steps here.
To keep things isolated, this tutorial uses a separate namespace called demo throughout this tutorial.
$ kubectl create namespace demo
namespace/demo created
$ kubectl get namespace
NAME STATUS AGE
demo Active 9s
Note: YAML files used in this tutorial are stored in examples/kafka/schemaregistry/ folder in GitHub repository kubedb/docs.
We have designed this tutorial to demonstrate a production setup of KubeDB managed Schema Registry. If you just want to try out KubeDB, you can bypass some safety features following the tips here.
Find Available SchemaRegistry Versions
When you install the KubeDB operator, it registers a CRD named SchemaRegistryVersion. The installation process comes with a set of tested SchemaRegistryVersion objects. Let’s check available SchemaRegistryVersions by,
$ kubectl get ksrversion
NAME VERSION DB_IMAGE DEPRECATED AGE
NAME VERSION DISTRIBUTION REGISTRY_IMAGE DEPRECATED AGE
2.5.11.final 2.5.11 Apicurio apicurio/apicurio-registry-kafkasql:2.5.11.Final 3d
3.15.0 3.15.0 Aiven ghcr.io/aiven-open/karapace:3.15.0 3d
Note: Currently Schema Registry is supported only for Apicurio distribution. Use version with distribution
Apicurioto create Schema Registry.
Notice the DEPRECATED column. Here, true means that this SchemaRegistryVersion is deprecated for the current KubeDB version. KubeDB will not work for deprecated KafkaVersion. You can also use the short from ksrversion to check available SchemaRegistryVersion.
In this tutorial, we will use 2.5.11.final SchemaRegistryVersion CR to create a Kafka Schema Registry.
Create a Kafka Schema Registry
The KubeDB operator implements a SchemaRegistry CRD to define the specification of SchemaRegistry.
The SchemaRegistry instance used for this tutorial:
apiVersion: kafka.kubedb.com/v1alpha1
kind: SchemaRegistry
metadata:
name: schemaregistry-quickstart
namespace: demo
spec:
version: 2.5.11.final
replicas: 2
kafkaRef:
name: kafka-quickstart
namespace: demo
deletionPolicy: WipeOut
Here,
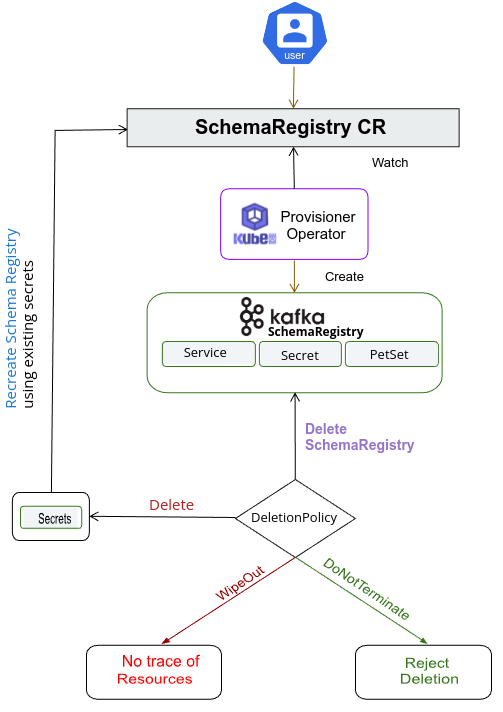
spec.version- is the name of the SchemaRegistryVersion CR. Here, a SchemaRegistry of version2.5.11.finalwill be created.spec.replicas- specifies the number of schema registry instances to run. Here, the SchemaRegistry will run with 2 replicas.spec.kafkaRefspecifies the Kafka instance that the SchemaRegistry will store its schema. Here, the SchemaRegistry will store schema to the Kafka instance namedkafka-quickstartin thedemonamespace. It is an appbinding reference of the Kafka instance.spec.deletionPolicyspecifies what KubeDB should do when a user try to delete SchemaRegistry CR. Deletion policyWipeOutwill delete all the instances, secret when the SchemaRegistry CR is deleted.
Note: If
spec.kafkaRefis not provided, the SchemaRegistry will runinMmemorymode. SchemaRegistry will store schema to its memory.
Before create SchemaRegistry, you have to deploy a Kafka cluster first. To deploy kafka cluster, follow the Kafka Quickstart guide. Let’s assume kafka-quickstart is already deployed using KubeDB.
Let’s create the SchemaRegistry CR that is shown above:
$ kubectl apply -f https://github.com/kubedb/docs/raw/v2024.9.30/docs/examples/kafka/schemaregistry/schemaregistry-apicurio.yaml
schemaregistry.kafka.kubedb.com/schemaregistry-quickstart created
The SchemaRegistry’s STATUS will go from Provisioning to Ready state within few minutes. Once the STATUS is Ready, you are ready to use the SchemaRegistry.
$ kubectl get schemaregistry -n demo -w
NAME TYPE VERSION STATUS AGE
schemaregistry-quickstart kafka.kubedb.com/v1alpha1 3.6.1 Provisioning 2s
schemaregistry-quickstart kafka.kubedb.com/v1alpha1 3.6.1 Provisioning 4s
.
.
schemaregistry-quickstart kafka.kubedb.com/v1alpha1 3.6.1 Ready 112s
Describe the SchemaRegistry object to observe the progress if something goes wrong or the status is not changing for a long period of time:
$ kubectl describe schemaregistry -n demo schemaregistry-quickstart
Name: schemaregistry-quickstart
Namespace: demo
Labels: <none>
Annotations: <none>
API Version: kafka.kubedb.com/v1alpha1
Kind: SchemaRegistry
Metadata:
Creation Timestamp: 2024-09-02T05:29:55Z
Finalizers:
kafka.kubedb.com/finalizer
Generation: 1
Resource Version: 174971
UID: 5a5f0c8f-778b-471f-973a-683004b26c78
Spec:
Deletion Policy: WipeOut
Health Checker:
Failure Threshold: 3
Period Seconds: 20
Timeout Seconds: 10
Kafka Ref:
Name: kafka-quickstart
Namespace: demo
Pod Template:
Controller:
Metadata:
Spec:
Containers:
Name: schema-registry
Resources:
Limits:
Memory: 1Gi
Requests:
Cpu: 500m
Memory: 1Gi
Security Context:
Allow Privilege Escalation: false
Capabilities:
Drop:
ALL
Run As Non Root: true
Run As User: 1001
Seccomp Profile:
Type: RuntimeDefault
Pod Placement Policy:
Name: default
Security Context:
Fs Group: 1001
Replicas: 2
Version: 2.5.11.final
Status:
Conditions:
Last Transition Time: 2024-09-02T05:29:55Z
Message: The KubeDB operator has started the provisioning of SchemaRegistry: demo/schemaregistry-quickstart
Observed Generation: 1
Reason: SchemaRegistryProvisioningStartedSuccessfully
Status: True
Type: ProvisioningStarted
Last Transition Time: 2024-09-02T05:30:47Z
Message: All desired replicas are ready.
Observed Generation: 1
Reason: AllReplicasReady
Status: True
Type: ReplicaReady
Last Transition Time: 2024-09-02T05:31:09Z
Message: The SchemaRegistry: demo/schemaregistry-quickstart is accepting client requests
Observed Generation: 1
Reason: DatabaseAcceptingConnectionRequest
Status: True
Type: AcceptingConnection
Last Transition Time: 2024-09-02T05:31:09Z
Message: The SchemaRegistry: demo/schemaregistry-quickstart is ready.
Observed Generation: 1
Reason: ReadinessCheckSucceeded
Status: True
Type: Ready
Last Transition Time: 2024-09-02T05:31:11Z
Message: The SchemaRegistry: demo/schemaregistry-quickstart is successfully provisioned.
Observed Generation: 1
Reason: DatabaseSuccessfullyProvisioned
Status: True
Type: Provisioned
Phase: Ready
Events: <none>
KubeDB Operator Generated Resources
On deployment of a SchemaRegistry CR, the operator creates the following resources:
$ kubectl get all,secret,petset -n demo -l 'app.kubernetes.io/instance=schemaregistry-quickstart'
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
pod/schemaregistry-quickstart-0 1/1 Running 0 4m14s
pod/schemaregistry-quickstart-1 1/1 Running 0 3m28s
NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE
service/schemaregistry-quickstart ClusterIP 10.96.187.98 <none> 8080/TCP 4m17s
service/schemaregistry-quickstart-pods ClusterIP None <none> 8080/TCP 4m17s
NAME TYPE DATA AGE
secret/schemaregistry-quickstart-config Opaque 1 4m17s
NAME AGE
petset.apps.k8s.appscode.com/schemaregistry-quickstart 4m14s
PetSet- a PetSet named after the SchemaRegistry instance.Services- For a SchemaRegistry instance headless service is created with name{SchemaRegistry-name}-{pods}and a primary service created with name{SchemaRegistry-name}.Secrets- default configuration secrets are generated for SchemaRegistry.{SchemaRegistry-Name}-config- the default configuration secret created by the operator.
Accessing Schema Registry(Rest API)
You can access the Schema Registry using the REST API. The Schema Registry REST API is available at port 8080 of the Schema Registry service.
To access the Schema Registry REST API, you can use kubectl port-forward command to forward the port to your local machine.
$ kubectl port-forward service/schemaregistry-quickstart 8080:8080 -n demo
Forwarding from 127.0.0.1:8080 -> 8080
Forwarding from [::1]:8080 -> 8080
In another terminal, you can use curl to get, create or update schema using the Schema Registry REST API.
Create a new schema with the following command:
$ curl -X POST -H "Content-Type: application/json; artifactType=AVRO" -H "X-Registry-ArtifactId: share-price" \
--data '{"type":"record","name":"price","namespace":"com.example", \
"fields":[{"name":"symbol","type":"string"},{"name":"price","type":"string"}]}' \
localhost:8080/apis/registry/v2/groups/quickstart-group/artifacts | jq
{
"createdBy": "",
"createdOn": "2024-09-02T05:53:03+0000",
"modifiedBy": "",
"modifiedOn": "2024-09-02T05:53:03+0000",
"id": "share-price",
"version": "1",
"type": "AVRO",
"globalId": 2,
"state": "ENABLED",
"groupId": "quickstart-group",
"contentId": 2,
"references": []
}
Get all the groups:
$ curl localhost:8080/apis/registry/v2/groups | jq .
{
"groups": [
{
"id": "quickstart-group",
"createdOn": "2024-09-02T05:49:33+0000",
"createdBy": "",
"modifiedBy": ""
}
],
"count": 1
}
Get all the artifacts in the group quickstart-group:
$ curl localhost:8080/apis/registry/v2/groups/quickstart-group/artifacts | jq
{
"artifacts": [
{
"id": "share-price",
"createdOn": "2024-09-02T05:53:03+0000",
"createdBy": "",
"type": "AVRO",
"state": "ENABLED",
"modifiedOn": "2024-09-02T05:53:03+0000",
"modifiedBy": "",
"groupId": "quickstart-group"
}
],
"count": 1
}
Note: You can also use Schema Registry with Confluent 7 compatible REST APIs. To use confluent compatible REST APIs, you have to add
apis/ccompat/v7after url address.(e.g.localhost:8081/subjects->localhost:8080/apis/ccompat/v7/subjects)
Accessing Schema Registry(UI)
You can also use the Schema Registry UI to interact with the Schema Registry. The Schema Registry UI is available at port 8080 of the Schema Registry service.
Use http://localhost:8080/ui/artifacts to access the Schema Registry UI.
You will see the following screen:
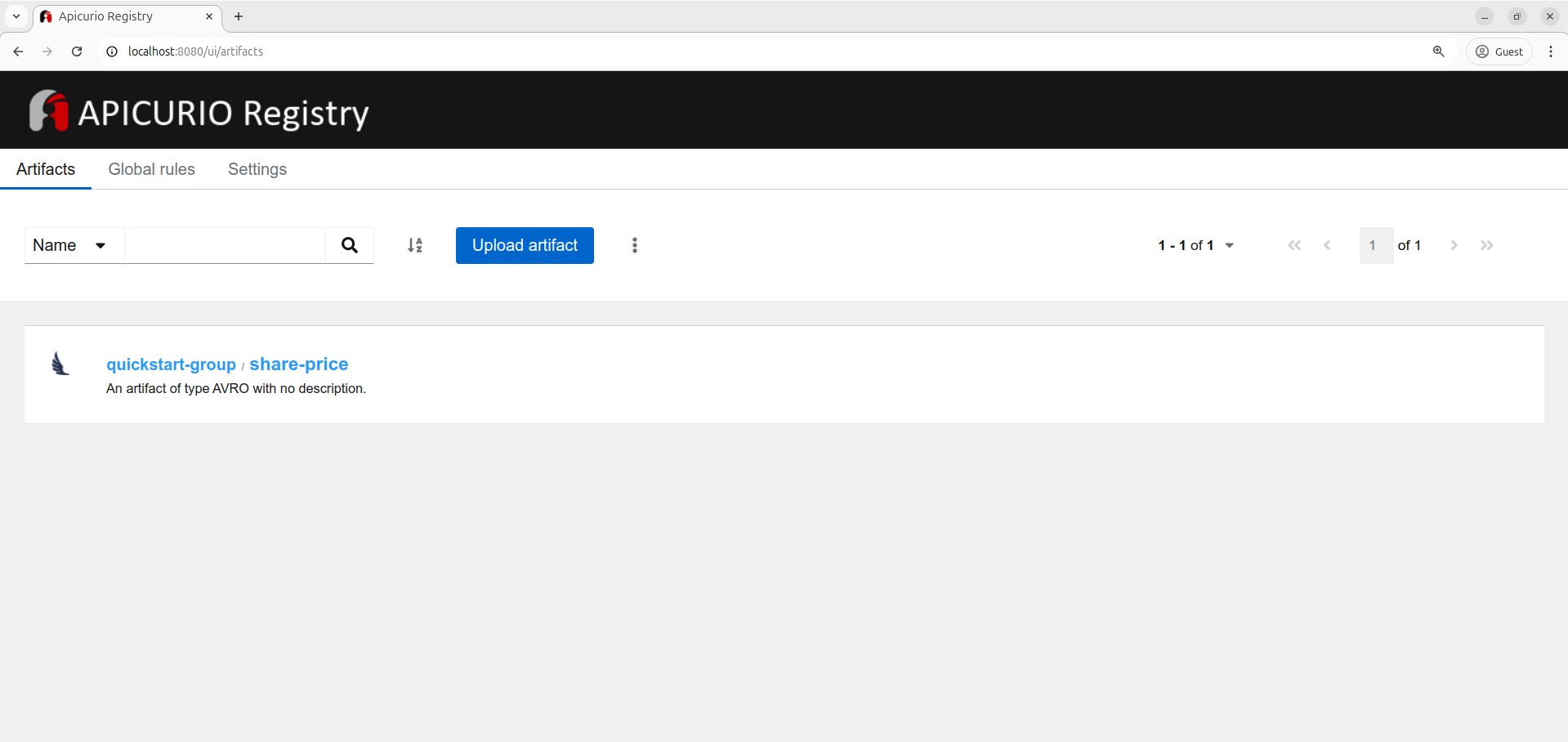
From the UI, you can create, update, delete, and view the schema. Also add compatibility level, view the schema history, etc.
Cleaning up
To clean up the Kubernetes resources created by this tutorial, run:
$ kubectl patch -n demo schemaregistry schemaregistry-quickstart -p '{"spec":{"deletionPolicy":"WipeOut"}}' --type="merge"
schemaregistry.kafka.kubedb.com/schemaregistry-quickstart patched
$ kubectl delete ksr schemaregistry-quickstart -n demo
schemaregistry.kafka.kubedb.com "schemaregistry-quickstart" deleted
$ kubectl delete kafka kafka-quickstart -n demo
kafka.kubedb.com "kafka-quickstart" deleted
$ kubectl delete namespace demo
namespace "demo" deleted
Tips for Testing
If you are just testing some basic functionalities, you might want to avoid additional hassles due to some safety features that are great for the production environment. You can follow these tips to avoid them.
1 Use deletionPolicy: Delete. It is nice to be able to resume the cluster from the previous one. So, we preserve auth Secrets. If you don’t want to resume the cluster, you can just use spec.deletionPolicy: WipeOut. It will clean up every resource that was created with the SchemaRegistry CR. For more details, please visit here.
Next Steps
- Quickstart Kafka with KubeDB Operator.
- Quickstart ConnectCluster with KubeDB Operator.
- Use kubedb cli to manage databases like kubectl for Kubernetes.
- Detail concepts of ConnectCluster object.
- Want to hack on KubeDB? Check our contribution guidelines.



































