You are looking at the documentation of a prior release. To read the documentation of the latest release, please
visit here.
New to KubeDB? Please start here.
Reconfiguring Memcached
This guide will give an overview on how KubeDB Ops-manager operator reconfigures Memcached database.
Before You Begin
- You should be familiar with the following
KubeDBconcepts:
How Reconfiguring Memcached Process Works
The following diagram shows how KubeDB Ops-manager operator reconfigures Memcached database components. Open the image in a new tab to see the enlarged version.
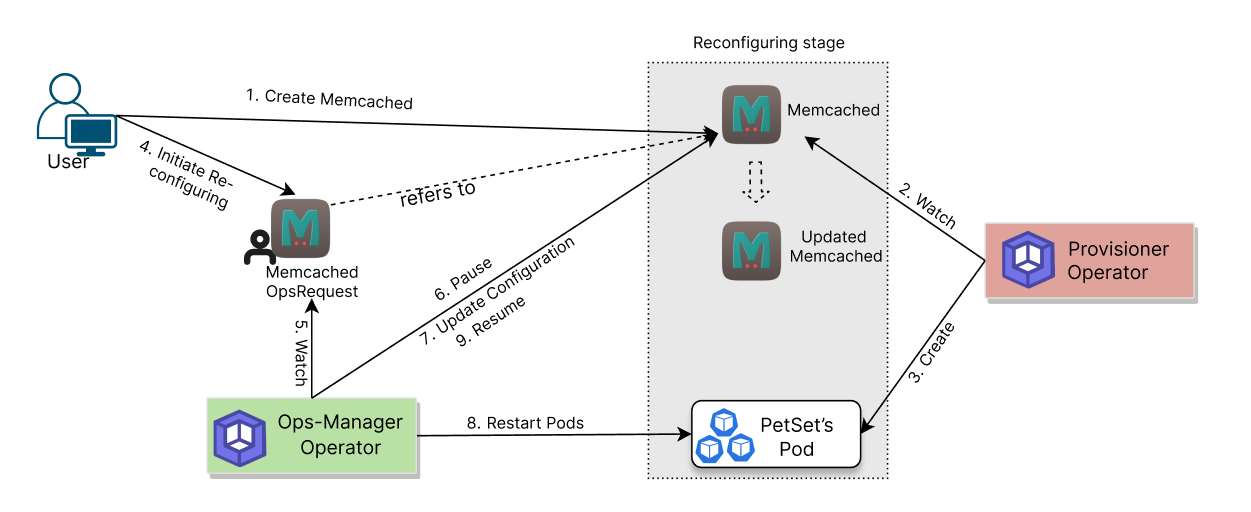
The Reconfiguring Memcached process consists of the following steps:
At first, a user creates a
MemcachedCustom Resource (CR).KubeDBoperator watches theMemcachedCR.When the operator finds a
MemcachedCR, it creates required number ofPetSetsand related necessary stuff like secrets, services, etc.Then, in order to reconfigure the
Memcacheddatabase the user creates aMemcachedOpsRequestCR with desired information.KubeDBOps-manager operator watches theMemcachedOpsRequestCR.When it finds a
MemcachedOpsRequestCR, it halts theMemcachedobject which is referred from theMemcachedOpsRequest. So, theKubeDBProvisioner operator doesn’t perform any operations on theMemcachedobject during the reconfiguring process.Then the
KubeDBOps-manager operator will replace the existing configuration with the new configuration provided or merge the new configuration with the existing configuration according to theMemcachedOpsRequestCR.Then the
KubeDBOps-manager operator will restart the related PetSet Pods so that they restart with the new configuration defined in theMemcachedOpsRequestCR.After the successful reconfiguring of the
Memcachedcomponents, theKubeDBOps-manager operator resumes theMemcachedobject so that theKubeDBProvisioner operator resumes its usual operations.
In the next docs, we are going to show a step by step guide on reconfiguring Memcached database components using MemcachedOpsRequest CRD.



































