You are looking at the documentation of a prior release. To read the documentation of the latest release, please
visit here.
New to KubeDB? Please start here.
Reconfigure Druid Cluster
This guide will show you how to use KubeDB Ops-manager operator to reconfigure a Druid Topology cluster.
Before You Begin
At first, you need to have a Kubernetes cluster, and the
kubectlcommand-line tool must be configured to communicate with your cluster.Install
KubeDBProvisioner and Ops-manager operator in your cluster following the steps here.You should be familiar with the following
KubeDBconcepts:
To keep everything isolated, we are going to use a separate namespace called demo throughout this tutorial.
$ kubectl create ns demo
namespace/demo created
Note: YAML files used in this tutorial are stored in /docs/guides/druid/reconfigure/yamls directory of kubedb/docs repository.
Now, we are going to deploy a Druid cluster using a supported version by KubeDB operator. Then we are going to apply DruidOpsRequest to reconfigure its configuration.
Prepare Druid Cluster
Now, we are going to deploy a Druid topology cluster with version 28.0.1.
Create External Dependency (Deep Storage)
Before proceeding further, we need to prepare deep storage, which is one of the external dependency of Druid and used for storing the segments. It is a storage mechanism that Apache Druid does not provide. Amazon S3, Google Cloud Storage, or Azure Blob Storage, S3-compatible storage (like Minio), or HDFS are generally convenient options for deep storage.
In this tutorial, we will run a minio-server as deep storage in our local kind cluster using minio-operator and create a bucket named druid in it, which the deployed druid database will use.
$ helm repo add minio https://operator.min.io/
$ helm repo update minio
$ helm upgrade --install --namespace "minio-operator" --create-namespace "minio-operator" minio/operator --set operator.replicaCount=1
$ helm upgrade --install --namespace "demo" --create-namespace druid-minio minio/tenant \
--set tenant.pools[0].servers=1 \
--set tenant.pools[0].volumesPerServer=1 \
--set tenant.pools[0].size=1Gi \
--set tenant.certificate.requestAutoCert=false \
--set tenant.buckets[0].name="druid" \
--set tenant.pools[0].name="default"
Now we need to create a Secret named deep-storage-config. It contains the necessary connection information using which the druid database will connect to the deep storage.
apiVersion: v1
kind: Secret
metadata:
name: deep-storage-config
namespace: demo
stringData:
druid.storage.type: "s3"
druid.storage.bucket: "druid"
druid.storage.baseKey: "druid/segments"
druid.s3.accessKey: "minio"
druid.s3.secretKey: "minio123"
druid.s3.protocol: "http"
druid.s3.enablePathStyleAccess: "true"
druid.s3.endpoint.signingRegion: "us-east-1"
druid.s3.endpoint.url: "http://myminio-hl.demo.svc.cluster.local:9000/"
Let’s create the deep-storage-config Secret shown above:
$ kubectl create -f https://github.com/kubedb/docs/raw/v2025.1.9/docs/guides/druid/restart/yamls/deep-storage-config.yaml
secret/deep-storage-config created
Now, lets go ahead and create a druid database.
apiVersion: kubedb.com/v1alpha2
kind: Druid
metadata:
name: druid-cluster
namespace: demo
spec:
version: 28.0.1
deepStorage:
type: s3
configSecret:
name: deep-storage-config
topology:
routers:
replicas: 1
deletionPolicy: Delete
Let’s create the Druid CR we have shown above,
$ kubectl create -f https://github.com/kubedb/docs/raw/v2025.1.9/docs/guides/druid/update-version/yamls/druid-cluster.yaml
druid.kubedb.com/druid-cluster created
Reconfigure using config secret
Say we want to change the default maximum number of tasks the MiddleManager can accept. Let’s create the middleManagers.properties file with our desire configurations.
middleManagers.properties:
druid.worker.capacity=5
historicals.properties:
druid.processing.numThreads=3
Then, we will create a new secret with this configuration file.
apiVersion: v1
kind: Secret
metadata:
name: config-secret
namespace: demo
stringData:
middleManagers.properties: |-
druid.worker.capacity=5
historicals.properties: |-
druid.processing.numThreads=3
$ kubectl apply -f https://github.com/kubedb/docs/raw/v2025.1.9/docs/guides/druid/update-version/yamls/config-secret.yaml
secret/new-config created
Check Current Configuration
Before creating the druidOpsRequest, first Lets exec into one of the druid middleManagers pod that we have created and check the default configuration:
Exec into the Druid middleManagers:
$ kubectl exec -it -n demo druid-cluster-middleManagers-0 -- bash
Defaulted container "druid" out of: druid, init-druid (init)
bash-5.1$
Now, execute the following commands to see the configurations:
bash-5.1$ cat conf/druid/cluster/data/middleManager/runtime.properties | grep druid.worker.capacity
druid.worker.capacity=2
Here, we can see that our given configuration is applied to the Druid cluster for all brokers.
Now, lets exec into one of the druid historicals pod that we have created and check the configurations are applied or not:
Exec into the Druid historicals:
$ kubectl exec -it -n demo druid-cluster-historicals-0 -- bash
Defaulted container "druid" out of: druid, init-druid (init)
bash-5.1$
Now, execute the following commands to see the metadata storage directory:
bash-5.1$ cat conf/druid/cluster/data/historical/runtime.properties | grep druid.processing.numThreads
druid.processing.numThreads=2
Here, we can see that our given configuration is applied to the historicals.
Check Configuration from Druid UI
You can also see the configuration changes from the druid ui. For that, follow the following steps:
First port-forward the port 8888 to local machine:
$ kubectl port-forward -n demo svc/druid-cluster-routers 8888
Forwarding from 127.0.0.1:8888 -> 8888
Forwarding from [::1]:8888 -> 8888
Now hit the http://localhost:8888 from any browser, and you will be prompted to provide the credential of the druid database. By following the steps discussed below, you can get the credential generated by the KubeDB operator for your Druid database.
Connection information:
Username:
$ kubectl get secret -n demo druid-cluster-auth -o jsonpath='{.data.username}' | base64 -d adminPassword:
$ kubectl get secret -n demo druid-cluster-auth -o jsonpath='{.data.password}' | base64 -d LzJtVRX5E8MorFaf
After providing the credentials correctly, you should be able to access the web console like shown below.
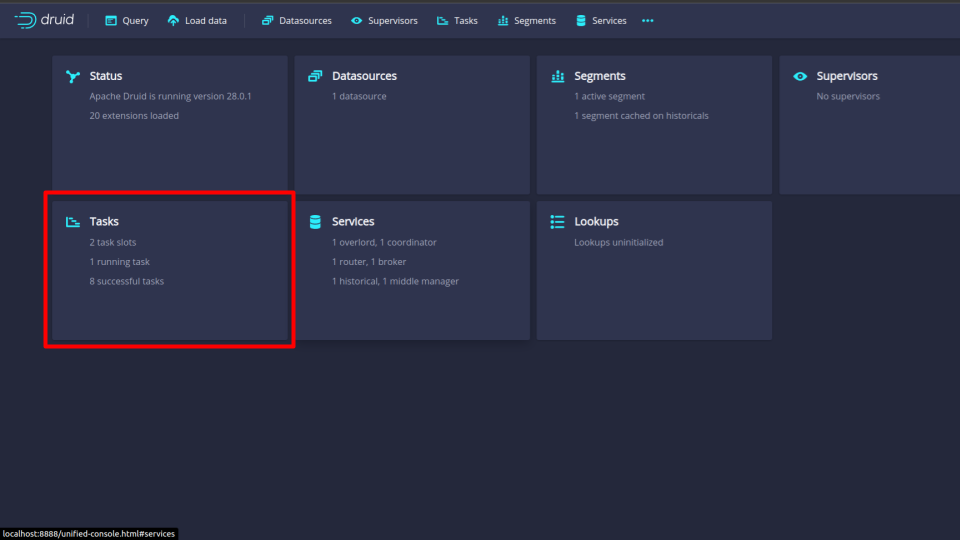
You can see that there are 2 task slots reflecting with the configuration druid.worker.capacity=2.
Create DruidOpsRequest
Now, we will use this secret to replace the previous secret using a DruidOpsRequest CR. The DruidOpsRequest yaml is given below,
apiVersion: ops.kubedb.com/v1alpha1
kind: DruidOpsRequest
metadata:
name: reconfigure-drops
namespace: demo
spec:
type: Reconfigure
databaseRef:
name: druid-cluster
configuration:
configSecret:
name: new-config
Here,
spec.databaseRef.namespecifies that we are reconfiguringdruid-proddatabase.spec.typespecifies that we are performingReconfigureon our database.spec.configSecret.namespecifies the name of the new secret.
Let’s create the DruidOpsRequest CR we have shown above,
$ kubectl apply -f https://github.com/kubedb/docs/raw/v2025.1.9/docs/guides/druid/reconfigure/yamls/reconfigure-druid-ops.yaml
druidopsrequest.ops.kubedb.com/reconfigure-drops created
Check new configuration
If everything goes well, KubeDB Ops-manager operator will update the configSecret of Druid object.
Let’s wait for DruidOpsRequest to be Successful. Run the following command to watch DruidOpsRequest CR,
$ kubectl get druidopsrequests -n demo
NAME TYPE STATUS AGE
reconfigure-drops Reconfigure Successful 4m55s
We can see from the above output that the DruidOpsRequest has succeeded. If we describe the DruidOpsRequest we will get an overview of the steps that were followed to reconfigure the database.
$ kubectl describe druidopsrequest -n demo reconfigure-drops
Name: reconfigure-drops
Namespace: demo
Labels: <none>
Annotations: <none>
API Version: ops.kubedb.com/v1alpha1
Kind: DruidOpsRequest
Metadata:
Creation Timestamp: 2024-08-02T05:08:37Z
Generation: 1
Resource Version: 332491
UID: b6e8cb1b-d29f-445e-bb01-60d29012c7eb
Spec:
Apply: IfReady
Configuration:
Config Secret:
Name: new-kf-topology-custom-config
Database Ref:
Name: druid-prod
Timeout: 5m
Type: Reconfigure
Status:
Conditions:
Last Transition Time: 2024-08-02T05:08:37Z
Message: Druid ops-request has started to reconfigure druid nodes
Observed Generation: 1
Reason: Reconfigure
Status: True
Type: Reconfigure
Last Transition Time: 2024-08-02T05:08:45Z
Message: check reconcile; ConditionStatus:False
Observed Generation: 1
Status: False
Type: CheckReconcile
Last Transition Time: 2024-08-02T05:09:42Z
Message: successfully reconciled the Druid with new configure
Observed Generation: 1
Reason: UpdatePetSets
Status: True
Type: UpdatePetSets
Last Transition Time: 2024-08-02T05:09:47Z
Message: get pod; ConditionStatus:True; PodName:druid-prod-historicals-0
Observed Generation: 1
Status: True
Type: GetPod--druid-prod-historicals-0
Last Transition Time: 2024-08-02T05:09:47Z
Message: evict pod; ConditionStatus:True; PodName:druid-prod-historicals-0
Observed Generation: 1
Status: True
Type: EvictPod--druid-prod-historicals-0
Last Transition Time: 2024-08-02T05:10:02Z
Message: check pod running; ConditionStatus:True; PodName:druid-prod-historicals-0
Observed Generation: 1
Status: True
Type: CheckPodRunning--druid-prod-historicals-0
Last Transition Time: 2024-08-02T05:10:07Z
Message: get pod; ConditionStatus:True; PodName:druid-prod-historicals-1
Observed Generation: 1
Status: True
Type: GetPod--druid-prod-historicals-1
Last Transition Time: 2024-08-02T05:10:07Z
Message: evict pod; ConditionStatus:True; PodName:druid-prod-historicals-1
Observed Generation: 1
Status: True
Type: EvictPod--druid-prod-historicals-1
Last Transition Time: 2024-08-02T05:10:22Z
Message: check pod running; ConditionStatus:True; PodName:druid-prod-historicals-1
Observed Generation: 1
Status: True
Type: CheckPodRunning--druid-prod-historicals-1
Last Transition Time: 2024-08-02T05:10:27Z
Message: get pod; ConditionStatus:True; PodName:druid-prod-middleManagers-0
Observed Generation: 1
Status: True
Type: GetPod--druid-prod-middleManagers-0
Last Transition Time: 2024-08-02T05:10:27Z
Message: evict pod; ConditionStatus:True; PodName:druid-prod-middleManagers-0
Observed Generation: 1
Status: True
Type: EvictPod--druid-prod-middleManagers-0
Last Transition Time: 2024-08-02T05:11:12Z
Message: check pod running; ConditionStatus:True; PodName:druid-prod-middleManagers-0
Observed Generation: 1
Status: True
Type: CheckPodRunning--druid-prod-middleManagers-0
Last Transition Time: 2024-08-02T05:11:17Z
Message: get pod; ConditionStatus:True; PodName:druid-prod-middleManagers-1
Observed Generation: 1
Status: True
Type: GetPod--druid-prod-middleManagers-1
Last Transition Time: 2024-08-02T05:11:17Z
Message: evict pod; ConditionStatus:True; PodName:druid-prod-middleManagers-1
Observed Generation: 1
Status: True
Type: EvictPod--druid-prod-middleManagers-1
Last Transition Time: 2024-08-02T05:11:32Z
Message: check pod running; ConditionStatus:True; PodName:druid-prod-middleManagers-1
Observed Generation: 1
Status: True
Type: CheckPodRunning--druid-prod-middleManagers-1
Last Transition Time: 2024-08-02T05:11:37Z
Message: Successfully restarted all nodes
Observed Generation: 1
Reason: RestartNodes
Status: True
Type: RestartNodes
Last Transition Time: 2024-08-02T05:11:39Z
Message: Successfully completed reconfigure druid
Observed Generation: 1
Reason: Successful
Status: True
Type: Successful
Observed Generation: 1
Phase: Successful
Events:
Type Reason Age From Message
---- ------ ---- ---- -------
Normal Starting 3m7s KubeDB Ops-manager Operator Start processing for DruidOpsRequest: demo/reconfigure-drops
Normal Starting 3m7s KubeDB Ops-manager Operator Pausing Druid databse: demo/druid-prod
Normal Successful 3m7s KubeDB Ops-manager Operator Successfully paused Druid database: demo/druid-prod for DruidOpsRequest: reconfigure-drops
Warning check reconcile; ConditionStatus:False 2m59s KubeDB Ops-manager Operator check reconcile; ConditionStatus:False
Normal UpdatePetSets 2m2s KubeDB Ops-manager Operator successfully reconciled the Druid with new configure
Warning get pod; ConditionStatus:True; PodName:druid-prod-historicals-0 117s KubeDB Ops-manager Operator get pod; ConditionStatus:True; PodName:druid-prod-historicals-0
Warning evict pod; ConditionStatus:True; PodName:druid-prod-historicals-0 117s KubeDB Ops-manager Operator evict pod; ConditionStatus:True; PodName:druid-prod-historicals-0
Warning check pod running; ConditionStatus:False; PodName:druid-prod-historicals-0 112s KubeDB Ops-manager Operator check pod running; ConditionStatus:False; PodName:druid-prod-historicals-0
Warning check pod running; ConditionStatus:True; PodName:druid-prod-historicals-0 102s KubeDB Ops-manager Operator check pod running; ConditionStatus:True; PodName:druid-prod-historicals-0
Warning get pod; ConditionStatus:True; PodName:druid-prod-historicals-1 97s KubeDB Ops-manager Operator get pod; ConditionStatus:True; PodName:druid-prod-historicals-1
Warning evict pod; ConditionStatus:True; PodName:druid-prod-historicals-1 97s KubeDB Ops-manager Operator evict pod; ConditionStatus:True; PodName:druid-prod-historicals-1
Warning check pod running; ConditionStatus:False; PodName:druid-prod-historicals-1 92s KubeDB Ops-manager Operator check pod running; ConditionStatus:False; PodName:druid-prod-historicals-1
Warning check pod running; ConditionStatus:True; PodName:druid-prod-historicals-1 82s KubeDB Ops-manager Operator check pod running; ConditionStatus:True; PodName:druid-prod-historicals-1
Warning get pod; ConditionStatus:True; PodName:druid-prod-middleManagers-0 77s KubeDB Ops-manager Operator get pod; ConditionStatus:True; PodName:druid-prod-middleManagers-0
Warning evict pod; ConditionStatus:True; PodName:druid-prod-middleManagers-0 77s KubeDB Ops-manager Operator evict pod; ConditionStatus:True; PodName:druid-prod-middleManagers-0
Warning check pod running; ConditionStatus:False; PodName:druid-prod-middleManagers-0 72s KubeDB Ops-manager Operator check pod running; ConditionStatus:False; PodName:druid-prod-middleManagers-0
Warning check pod running; ConditionStatus:True; PodName:druid-prod-middleManagers-0 32s KubeDB Ops-manager Operator check pod running; ConditionStatus:True; PodName:druid-prod-middleManagers-0
Warning get pod; ConditionStatus:True; PodName:druid-prod-middleManagers-1 27s KubeDB Ops-manager Operator get pod; ConditionStatus:True; PodName:druid-prod-middleManagers-1
Warning evict pod; ConditionStatus:True; PodName:druid-prod-middleManagers-1 27s KubeDB Ops-manager Operator evict pod; ConditionStatus:True; PodName:druid-prod-middleManagers-1
Warning check pod running; ConditionStatus:False; PodName:druid-prod-middleManagers-1 22s KubeDB Ops-manager Operator check pod running; ConditionStatus:False; PodName:druid-prod-middleManagers-1
Warning check pod running; ConditionStatus:True; PodName:druid-prod-middleManagers-1 12s KubeDB Ops-manager Operator check pod running; ConditionStatus:True; PodName:druid-prod-middleManagers-1
Normal RestartNodes 7s KubeDB Ops-manager Operator Successfully restarted all nodes
Normal Starting 5s KubeDB Ops-manager Operator Resuming Druid database: demo/druid-prod
Normal Successful 5s KubeDB Ops-manager Operator Successfully resumed Druid database: demo/druid-prod for DruidOpsRequest: reconfigure-drops
Now let’s exec one of the instance and run a druid-configs.sh command to check the new configuration we have provided.
$ kubectl exec -it -n demo druid-prod-middleManagers-0 -- druid-configs.sh --bootstrap-server localhost:9092 --command-config /opt/druid/config/clientauth.properties --describe --entity-type middleManagerss --all | grep 'log.retention.hours'
log.retention.hours=125 sensitive=false synonyms={STATIC_BROKER_CONFIG:log.retention.hours=125, DEFAULT_CONFIG:log.retention.hours=168}
log.retention.hours=125 sensitive=false synonyms={STATIC_BROKER_CONFIG:log.retention.hours=125, DEFAULT_CONFIG:log.retention.hours=168}
As we can see from the configuration of ready druid, the value of log.retention.hours has been changed from 100 to 125. So the reconfiguration of the cluster is successful.
Reconfigure using apply config
Now we will reconfigure this cluster again to set log.retention.hours to 150. This time we won’t use a new secret. We will use the applyConfig field of the DruidOpsRequest. This will merge the new config in the existing secret.
Create DruidOpsRequest
Now, we will use the new configuration in the applyConfig field in the DruidOpsRequest CR. The DruidOpsRequest yaml is given below,
apiVersion: ops.kubedb.com/v1alpha1
kind: DruidOpsRequest
metadata:
name: kfops-reconfigure-apply-topology
namespace: demo
spec:
type: Reconfigure
databaseRef:
name: druid-prod
configuration:
applyConfig:
middleManagers.properties: |-
log.retention.hours=150
historicals.properties: |-
historicals.quorum.election.timeout.ms=4000
historicals.quorum.fetch.timeout.ms=5000
timeout: 5m
apply: IfReady
Here,
spec.databaseRef.namespecifies that we are reconfiguringdruid-prodcluster.spec.typespecifies that we are performingReconfigureon druid.spec.configuration.applyConfigspecifies the new configuration that will be merged in the existing secret.
Let’s create the DruidOpsRequest CR we have shown above,
$ kubectl apply -f https://github.com/kubedb/docs/raw/v2025.1.9/docs/examples/druid/reconfigure/druid-reconfigure-apply-topology.yaml
druidopsrequest.ops.kubedb.com/kfops-reconfigure-apply-topology created
Verify new configuration
If everything goes well, KubeDB Ops-manager operator will merge this new config with the existing configuration.
Let’s wait for DruidOpsRequest to be Successful. Run the following command to watch DruidOpsRequest CR,
$ kubectl get druidopsrequests -n demo kfops-reconfigure-apply-topology
NAME TYPE STATUS AGE
kfops-reconfigure-apply-topology Reconfigure Successful 55s
We can see from the above output that the DruidOpsRequest has succeeded. If we describe the DruidOpsRequest we will get an overview of the steps that were followed to reconfigure the cluster.
$ kubectl describe druidopsrequest -n demo kfops-reconfigure-apply-topology
Name: kfops-reconfigure-apply-topology
Namespace: demo
Labels: <none>
Annotations: <none>
API Version: ops.kubedb.com/v1alpha1
Kind: DruidOpsRequest
Metadata:
Creation Timestamp: 2024-08-02T05:14:42Z
Generation: 1
Resource Version: 332996
UID: 551d2c92-9431-47a7-a699-8f8115131b49
Spec:
Apply: IfReady
Configuration:
Apply Config:
middleManagers.properties: log.retention.hours=150
historicals.properties: historicals.quorum.election.timeout.ms=4000
historicals.quorum.fetch.timeout.ms=5000
Database Ref:
Name: druid-prod
Timeout: 5m
Type: Reconfigure
Status:
Conditions:
Last Transition Time: 2024-08-02T05:14:42Z
Message: Druid ops-request has started to reconfigure druid nodes
Observed Generation: 1
Reason: Reconfigure
Status: True
Type: Reconfigure
Last Transition Time: 2024-08-02T05:14:45Z
Message: Successfully prepared user provided custom config secret
Observed Generation: 1
Reason: PrepareCustomConfig
Status: True
Type: PrepareCustomConfig
Last Transition Time: 2024-08-02T05:14:52Z
Message: successfully reconciled the Druid with new configure
Observed Generation: 1
Reason: UpdatePetSets
Status: True
Type: UpdatePetSets
Last Transition Time: 2024-08-02T05:14:57Z
Message: get pod; ConditionStatus:True; PodName:druid-prod-historicals-0
Observed Generation: 1
Status: True
Type: GetPod--druid-prod-historicals-0
Last Transition Time: 2024-08-02T05:14:57Z
Message: evict pod; ConditionStatus:True; PodName:druid-prod-historicals-0
Observed Generation: 1
Status: True
Type: EvictPod--druid-prod-historicals-0
Last Transition Time: 2024-08-02T05:15:07Z
Message: check pod running; ConditionStatus:True; PodName:druid-prod-historicals-0
Observed Generation: 1
Status: True
Type: CheckPodRunning--druid-prod-historicals-0
Last Transition Time: 2024-08-02T05:15:12Z
Message: get pod; ConditionStatus:True; PodName:druid-prod-historicals-1
Observed Generation: 1
Status: True
Type: GetPod--druid-prod-historicals-1
Last Transition Time: 2024-08-02T05:15:12Z
Message: evict pod; ConditionStatus:True; PodName:druid-prod-historicals-1
Observed Generation: 1
Status: True
Type: EvictPod--druid-prod-historicals-1
Last Transition Time: 2024-08-02T05:15:27Z
Message: check pod running; ConditionStatus:True; PodName:druid-prod-historicals-1
Observed Generation: 1
Status: True
Type: CheckPodRunning--druid-prod-historicals-1
Last Transition Time: 2024-08-02T05:15:32Z
Message: get pod; ConditionStatus:True; PodName:druid-prod-middleManagers-0
Observed Generation: 1
Status: True
Type: GetPod--druid-prod-middleManagers-0
Last Transition Time: 2024-08-02T05:15:32Z
Message: evict pod; ConditionStatus:True; PodName:druid-prod-middleManagers-0
Observed Generation: 1
Status: True
Type: EvictPod--druid-prod-middleManagers-0
Last Transition Time: 2024-08-02T05:16:07Z
Message: check pod running; ConditionStatus:True; PodName:druid-prod-middleManagers-0
Observed Generation: 1
Status: True
Type: CheckPodRunning--druid-prod-middleManagers-0
Last Transition Time: 2024-08-02T05:16:12Z
Message: get pod; ConditionStatus:True; PodName:druid-prod-middleManagers-1
Observed Generation: 1
Status: True
Type: GetPod--druid-prod-middleManagers-1
Last Transition Time: 2024-08-02T05:16:12Z
Message: evict pod; ConditionStatus:True; PodName:druid-prod-middleManagers-1
Observed Generation: 1
Status: True
Type: EvictPod--druid-prod-middleManagers-1
Last Transition Time: 2024-08-02T05:16:27Z
Message: check pod running; ConditionStatus:True; PodName:druid-prod-middleManagers-1
Observed Generation: 1
Status: True
Type: CheckPodRunning--druid-prod-middleManagers-1
Last Transition Time: 2024-08-02T05:16:32Z
Message: Successfully restarted all nodes
Observed Generation: 1
Reason: RestartNodes
Status: True
Type: RestartNodes
Last Transition Time: 2024-08-02T05:16:35Z
Message: Successfully completed reconfigure druid
Observed Generation: 1
Reason: Successful
Status: True
Type: Successful
Observed Generation: 1
Phase: Successful
Events:
Type Reason Age From Message
---- ------ ---- ---- -------
Normal Starting 2m6s KubeDB Ops-manager Operator Start processing for DruidOpsRequest: demo/kfops-reconfigure-apply-topology
Normal Starting 2m6s KubeDB Ops-manager Operator Pausing Druid databse: demo/druid-prod
Normal Successful 2m6s KubeDB Ops-manager Operator Successfully paused Druid database: demo/druid-prod for DruidOpsRequest: kfops-reconfigure-apply-topology
Normal UpdatePetSets 116s KubeDB Ops-manager Operator successfully reconciled the Druid with new configure
Warning get pod; ConditionStatus:True; PodName:druid-prod-historicals-0 111s KubeDB Ops-manager Operator get pod; ConditionStatus:True; PodName:druid-prod-historicals-0
Warning evict pod; ConditionStatus:True; PodName:druid-prod-historicals-0 111s KubeDB Ops-manager Operator evict pod; ConditionStatus:True; PodName:druid-prod-historicals-0
Warning check pod running; ConditionStatus:False; PodName:druid-prod-historicals-0 106s KubeDB Ops-manager Operator check pod running; ConditionStatus:False; PodName:druid-prod-historicals-0
Warning check pod running; ConditionStatus:True; PodName:druid-prod-historicals-0 101s KubeDB Ops-manager Operator check pod running; ConditionStatus:True; PodName:druid-prod-historicals-0
Warning get pod; ConditionStatus:True; PodName:druid-prod-historicals-1 96s KubeDB Ops-manager Operator get pod; ConditionStatus:True; PodName:druid-prod-historicals-1
Warning evict pod; ConditionStatus:True; PodName:druid-prod-historicals-1 96s KubeDB Ops-manager Operator evict pod; ConditionStatus:True; PodName:druid-prod-historicals-1
Warning check pod running; ConditionStatus:False; PodName:druid-prod-historicals-1 91s KubeDB Ops-manager Operator check pod running; ConditionStatus:False; PodName:druid-prod-historicals-1
Warning check pod running; ConditionStatus:True; PodName:druid-prod-historicals-1 81s KubeDB Ops-manager Operator check pod running; ConditionStatus:True; PodName:druid-prod-historicals-1
Warning get pod; ConditionStatus:True; PodName:druid-prod-middleManagers-0 76s KubeDB Ops-manager Operator get pod; ConditionStatus:True; PodName:druid-prod-middleManagers-0
Warning evict pod; ConditionStatus:True; PodName:druid-prod-middleManagers-0 76s KubeDB Ops-manager Operator evict pod; ConditionStatus:True; PodName:druid-prod-middleManagers-0
Warning check pod running; ConditionStatus:False; PodName:druid-prod-middleManagers-0 71s KubeDB Ops-manager Operator check pod running; ConditionStatus:False; PodName:druid-prod-middleManagers-0
Warning check pod running; ConditionStatus:True; PodName:druid-prod-middleManagers-0 41s KubeDB Ops-manager Operator check pod running; ConditionStatus:True; PodName:druid-prod-middleManagers-0
Warning get pod; ConditionStatus:True; PodName:druid-prod-middleManagers-1 36s KubeDB Ops-manager Operator get pod; ConditionStatus:True; PodName:druid-prod-middleManagers-1
Warning evict pod; ConditionStatus:True; PodName:druid-prod-middleManagers-1 36s KubeDB Ops-manager Operator evict pod; ConditionStatus:True; PodName:druid-prod-middleManagers-1
Warning check pod running; ConditionStatus:False; PodName:druid-prod-middleManagers-1 31s KubeDB Ops-manager Operator check pod running; ConditionStatus:False; PodName:druid-prod-middleManagers-1
Warning check pod running; ConditionStatus:True; PodName:druid-prod-middleManagers-1 21s KubeDB Ops-manager Operator check pod running; ConditionStatus:True; PodName:druid-prod-middleManagers-1
Normal RestartNodes 15s KubeDB Ops-manager Operator Successfully restarted all nodes
Normal Starting 14s KubeDB Ops-manager Operator Resuming Druid database: demo/druid-prod
Normal Successful 14s KubeDB Ops-manager Operator Successfully resumed Druid database: demo/druid-prod for DruidOpsRequest: kfops-reconfigure-apply-topology
Lets exec into one of the druid middleManagers pod that have updated and check the new configurations are applied or not:
Exec into the Druid middleManagers:
$ kubectl exec -it -n demo druid-with-config-middleManagers-0 -- bash
Defaulted container "druid" out of: druid, init-druid (init)
bash-5.1$
Now, execute the following commands to see the configurations:
bash-5.1$ cat conf/druid/cluster/data/middleManager/runtime.properties | grep druid.worker.capacity
druid.worker.capacity=5
Here, we can see that our given configuration is applied to the Druid cluster for all brokers.
Now, lets exec into one of the druid historicals pod that have updated and check the new configurations are applied or not:
Exec into the Druid historicals:
$ kubectl exec -it -n demo druid-with-config-historicals-0 -- bash
Defaulted container "druid" out of: druid, init-druid (init)
bash-5.1$
Now, execute the following commands to see the metadata storage directory:
bash-5.1$ cat conf/druid/cluster/data/historical/runtime.properties | grep druid.processing.numThreads
druid.processing.numThreads=3
Here, we can see that our given configuration is applied to the historicals.
Verify Configuration Change from Druid UI
You can access the UI similarly by doing port-forward as mentioned in Check Configuration from Druid UI
You should be able to see the following changes in the UI:
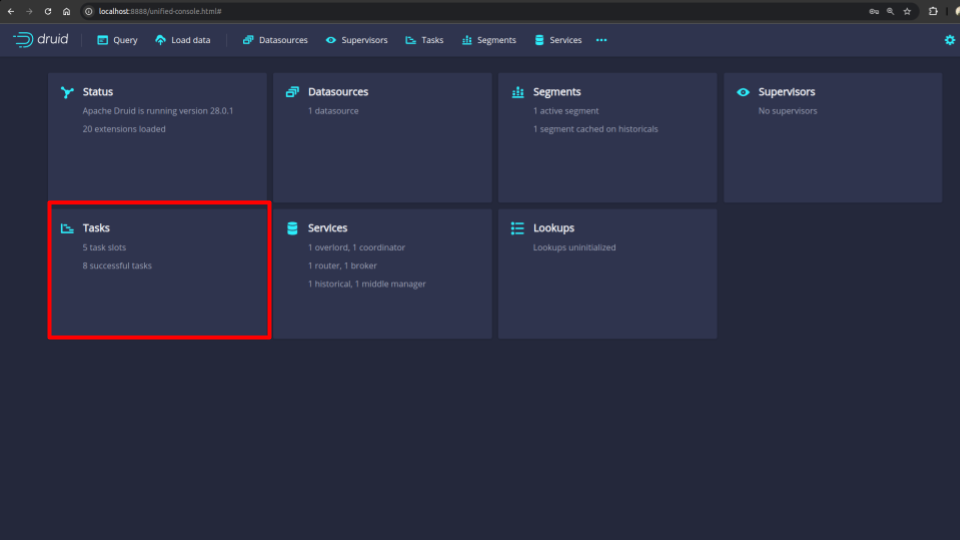
You can see that there are 5 task slots reflecting with our provided custom configuration of druid.worker.capacity=5.
Cleaning Up
To clean up the Kubernetes resources created by this tutorial, run:
kubectl delete kf -n demo druid-cluster
kubectl delete druidopsrequest -n demo reconfigure-drops
kubectl delete secret -n demo new-config
kubectl delete ns demo
Next Steps
- Detail concepts of Druid object.
- Different Druid topology clustering modes here.
- Monitor your Druid database with KubeDB using out-of-the-box Prometheus operator.
- Want to hack on KubeDB? Check our contribution guidelines.



































