You are looking at the documentation of a prior release. To read the documentation of the latest release, please
visit here.
New to KubeDB? Please start here.
GitOps Overview for PostgreSQL
This guide will give you an overview of how KubeDB gitops operator works with PostgreSQL databases using the gitops.kubedb.com/v1alpha1 API. It will help you understand the GitOps workflow for managing PostgreSQL databases in Kubernetes.
Before You Begin
- You should be familiar with the following
KubeDBconcepts:
Workflow GitOps with PostgreSQL
The following diagram shows how the KubeDB GitOps Operator used to sync with your database. Open the image in a new tab to see the enlarged version.
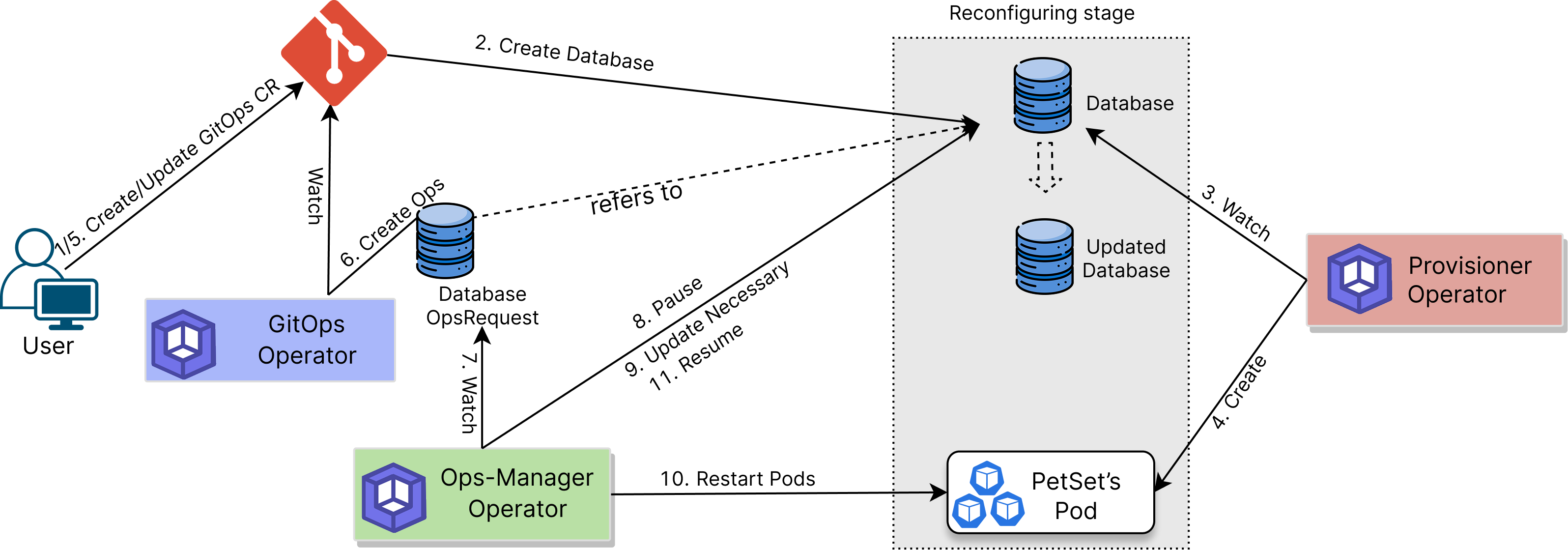
- Define GitOps Postgres: Create Custom Resource (CR) of kind
Postgresusing thegitops.kubedb.com/v1alpha1API. - Store in Git: Push the CR to a Git repository.
- Automated Deployment: Use a GitOps tool (like
ArgoCDorFluxCD) to monitor the Git repository and synchronize the state of the Kubernetes cluster with the desired state defined in Git. - Create Database: The GitOps operator creates a corresponding KubeDB Postgres CR in the Kubernetes cluster to deploy the database.
- Handle Updates: When you update the PostgresGitOps CR, the operator generates an Ops Request to safely apply the update(e.g.
VerticalScaling,HorizontalScaling,VolumeExapnsion,Reconfigure,RotateAuth,ReconfigureTLS,VersionUpdate, ansRestart.
This flow makes managing PostgreSQL databases efficient, reliable, and fully integrated with GitOps practices.
In the next doc, we are going to show a step by step guide on running postgres using GitOps.



































