You are looking at the documentation of a prior release. To read the documentation of the latest release, please
visit here.
New to KubeDB? Please start here.
Ignite QuickStart
This tutorial will show you how to use KubeDB to run a Ignite server.
Note: The yaml files used in this tutorial are stored in docs/examples/ignite folder in GitHub repository kubedb/docs.
Before You Begin
At first, you need to have a Kubernetes cluster, and the
kubectlcommand-line tool must be configured to communicate with your cluster. If you do not already have a cluster, you can create one by using kind.Now, install KubeDB cli on your workstation and KubeDB operator in your cluster following the steps here.
To keep things isolated, this tutorial uses a separate namespace called
demothroughout this tutorial. Run the following command to prepare your cluster for this tutorial:
$ kubectl create ns demo
namespace/demo created
$ kubectl get ns demo
NAME STATUS AGE
demo Active 1s
Find Available IgniteVersion
When you have installed KubeDB, it has created IgniteVersion crd for all supported Ignite versions. Check 0
$ kubectl get igniteversions
NAME VERSION DB_IMAGE DEPRECATED AGE
2.17.0 2.17.0 ghcr.io/appscode-images/ignite:2.17.0 2h
Create a Ignite server
KubeDB implements a Ignite CRD to define the specification of a Ignite server. Below is the Ignite object created in this tutorial.
apiVersion: kubedb.com/v1alpha2
kind: Ignite
metadata:
name: ignite-quickstart
namespace: demo
spec:
replicas: 3
version: 2.17.0
storage:
accessModes:
- ReadWriteOnce
resources:
requests:
storage: 1Gi
deletionPolicy: WipeOut
$ kubectl create -f https://github.com/kubedb/docs/raw/v2025.7.31/docs/examples/ignite/quickstart/demo.yaml
ignite.kubedb.com/ignite-quickstart created
Here,
spec.replicasis an optional field that specifies the number of desired Instances/Replicas of Ignite server. It defaults to 1.spec.versionis the version of Ignite server. In this tutorial, a Ignite 2.17.0 database is going to be created..spec.podTemplate.spec.containers[].resourcesis an optional field that specifies how much CPU and memory (RAM) each Container needs. To learn details about Managing Compute Resources for Containers, please visit here.spec.deletionPolicygives flexibility whether tonullify(reject) the delete operation ofIgnitecrd or which resources KubeDB should keep or delete when you deleteIgnitecrd. If admission webhook is enabled, It prevents users from deleting the database as long as thespec.deletionPolicyis set toDoNotTerminate. Learn details of allDeletionPolicyhere
KubeDB operator watches for Ignite objects using Kubernetes api. When a Ignite object is created, KubeDB operator will create a new PetSet and a Service with the matching Ignite object name.
$ kubectl get ig -n demo
NAME TYPE VERSION STATUS AGE
ignite-quickstart kubedb.com/v1alpha2 2.17.0 Ready 2m
$ kubectl describe ig -n demo ignite-quickstart
Name: ignite-quickstart
Namespace: demo
Labels: <none>
Annotations: <none>
API Version: kubedb.com/v1alpha2
Kind: Ignite
Metadata:
Creation Timestamp: 2025-05-30T08:52:28Z
Finalizers:
kubedb.com/ignite
Generation: 2
Resource Version: 1307753
UID: bdf6fce9-bfa5-4695-9843-9797a82b0a3d
Spec:
Deletion Policy: WipeOut
Health Checker:
Failure Threshold: 3
Period Seconds: 10
Timeout Seconds: 10
Pod Template:
Controller:
Metadata:
Spec:
Containers:
Name: ignite
Resources:
Limits:
Memory: 1Gi
Requests:
Cpu: 500m
Memory: 1Gi
Security Context:
Allow Privilege Escalation: false
Capabilities:
Drop:
ALL
Run As Non Root: true
Run As User: 70
Seccomp Profile:
Type: RuntimeDefault
Init Containers:
Name: ignite-init
Resources:
Security Context:
Allow Privilege Escalation: false
Capabilities:
Drop:
ALL
Run As Non Root: true
Run As User: 70
Seccomp Profile:
Type: RuntimeDefault
Pod Placement Policy:
Name: default
Security Context:
Fs Group: 70
Replicas: 3
Storage:
Access Modes:
ReadWriteOnce
Resources:
Requests:
Storage: 1Gi
Storage Type: Durable
Version: 2.17.0
Status:
Conditions:
Last Transition Time: 2025-05-30T08:52:28Z
Message: The KUbeDB operator has started the provisioning of Ignite: demo ignite-quickstart
Observed Generation: 2
Reason: DatabaseProvisioningStartedSuccessfully
Status: True
Type: ProvisioningStarted
Last Transition Time: 2025-05-30T08:53:34Z
Message: All desired replicas are ready.
Observed Generation: 2
Reason: AllReplicasReady
Status: True
Type: ReplicaReady
Last Transition Time: 2025-05-30T08:53:45Z
Message: The Ignite: demo/ignite-quickstart is accepting connection
Observed Generation: 2
Reason: DatabaseAcceptingConnectionRequest
Status: True
Type: AcceptingConnection
Last Transition Time: 2025-05-30T08:53:45Z
Message: The Ignite: demo/ignite-quickstart is accepting write request.
Observed Generation: 2
Reason: DatabaseWriteAccessCheckSucceeded
Status: True
Type: DatabaseWriteAccess
Last Transition Time: 2025-05-30T08:53:45Z
Message: The Ignite: demo/ignite-quickstart is accepting read request.
Observed Generation: 2
Reason: DatabaseReadAccessCheckSucceeded
Status: True
Type: DatabaseReadAccess
Last Transition Time: 2025-05-30T08:53:45Z
Message: The Ignite: demo/ignite-quickstart is ready
Observed Generation: 2
Reason: AllReplicasReady,AcceptingConnection,ReadinessCheckSucceeded,DatabaseWriteAccessCheckSucceeded
Status: True
Type: Ready
Last Transition Time: 2025-05-30T08:53:46Z
Message: The Ignite: demo/ignite-quickstart is successfully provisioned.
Observed Generation: 2
Reason: DatabaseSuccessfullyProvisioned
Status: True
Type: Provisioned
Phase: Ready
Events: <none>
$ kubectl get petset -n demo
NAME AGE
ignite-quickstart 2m
$ kubectl get service -n demo
NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE
ignite-quickstart ClusterIP 10.96.163.80 <none> 8080/TCP,10800/TCP,47500/TCP,47100/TCP 4m8s
ignite-quickstart-pods ClusterIP None <none> 8080/TCP,10800/TCP,47500/TCP,47100/TCP 4m8s
KubeDB operator sets the status.phase to Running once the database is successfully created. Run the following command to see the modified Ignite object:
$ kubectl get ig -n demo ignite-quickstart -o yaml
apiVersion: kubedb.com/v1alpha2
kind: Ignite
metadata:
annotations:
kubectl.kubernetes.io/last-applied-configuration: |
{"apiVersion":"kubedb.com/v1alpha2","kind":"Ignite","metadata":{"annotations":{},"name":"ignite-quickstart","namespace":"demo"},"spec":{"deletionPolicy":"WipeOut","replicas":3,"storage":{"accessModes":["ReadWriteOnce"],"resources":{"requests":{"storage":"1Gi"}}},"version":"2.17.0"}}
creationTimestamp: "2025-05-30T08:52:28Z"
finalizers:
- kubedb.com/ignite
generation: 2
name: ignite-quickstart
namespace: demo
resourceVersion: "1307753"
uid: bdf6fce9-bfa5-4695-9843-9797a82b0a3d
spec:
deletionPolicy: WipeOut
healthChecker:
failureThreshold: 3
periodSeconds: 10
timeoutSeconds: 10
podTemplate:
controller: {}
metadata: {}
spec:
containers:
- name: ignite
resources:
limits:
memory: 1Gi
requests:
cpu: 500m
memory: 1Gi
securityContext:
allowPrivilegeEscalation: false
capabilities:
drop:
- ALL
runAsNonRoot: true
runAsUser: 70
seccompProfile:
type: RuntimeDefault
initContainers:
- name: ignite-init
resources: {}
securityContext:
allowPrivilegeEscalation: false
capabilities:
drop:
- ALL
runAsNonRoot: true
runAsUser: 70
seccompProfile:
type: RuntimeDefault
podPlacementPolicy:
name: default
securityContext:
fsGroup: 70
replicas: 3
storage:
accessModes:
- ReadWriteOnce
resources:
requests:
storage: 1Gi
storageType: Durable
version: 2.17.0
status:
conditions:
- lastTransitionTime: "2025-05-30T08:52:28Z"
message: 'The KUbeDB operator has started the provisioning of Ignite: demo ignite-quickstart'
observedGeneration: 2
reason: DatabaseProvisioningStartedSuccessfully
status: "True"
type: ProvisioningStarted
- lastTransitionTime: "2025-05-30T08:53:34Z"
message: All desired replicas are ready.
observedGeneration: 2
reason: AllReplicasReady
status: "True"
type: ReplicaReady
- lastTransitionTime: "2025-05-30T08:53:45Z"
message: 'The Ignite: demo/ignite-quickstart is accepting connection'
observedGeneration: 2
reason: DatabaseAcceptingConnectionRequest
status: "True"
type: AcceptingConnection
- lastTransitionTime: "2025-05-30T08:53:45Z"
message: 'The Ignite: demo/ignite-quickstart is accepting write request.'
observedGeneration: 2
reason: DatabaseWriteAccessCheckSucceeded
status: "True"
type: DatabaseWriteAccess
- lastTransitionTime: "2025-05-30T08:53:45Z"
message: 'The Ignite: demo/ignite-quickstart is accepting read request.'
observedGeneration: 2
reason: DatabaseReadAccessCheckSucceeded
status: "True"
type: DatabaseReadAccess
- lastTransitionTime: "2025-05-30T08:53:45Z"
message: 'The Ignite: demo/ignite-quickstart is ready'
observedGeneration: 2
reason: AllReplicasReady,AcceptingConnection,ReadinessCheckSucceeded,DatabaseWriteAccessCheckSucceeded
status: "True"
type: Ready
- lastTransitionTime: "2025-05-30T08:53:46Z"
message: 'The Ignite: demo/ignite-quickstart is successfully provisioned.'
observedGeneration: 2
reason: DatabaseSuccessfullyProvisioned
status: "True"
type: Provisioned
phase: Ready
Connect with Ignite database
Now, you can connect to this database using sqlline.
Here, firstly we will exec one of the running pod:
$ kubectl exec -it -n demo ignite-quickstart-0 -c ignite -- bash
ignite@ignite-quickstart-0:/# apache-ignite/bin/sqlline.sh -u jdbc:ignite:thin://127.0.0.1/ -n ignite -p 'pyX39AdZlOog!3Lt'
sqlline version 1.9.0
0: jdbc:ignite:thin://127.0.0.1/> CREATE TABLE City (id LONG PRIMARY KEY, name VARCHAR);
No rows affected (0.087 seconds)
0: jdbc:ignite:thin://127.0.0.1/> INSERT INTO City (id, name) VALUES (1, 'Forest Hill');
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . > INSERT INTO City (id, name) VALUES (2, 'Denver');
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . > INSERT INTO City (id, name) VALUES (3, 'St. Petersburg');
1 row affected (0.052 seconds)
1 row affected (0.016 seconds)
1 row affected (0.002 seconds)
0: jdbc:ignite:thin://127.0.0.1/> SELECT * FROM City;
+----+----------------+
| ID | NAME |
+----+----------------+
| 2 | Denver |
| 3 | St. Petersburg |
| 1 | Forest Hill |
+----+----------------+
3 rows selected (0.039 seconds)
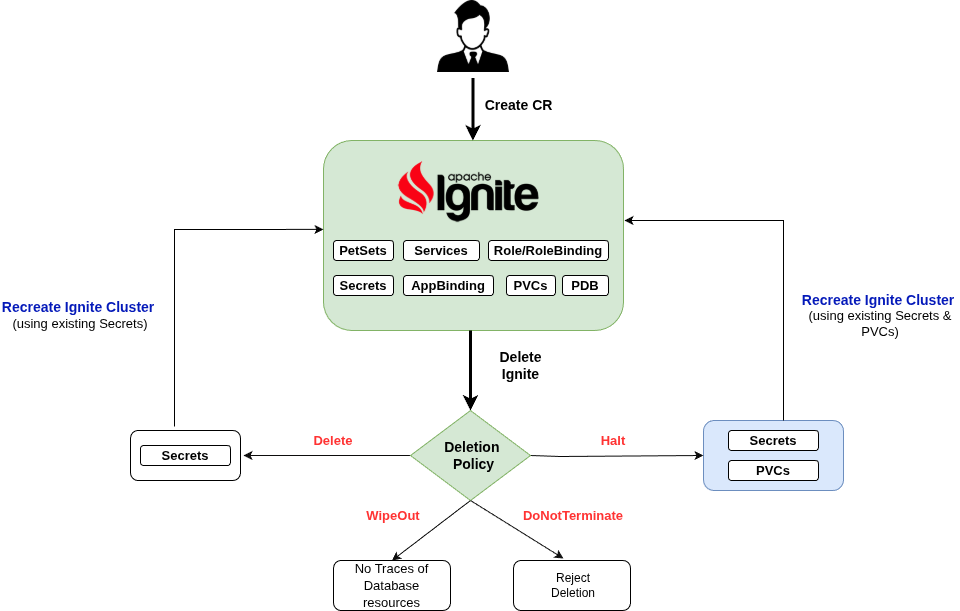
Database DeletionPolicy
This field is used to regulate the deletion process of the related resources when Ignite object is deleted. User can set the value of this field according to their needs. The available options and their use case scenario is described below:
DoNotTerminate:
When deletionPolicy is set to DoNotTerminate, KubeDB takes advantage of ValidationWebhook feature in Kubernetes 1.9.0 or later clusters to implement DoNotTerminate feature. If admission webhook is enabled, It prevents users from deleting the database as long as the spec.deletionPolicy is set to DoNotTerminate. You can see this below:
$ kubectl delete ig ignite-quickstart -n demo
Error from server (Forbidden): admission webhook "ignitewebhook.validators.kubedb.com" denied the request: ignite demo/ignite-quickstart is can't terminated. To delete, change spec.deletionPolicy
Learn details of all DeletionPolicy here.
Delete:
If you want to delete the existing database but want to keep secrets then you might want to set the Ignite object deletionPolicy to Delete. In this setting, PetSet and Services will be deleted.
When the DeletionPolicy is set to Delete and the Ignite object is deleted, the KubeDB operator will delete the PetSet and its pods but leaves the secret intact.
Suppose, we have a database with deletionPolicy set to Delete. Now, are going to delete the database using the following command:
$ kubectl delete -n demo ig/ignite-quickstart
ignite.kubedb.com "ignite-quickstart" deleted
Now, run the following command to get all ignite resources in demo namespaces,
$ kubectl get petset,svc,secret,pvc -n demo
NAME TYPE DATA AGE
secret/ignite-quickstart-auth kubernetes.io/basic-auth 2 27m
secret/ignite-quickstart-config Opaque 1 27m
From the above output, you can see that all ignite resources(PetSet, Service etc.) are deleted except Secret.
If you don’t set the
deletionPolicythen the kubeDB set the DeletionPolicy toDeleteby-default.
WipeOut:
You can totally delete the Ignite database and relevant resources without any tracking by setting deletionPolicy to WipeOut. KubeDB operator will delete all relevant resources of this Ignite database (i.e, PetSet, Secrets, Services) when the deletionPolicy is set to WipeOut.
Suppose, we have a database with deletionPolicy set to WipeOut. Now, are going to delete the database using the following command:
$ kubectl delete -n demo ig/ignite-quickstart
ignite.kubedb.com "ignite-quickstart" deleted
Now, run the following command to get all ignite resources in demo namespaces,
$ kubectl get petsets,svc,secret -n demo
No resources found in demo namespace.
From the above output, you can see that all ignite resources are deleted. there is no option to recreate/reinitialize your database if deletionPolicy is set to Delete.
Be careful when you set the
deletionPolicytoDelete. Because there is no option to trace the database resources if once deleted the database.
Cleaning up
To cleanup the Kubernetes resources created by this tutorial, run:
$ kubectl patch -n demo ig/ignite-quickstart -p '{"spec":{"deletionPolicy":"WipeOut"}}' --type="merge"
ignite.kubedb.com/ignite-quickstart patched
$ kubectl delete -n demo ig/ignite-quickstart
ignite.kubedb.com "ignite-quickstart" deleted
$ kubectl delete ns demo
namespace "demo" deleted
Tips for Testing
If you are just testing some basic functionalities, you might want to avoid additional hassles due to some safety features that are great for production environment. You can follow these tips to avoid them.
- Use
deletionPolicy: WipeOut. It is nice to be able to delete everything created by KubeDB for a particular Ignite crd when you delete the crd. For more details aboutdeletion policy, please visit here.
Next Steps
- Monitor your Ignite server with KubeDB using out-of-the-box Prometheus operator.
- Monitor your Ignite server with KubeDB using out-of-the-box builtin-Prometheus.
- Use private Docker registry to deploy Ignite with KubeDB.
- Detail concepts of Ignite object.
- Want to hack on KubeDB? Check our contribution guidelines.



































